You will learn about the top 10 welding processes used today. Arc welding is the most common and has 42% of the market. Resistance welding is still very important in car and big machine factories. Picking the right welding process is important. Each method works best with certain materials and project sizes. For example, TIG welding is good for careful work. Stick welding is better for fixing things outside. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. offers advanced welding services with trained workers. You will get helpful tips here. This will help you choose the best process and know the Welding Processes Pros for your needs.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Arc welding is used the most. It is flexible and makes strong welds. It works on many metals and in many places.
- Resistance welding joins metals fast. It does not need filler. It is good for cars and electronics.
- Gas welding uses a flame to join thin metals. It is good for repairs. It is easy to move and controls heat well.
- Brazing joins different metals with less heat. It makes clean and strong joints. It is good for delicate or mixed materials.
- Shielded metal arc welding (stick) works well outside. It is good in hard conditions. The tools are simple and easy to carry.
- MIG welding feeds wire by itself. It makes fast and clean welds. It is great for making many things and for different metals.
- TIG welding is very precise. It makes neat welds. It is best for thin or special metals. It is used in planes and food factories.
- AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. gives expert welding services. They check for quality. They work with many metals and project sizes.
Types of Welding Processes
There are four main groups of welding processes. These are arc welding, resistance welding, gas welding, and brazing. Each group uses its tools and ways to weld. Some groups, like OSHA, AWS, and ASME, make rules for safety and quality. These rules help keep workers safe and make sure welds are strong. You can see how these rules fit with welding in the table below:
| Standard/Regulatory Body | Scope and Definition Related to Welding Categories |
|---|---|
| OSHA (29 CFR 1910 Subpart Q) | Safety rules for welding, like fire safety and gear. |
| AWS D1.1 | Rules for welding steel, including tests and checks. |
| ASME Section IX | Welding steps and tests for pipes and tanks. |
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. knows all the main welding types. Their team can pick the best process for your job. Next, you will learn about the top 10 welding processes.
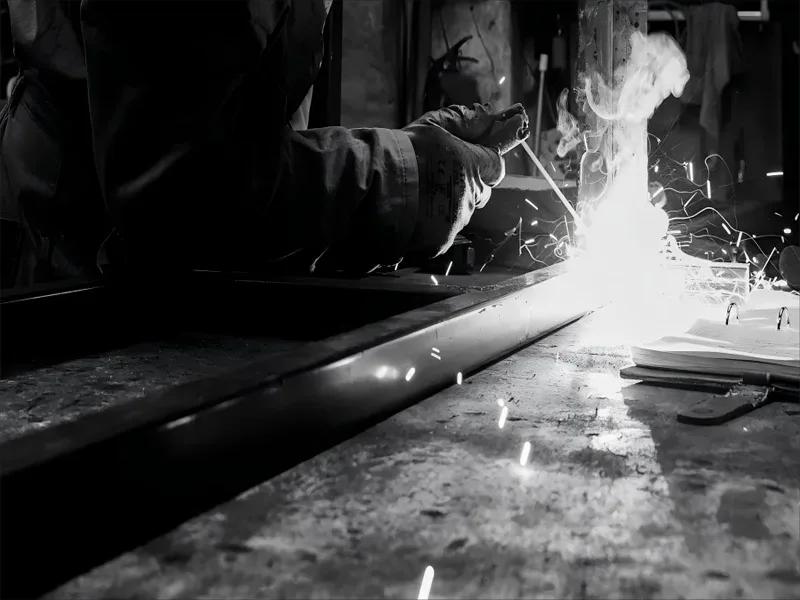
Arc Welding

Arc welding is the most commonly used welding type. It uses an electric arc to join metal pieces. The arc makes a lot of heat and melts the metal edges. When the metal cools, it sticks together very well. Arc welding machines are easy to move and use. You can use them in many places, like factories or outside.
There are different kinds of arc welding. Each kind is good for certain jobs. Some types are stick welding, MIG welding, TIG welding, flux-cored arc welding, plasma arc welding, and electroslag welding. Stick welding is good for fixing things outside. MIG welding is fast and used in car factories. TIG welding is neat and used for planes and nuclear work.
Arc welding can join many metals, like steel, aluminum, titanium, and nickel alloys. You can use it even if the metal pieces do not fit just right. This helps when working in tough places. You can also change the voltage and speed to match the job.
Many workers use arc welding. Car makers, shipbuilders, and builders use it a lot. It is also good for fixing and keeping things working. The different types let you pick for speed, neatness, or strong welds. Argon gas is often used to keep the weld clean and strong.
Tip: If you need a strong weld in hard places, arc welding is a good pick. You can choose the type that fits your job best.
Resistance Welding

Resistance welding is another big group of welding processes. It uses pressure and electric current to join metal. The heat comes from the metal fighting the electric current. You do not need extra filler for this welding.
Car factories use resistance welding a lot. Spot welding joins car panels, wheels, and pipes. Most car welding uses this method. It is also used for frames, parts, and engines. Planes, electronics, and home items use it too.
Here is a table that shows where resistance welding is used:
| Industry | Primary Applications | Example Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Joining car panels, frames, and hinges | Steel, aluminum |
| Aerospace | Joining light plane parts | Aluminum, titanium alloys |
| Electronics | Joining small parts like wires | Copper, gold |
| Consumer Goods | Making home items like fridges | Stainless steel, aluminum |
| Construction | Joining steel bars and building parts | Steel |
Resistance welding is fast and can be done over and over. This makes it great for making lots of things.
Gas Welding
Gas welding is one of the oldest welding types. It uses a flame from burning gases, like oxygen and acetylene, to melt and join metal. This way works best for thin metal, pipes, and tubes.

People use gas welding for fixing and keeping things working. It is common in car shops, on farms, and in heating and cooling work. You can weld gas tanks, water pipes, and boilers. Gas welding is easy to move and set up. You can use it in small spaces. It is also used for making jewelry and fixing cast iron.
Gas welding lets you control the heat and weld. This is good for careful work on thin metal. Newer ways have replaced gas welding in some jobs, but it is still useful for special work.
Now you know the main welding types. Next, you will learn more about each one and how AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. can help you pick the best.
Brazing
Brazing is a special way to join metals. You use a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the main pieces. The base metals do not melt during brazing. The melted filler metal moves into the gap by capillary action. When it cools, it forms a strong bond.

You can use many heat sources for brazing. Some common ones are a torch, furnace, induction heater, or resistance heater. Brazing works at over 840°F (450°C), but this is cooler than most welding. The lower heat keeps the base metals strong. It also helps stop warping or bending.
Brazing is different because it joins many kinds of metals. You can connect copper to steel or even metal to ceramic. This is hard to do with regular welding. Brazing also makes for cleaner joints. You do not need much grinding or finishing. Many industries like brazing for its neat and careful results.
Here is a table that shows how brazing and welding are different:
| Aspect | Brazing | Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Base Metal | Does not melt; uses low-melting filler | Melts base and filler metals together |
| Heat Source | Torch, furnace, induction, resistance | Electricity; very high temperatures |
| Joining Capability | Joins dissimilar metals and non-metals | Best for similar metals |
| Joint Strength | Strong; base metals keep their properties | Strong; fusion of base and filler metals |
| Thermal Impact | Less distortion and warping | More risk of distortion if not controlled |
| Precision & Cleanliness | Cleaner joints; less post-processing | May need more finishing |
| Cost & Equipment | More cost-effective; easier to automate | Higher costs; needs skilled labor |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, electronics, HVAC, automotive, jewelry | Heavy structures, bridges, pipelines, repairs |
You can find brazing in many places. Electronics makers use it for tiny parts. Aerospace companies use it for special alloys. Car makers use brazing for radiators and air conditioning. HVAC workers use it to join copper pipes. Jewelers use brazing to make fine jewelry.
Brazing is easy to learn. You do not have to watch the heat as closely. It is also easier to automate. This helps factories make lots of parts fast. Brazing works for both small and big jobs.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. offers advanced brazing services. Their team can join copper, steel, aluminum, and ceramics. They use modern tools to keep joints clean and strong. You get good results with less risk of damage.
Tip: If you need to join different metals or want a clean, strong joint with less heat, brazing could be your best choice.
Brazing gives you many options and careful work. You can use it for tiny electronics or strong machine parts. With AFI’s help, you get high-quality brazed joints that last.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
Process
Shielded metal arc welding, also called stick welding, is one of the oldest arc welding methods. You use a metal rod, called an electrode, that has a special coating. When you strike the electrode against the metal, it creates an electric arc. This arc melts both the electrode and the base metal. The coating on the electrode turns into a gas and a layer of slag. These protect the weld from air and keep it clean.
You start by cleaning the metal to remove dirt and oil. Next, you pick the right electrode for your job. You set the welding machine to the correct current and polarity. Then, you hold the electrode at the right angle and move it along the joint. You need to keep a steady hand to make a strong weld. After you finish, you check the weld for cracks or holes. Sometimes, you use special tests like X-rays or sound waves to look inside the weld.
Many standards help you make safe and strong welds. Some of these are AWS D1.1 for structural steel welding, ISO 2560, and EN 499. These rules tell you how to set up the welding process and how to check your work.
Welding Applications
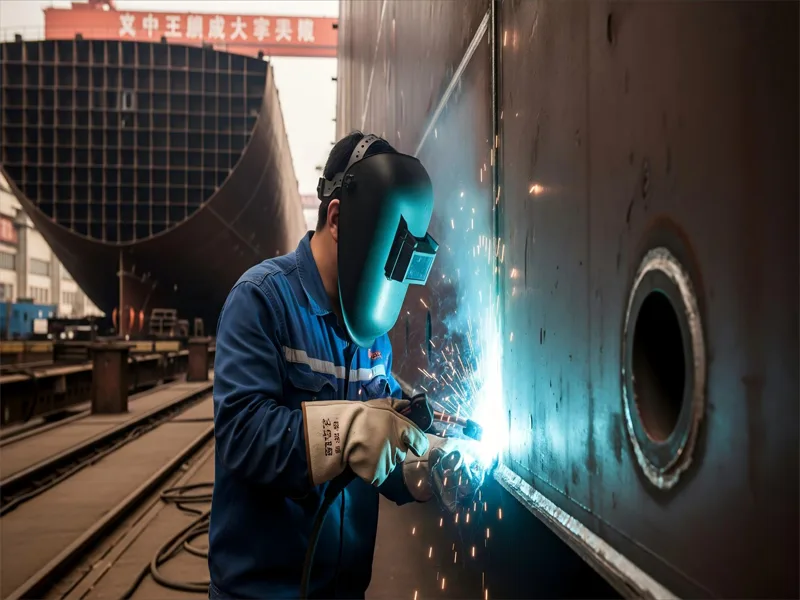

You will find shielded metal arc welding in many industries. It works well for outdoor welding and heavy-duty jobs. Construction workers use it for structural steel welding, pipeline building, and making strong frames. Shipbuilding uses this arc welding process to join large sections of ships. You also see it in manufacturing, where you need tough welds that can handle heavy loads.
Here are some common applications for shielded metal arc welding:
- Building bridges and skyscrapers
- Repairing heavy equipment
- Welding pipelines for oil and gas
- Assembling large sections of ships in shipbuilding yards
This welding process is great for places where you cannot use fancy machines or extra gas. You can use it in rain, wind, or dust. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. has a lot of experience with outdoor and heavy-duty welding projects. Their team can handle big jobs, even in tough conditions.
Pros
Shielded metal arc welding gives you many advantages. You can use it on many types of metal, like steel, iron, and some alloys. You do not need much equipment, so you can carry it to remote places. The process works in any position—flat, vertical, or overhead. You do not need extra gas because the electrode coating makes its shield. This makes the welding process simple and portable.
You save money because the setup costs less than other arc welding methods. The welds are strong and have good durability, even in harsh weather. You can use this method for repairs, new builds, and fieldwork. The process is easy to learn, so you can train new welders quickly.
Tip: If you need a strong weld in a hard-to-reach place or outside, shielded metal arc welding is a smart choice. You get reliable results with simple tools.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (MIG)
Process
Gas metal arc welding, also called MIG welding, is a popular arc welding process. You use a welding gun that feeds a thin wire electrode into the weld joint. The wire melts and joins the metal pieces together. A shielding gas, like argon or carbon dioxide, flows out of the gun to protect the weld from air. This keeps the weld clean and strong.
You can use gas metal arc welding for both thick and thin metals. The process works well with steel, aluminum, and other alloys. The equipment includes a welding gun, a wire feed unit, a power supply, and a gas tank. You can control the speed of the wire and the amount of gas. This helps you make neat, even welds.
Gas metal arc welding is fast and easy to learn. You can use it by hand or set it up for robots. Many factories use this process because it works well for mass production. You do not need to stop and change electrodes, so you can weld for a long time without stopping. The process makes little spatter and no slag, so you spend less time cleaning up.
Tip: If you want to weld quickly and get clean results, gas metal arc welding is a smart choice for your project.
Applications
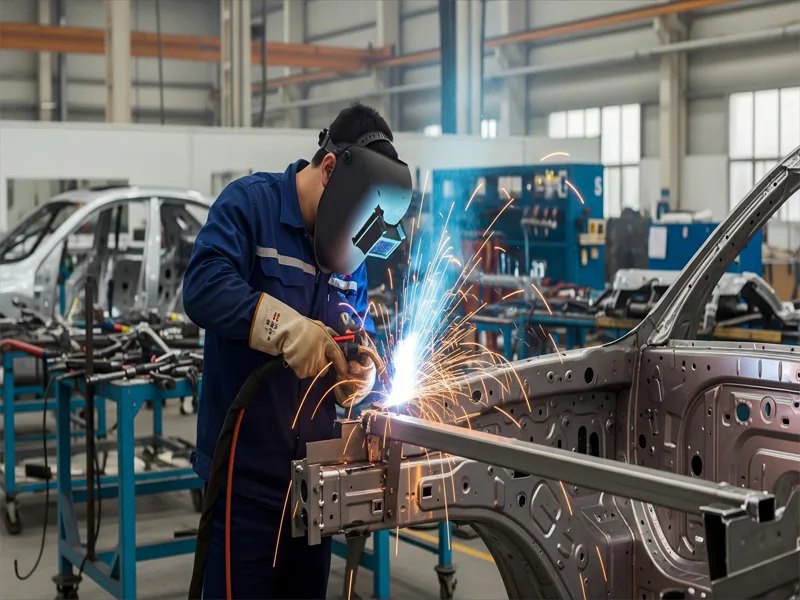

You will find gas metal arc welding in many industries. It is one of the most common arc welding methods for making cars, buildings, and machines. Here are some main applications:
- In the automotive industry, you use gas metal arc welding to make car frames, body panels, and exhaust systems. The process is fast and works well for both steel and aluminum parts.
- In construction, you use this arc welding process to join steel beams, columns, and frames. It is important for building bridges, pipelines, and large buildings.
- Aerospace and shipbuilding also use gas metal arc welding for strong, precise welds on thin and thick materials.
- You can use this process for repair work and for making new products in factories.
Gas metal arc welding is valued for its speed, precision, and ability to handle many types of metals. You can use it for both small and large projects. The process works best indoors or in controlled environments because the shielding gas cannot blow away outside.
| Industry | Main Application Areas | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Frames, panels, exhausts | Steel, aluminum |
| Construction | Beams, columns, building frames, pipelines | Steel, alloys |
| Aerospace | Aircraft parts, engine mounts | Aluminum, titanium |
| Shipbuilding | Hulls, decks, structural components | Steel, aluminum alloys |
Welding Processes Pros
Gas metal arc welding gives you many advantages over other arc welding methods:
- You can weld faster because the wire feeds automatically.
- The process works for both thick and thin materials, so you can use it for many jobs.
- You get high-quality welds with less spatter and almost no slag, so cleanup is easy.
- The process is easy to learn, so you can train new welders quickly.
- You can use one electrode size for different material thicknesses, which saves time and money.
- The process is great for long welds and for welding in hard-to-reach places.
- You can use gas metal arc welding with robots for mass production, making it perfect for factories.
Note: Gas metal arc welding is a top choice if you want fast, clean, and strong welds for many types of projects.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG)
Process
Gas tungsten arc welding, or TIG welding, gives you the most control. You use a tungsten electrode that does not melt. The electrode sits in a torch. The torch sends out shielding gas, like argon or a mix with helium. This gas keeps air away from the weld. You can change the heat with a foot pedal or hand switch. This helps you control the weld as you work. You often add filler metal by hand for extra strength.
First, set up the TIG welder and pick the right current. Use AC for aluminum or magnesium. Use DC for steel, stainless steel, or titanium. Pick the right tungsten electrode for your metal. Clean the metal to remove oil, rust, or dirt. Hold the parts together with clamps or tack welds. Hold the electrode close, about 1/8 inch from the metal. Start the arc. Move at a steady speed and control the heat. Add filler rod if you need it. When you finish, clean the weld to remove leftover stuff.
You need a TIG welder, tungsten electrodes, filler rods, shielding gas, a torch, and safety gear. This process is best for jobs that need neat, careful welds.
Applications
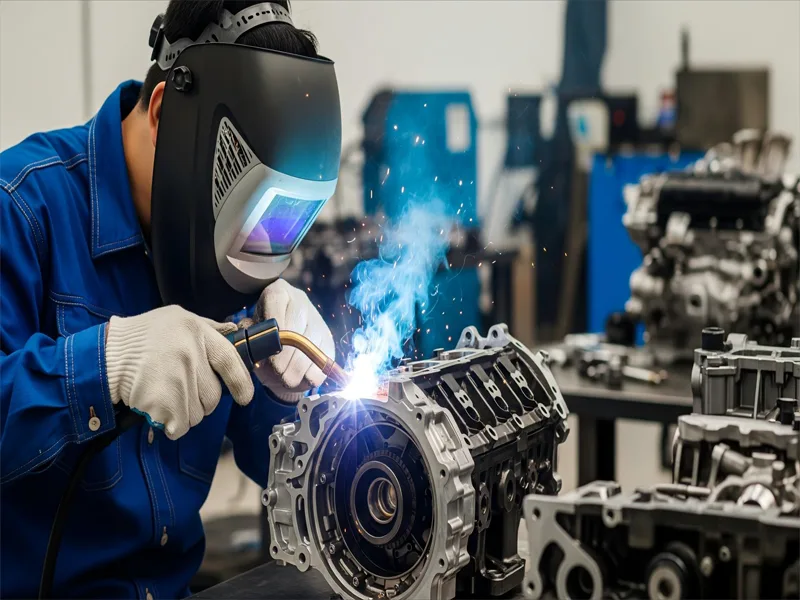

Gas tungsten arc welding is used in many jobs that need strong, clean welds. This welding is common in aerospace for thin parts and space vehicles. TIG welding is used for small tubes, like those in bikes. It is also good for fixing aluminum and magnesium parts.
Some common uses are:
- Welding stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals that are not iron
- Making exhausts, fuel lines, tanks, and engine parts for planes and cars
- Sealing nuclear fuel canisters
- Making food and drink equipment that needs smooth, clean welds
- Joining pipes that must not rust
TIG welding is very flexible. You can use it for custom metal work, repairs, and jobs that need nice-looking welds.
Pros
Gas tungsten arc welding has many good points over other welding types. You can control the heat and filler metal very well. This helps you make strong, clean welds with no dirt. The gas shield keeps air away, so the weld does not get ruined. There is almost no spatter or bending, which is great for thin metal.
TIG welding works with many metals, like stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium, copper alloys, and nickel alloys. You can weld thin metal without holes or warping. The welds look smooth and neat. TIG welding is good for tricky jobs that need care and strength.
Tip: If you want a high-quality weld on thin or special metals, pick gas tungsten arc welding. You will get good results and can use it for many jobs, like pipes and careful factory work.
Flux Cored Arc Welding
Process
Flux cored arc welding uses a special wire with flux inside. The wire is hollow and filled with flux. When you weld, the wire goes through the welding gun. The arc’s heat melts the wire and metal pieces. The flux inside the wire makes a gas shield. This gas keeps the weld safe from air. The weld stays clean and strong.
You can use this welding with or without extra gas. Some wires need shielding gas, but others do not. This makes the process flexible for many jobs. You can weld outside, even if it is windy. The flux also makes a layer of slag on the weld. You must chip off the slag after the weld cools.
The equipment has a wire feeder, a power supply, and a welding gun. The process is semi-automatic. You hold the gun, but the wire feeds by itself. This is faster than stick welding, which uses rods you move by hand.
Tip: If you need to weld dirty or rusty metal, flux cored arc welding works well. The flux helps protect the weld on less clean metal.
Applications

Many industries use flux cored arc welding. It is popular because it is fast and can do many jobs. Here is a table that shows where you might use this welding:
| Industrial Sector | Application Examples | Evidence of High Productivity Features |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Structural welding of steel structures, bridges | Continuous welding capability; high deposition rates; all-position welding |
| Shipbuilding and Marine Engineering | Hull fabrication; maintenance and repairs | Deep penetration; high deposition rates; suitable for thick plates |
| Manufacturing | Heavy equipment, automotive frames | High deposition efficiency (85%-90%); faster deposition speed (1.5-5x manual arc welding) |
| Pipeline and Pressure Vessel Fabrication | Oil and gas pipelines; storage tanks | Reliable, leak-proof joints; continuous welding without frequent stops |
| Maintenance and Repair Work | Field repairs across industries | Portability and adaptability; efficient on-site welding |
You can use this welding for bridges, ships, and fixing machines. It is also good for pipelines and tanks. The process is great for big jobs because you can weld for a long time. The wire keeps feeding, so you finish work quickly.
Pros
Flux cored arc welding has many good points over other welding types:
- You get high efficiency. The deposition rate is up to 90%.
- Welding is 1.5 times faster than manual arc welding in flat spots. In other spots, it can be 3 to 5 times faster.
- You can weld in any position—flat, up, or overhead.
- You can weld outside, even if it is windy, because the flux core protects the weld.
- The process is very flexible. You can use it on thick or thin metal, clean or rusty surfaces.
- The arc is steady, and there is little spatter. You spend less time cleaning up.
- The wire keeps feeding, so you do not stop to change rods.
Note: Flux cored arc welding is a smart pick if you want fast, strong welds in tough places. You can use it for many jobs, from building to repairs.
Submerged Arc Welding
Process
Submerged arc welding is a special type of arc welding. You use it when you need to join thick steel plates or make long, strong welds. The process starts when you clean and set up the metal pieces you want to join. You place the workpieces close together and make sure they are in the right position.
Next, you cover the area to be welded with a layer of granular flux. This flux looks like sand and protects the weld from air. You use a tubular electrode wire that matches the metal you are welding. The arc forms between the electrode and the metal, but you cannot see it because the flux covers it. The arc melts the electrode and the base metal, creating a pool of molten metal. The flux melts too and forms a layer of slag on top. This slag keeps the weld clean and strong.
You keep feeding the electrode wire into the weld pool. The welding head moves along the joint, making a long, even weld. After the weld cools, you remove the slag by chipping or grinding. You may also inspect the weld to make sure it is strong and free of defects.
The main equipment you use for submerged arc welding includes:
- A power source that gives a steady current or voltage.
- A welding head or boom to hold the torch.
- A wire feeder for the electrode.
- A flux hopper to deliver the granular flux.
- A system to collect and reuse leftover flux.
- Cooling devices to protect the equipment.
- A control panel to set welding parameters.
This process is different from other arc welding methods because the arc stays hidden under the flux. You get deep penetration and strong welds, especially on thick materials.
Applications

You will find submerged arc welding in many heavy industries. This arc welding process is perfect for jobs that need strong, reliable welds on thick steel. Here are some common uses:
- Shipbuilding: You use submerged arc welding to join thick steel plates for ship hulls, decks, and bulkheads. The process creates strong, corrosion-resistant welds that last a long time.
- Heavy industry: You weld structural steel for buildings, bridges, and large machines. The process is ideal for making pressure vessels, storage tanks, and heavy equipment.
- Pipeline construction: You use this arc welding method to join pipes for oil, gas, water, and wastewater. The welds can handle high pressure and tough conditions.
- Manufacturing: You build heavy machinery and parts that need to withstand big loads and repeated use.
Submerged arc welding became famous during World War II for building ships quickly and safely. Today, you still rely on it for large projects where strength and quality matter most.
Pros
Submerged arc welding gives you many benefits over other arc welding types. Here is a table that shows the main advantages:
| Advantage Category | Description |
|---|---|
| High Deposition Rate | You deposit more weld metal in less time, which boosts productivity. |
| Continuous Electrode Feed | You make long welds without stopping, saving time and effort. |
| Automation | You reduce mistakes and labor costs, and keep welds consistent. |
| Effective for Thick Materials | You weld thick sections in one pass, which saves time and labor. |
| Reduced Post-Weld Cleaning | The slag is easy to remove, so you spend less time cleaning. |
| Granular Flux Protection | The flux keeps the weld pool safe from air, giving you high-quality welds. |
| Uniform Weld Beads | You get smooth, even welds with few defects. |
| Strong, Durable Welds | The welds have great strength and toughness. |
| Low Hydrogen Content | The flux lowers hydrogen, which reduces the risk of cracks. |
| Reduced Welding Distortion | The heat spreads evenly, so the metal does not warp much. |
| Consistent Weld Quality | Automation helps you get the same high quality every time. |
You will notice that submerged arc welding stands out for its speed, strength, and ability to handle thick materials. The process also offers high efficiency, especially when you automate it for long welds. You can trust this arc welding method to deliver strong, reliable results in heavy-duty projects.
Tip: If you need to weld thick steel quickly and want top-quality results, choose submerged arc welding. You will see better efficiency and fewer defects compared to other arc welding processes.
Plasma Arc Welding
Process
Plasma arc welding is a special type of arc welding. You use a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create an electric arc. This arc forms inside a small copper nozzle. The nozzle squeezes the arc into a tight, hot jet called plasma. The plasma jet can reach temperatures up to 28,000°C. This high heat melts metal quickly and with great control.
You can adjust the plasma arc welding process for different jobs. Microplasma mode uses very low currents, from 0.1 to 15 amps. This lets you weld thin sheets and tiny parts without burning them. Keyhole mode uses high currents, over 100 amps, to make deep, narrow welds in thick metal. You can also use different gases, like argon or helium, to protect the weld and make it even hotter.
The equipment for plasma arc welding includes a power supply, a water-cooled torch, and controls for gas flow and current. You can set the machine to weld thin or thick materials. The focused arc gives you steady heat and less distortion. You get clean, strong welds every time.
Tip: Plasma arc welding gives you more control than other arc welding methods. You can weld very thin or very thick metals with the same machine.
Applications
You will find plasma arc welding in many high-tech industries. This arc welding process is perfect for jobs that need precision and strength. In aerospace, you use plasma arc welding to join thin parts for airplanes, fuel tanks, and engine parts. The process makes strong, light welds that meet strict safety rules. You can also use it to build complex shapes and weld tricky spots.
Electronics makers use plasma arc welding for tiny, delicate parts. The process works well for micro-welding and joining fine wires or connectors. You can weld thin metals with almost no warping. This is important for making computer chips, sensors, and other small devices.
Here are some common uses for plasma arc welding:
- Aerospace: Welding thin materials and complex shapes for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Electronics: Joining fine wires, connectors, and small components.
- Medical devices: Making surgical tools and implants.
- Automotive: Welding fuel injectors and sensors.
- Shipbuilding: Joining thick steel plates with deep, strong welds.
Plasma arc welding helps you make precise, clean welds in places where other arc welding methods might fail.
Pros
Plasma arc welding gives you many advantages over other arc welding types. The focused plasma jet lets you weld with great accuracy. You can make neat welds on thin sheets or deep welds in thick plates. The process works faster than gas tungsten arc welding and costs less than laser welding.
Here are some key benefits:
- Superior precision and control for thin and delicate materials.
- High welding speeds save you time on big projects.
- Deep penetration in keyhole mode allows single-pass welding of thick metal.
- Less heat spreads to the rest of the metal, so you get less distortion.
- The process handles gaps and misalignment better than laser or electron beam welding.
- You can add filler metal easily and keep the electrode clean.
- Stable arcs at low currents make it ideal for micro-welding in aerospace and electronics.
- Longer electrode life and reliable arc starting improve your workflow.
Note: Plasma arc welding stands out when you need high-quality, precise welds for advanced projects. You get the best mix of speed, control, and weld quality.
Laser Beam Welding
Process
Laser beam welding uses a powerful, focused laser to join metals. You direct the laser at the joint, and the intense light melts the metal quickly. The process creates a small, deep weld with very little heat spreading to the rest of the part. You can control the laser’s power, speed, and focus to match the thickness and type of metal. This lets you make either shallow or deep welds.
You can use different techniques with laser welding. Conduction welding works well for thin materials and makes shallow welds. Keyhole welding is best for thick parts and creates deep, narrow welds. Transition welding combines both methods for special jobs. You can also use shielding gases, like argon or nitrogen, to protect the weld from air and keep it clean.
Laser welding machines have advanced controls. You can set the laser’s power, spot size, and speed with great accuracy. The process is fast and works well with robots. This means you can run production lines all day with little downtime. The focused beam keeps the heat-affected zone small, so your parts stay strong and do not warp.
Tip: Laser welding gives you precise control over the weld, making it perfect for jobs that need accuracy and speed.
Applications
You will find laser welding in many high-tech industries. The process is popular because it makes strong, clean welds with little distortion. Here are some main uses:
- Automotive: You can join car body panels, frames, and battery packs. Laser welding helps make cars lighter and safer by creating strong joints with little heat damage.
- Medical Devices: You can weld implants, surgical tools, and pacemakers. The process keeps welds sterile and biocompatible, even when joining metals like titanium and stainless steel.
- Aerospace: You can weld fuel tanks, heat shields, and other parts that need to be light and strong. Laser welding keeps the material’s strength and shape.
- Electronics: You can join tiny parts on circuit boards and sensors. The focused laser protects sensitive components from heat.
- Military and Defense: You can make lightweight, tough parts for vehicles and weapons systems.
- Manufacturing and Metalworking: You can join metals with high accuracy and low distortion, which is important for making tools and machine parts.
- Jewelry and Art: You can join fine metals without damaging delicate designs.
Laser welding supports high-precision manufacturing. You get strong, reliable welds that meet strict standards for safety and performance.
Pros
Laser welding offers many advantages over other welding methods. You get:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Precision | You can make small, accurate welds with little heat spread. |
| Fast Welding Speeds | You finish jobs quickly, which is great for mass production. |
| Small Heat-Affected Zone | Your parts stay strong and do not warp or lose their shape. |
| Automation Ready | You can use robots for 24/7 operation with steady quality. |
| Versatile Techniques | You can weld thin or thick materials by changing the laser settings. |
| Clean Welds | Shielding gases keep the weld free from defects and contamination. |
| Minimal Post-Processing | You spend less time cleaning or fixing the weld after you finish. |
You can weld small or large parts with the same machine. The process works well for joining different metals. Laser welding helps you make products that are strong, light, and accurate. You can trust this method for jobs where quality and speed matter most.
Note: If you need fast, clean, and precise welds, laser welding is a top choice for your project.
Electron Beam Welding
Process
Electron beam welding joins metal using a focused beam of fast electrons. First, you clean the metal parts to remove dirt and oil. This helps make the weld strong. Next, you put the parts inside a vacuum chamber. The vacuum keeps air out and stops the metal from rusting.
Inside the chamber, an electron gun makes a beam of electrons. The gun uses very high voltage, from 20,000 to 150,000 volts. Electromagnetic lenses focus the beam into a tiny spot. When the beam hits the metal, it melts the surface. This makes a deep and narrow weld. You can change the speed and energy for different metal thicknesses. After welding, let the parts cool. Then, check the weld to make sure it is good.
The main equipment you need includes:
- An electron gun that makes and focuses the beam
- A vacuum chamber that keeps air out
- A high-voltage power supply
- Electromagnetic lenses for controlling the beam
- A cooling system to protect the machine
- Monitoring tools to check the weld
Tip: The vacuum helps you get clean and strong welds with almost no dirt.
Applications

Electron beam welding is used in jobs that need strong and exact welds. Aerospace companies use it for engine parts like turbine blades and compressor disks. They also use it for big parts like fuselages and wings. This process works well for rocket nozzles and combustion chambers. It can handle thick and strong metals.
Car factories use electron beam welding for gears, shafts, and engine blocks. It is also used for battery parts in electric cars. The process lets you weld tricky shapes and join different metals. You get fast and accurate welds. This helps when making lots of parts.
Here is a table showing some key uses:
| Industry | Application Examples | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, fuselage, rocket nozzles | Deep welds, little bending, very exact |
| Automotive | Gears, shafts, engine blocks, EV battery parts | Tricky shapes, different metals, fast speed |
Note: The vacuum and focused beam make this process great for parts that must be strong and light.
Pros
Electron beam welding has many good points:
- You can make deep and narrow welds with little heat spread. This means less bending and better strength.
- The vacuum stops rust and keeps the weld clean. You do not need to clean much after welding.
- You can weld almost any metal, like steel, titanium, nickel, and copper alloys. You can even join different metals together.
- You do not need extra filler for most jobs. This keeps the metal strong and makes welding easier.
- The high energy lets you weld thick parts in one go. You save time and get strong, reliable welds.
- CNC controls help you make exact welds every time.
Callout: If you need strong and clean welds on tough or thick metal, electron beam welding gives you the quality and accuracy you need.
Resistance Welding
Process
Resistance welding joins metal pieces using heat from electricity. You press the metal parts together. Then, a strong electric current goes through them. The metal gets hot where they touch. This heat melts the surfaces, so they stick together. You do not need extra filler or gas for this.
There are different types of resistance welding. The main ones are:
- Spot Welding: You join two thin metal sheets at small spots. Copper electrodes press and heat the metal.
- Seam Welding: You make a long weld along a joint. Rotating wheel electrodes press and heat the metal as it moves.
- Projection Welding: You weld at many points at once. Raised bumps on one metal piece help make the welds.
- Flash Welding: You join big parts by clamping them. Current melts the ends, then you press them together.
You control the time, pressure, and current for each weld. This helps you get enough heat and a strong joint. Resistance welding machines can be used by hand or run by themselves.
Tip: Resistance welding works best with metals that carry electricity well, like steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Applications
Resistance welding is used in many industries. Car factories use spot welding to make car bodies, doors, and frames. Appliance makers use it for fridges, washing machines, and ovens. Electronics makers use it to join wires and small parts.
Here are some common uses for resistance welding:
- Automotive: Joining panels, frames, and exhaust systems
- Aerospace: Making light parts and joining thin sheets
- Electronics: Welding battery tabs, connectors, and wire ends
- Construction: Building steel doors, windows, and fences
- Consumer Goods: Making metal furniture, kitchen tools, and home appliances
| Industry | Example Products | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Car bodies, frames, exhausts | Steel, aluminum |
| Electronics | Battery packs, connectors | Copper, nickel |
| Appliances | Fridge doors, washing machines | Stainless steel |
| Construction | Steel doors, window frames | Carbon steel |
You can use resistance welding for small or big projects. The process is fast and works well for making lots of things.
Pros
Resistance welding has many good points. You do not need extra filler or gas, so it is simple and clean. The welds are strong and last a long time. You can make many welds quickly, which saves time and money.
Here are some main benefits:
- Speed: You can join parts in just a few seconds. This is good for making lots of things.
- Consistency: Machines make each weld the same, so you get steady quality.
- Safety: There are no open flames or dangerous gases.
- Low Distortion: The heat stays at the weld spot, so the rest of the metal does not bend.
- Automation: You can use robots and machines for big batches.
Note: If you want a fast, clean, and reliable way to join metal sheets or wires, resistance welding is a smart choice. You will see it in many things you use every day.
Oxy-Acetylene Welding
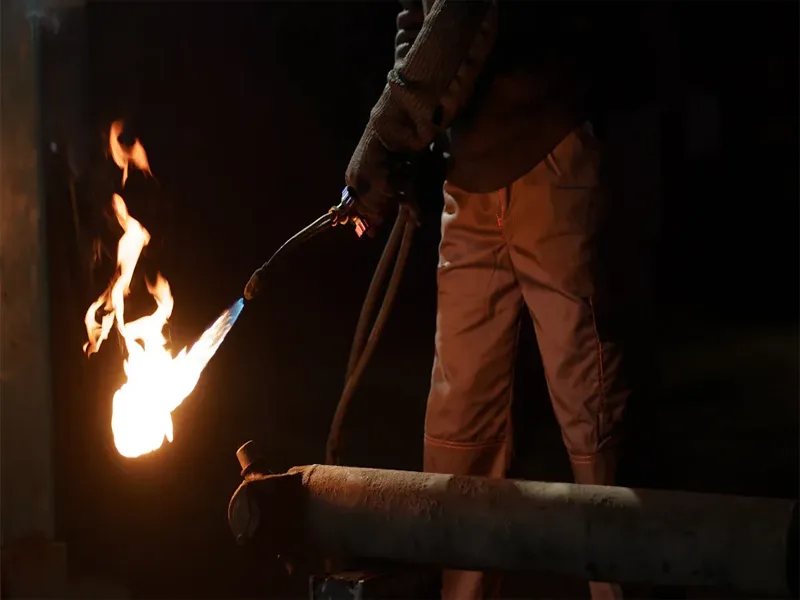
Process
Oxy-acetylene welding uses a flame to join metals. You mix oxygen and acetylene gas in a torch. When you light the torch, the gases burn and create a very hot flame. This flame can reach temperatures above 6,000°F (3,300°C). You hold the torch and move it along the joint where you want to weld. The flame melts the edges of the metal pieces. You can add a filler rod if you need extra metal in the joint. The melted metal flows together and forms a strong bond when it cools.
You control the size and shape of the flame by adjusting the valves on the torch. A neutral flame works best for most metals. You can also use a carburizing or oxidizing flame for special jobs. Before you start, always clean the metal to remove oil, rust, or paint. This helps you get a clean weld. You wear safety gear like goggles, gloves, and a welding jacket to protect yourself from sparks and heat.
Tip: Always check your gas hoses and connections for leaks before you start welding. Safety comes first.
Applications
You can use oxy-acetylene welding for many types of jobs. This process works well for thin metals and small repairs. Many auto repair shops use it to fix car frames, exhaust pipes, and body panels. Plumbers use it to join copper pipes. Artists use oxy-acetylene welding to create metal sculptures and decorative pieces.
Farmers and maintenance workers often use this method for on-site repairs. You can weld, cut, or even heat metal parts with the same torch. This makes oxy-acetylene welding very flexible. You do not need electricity, so you can use it in remote places.
Here is a table showing common uses:
| Field | Example Jobs | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Frame repair, exhaust welding | Steel, aluminum |
| Plumbing | Pipe joining, leak repair | Copper, brass |
| Art & Sculpture | Metal artwork, decorative welding | Steel, bronze |
| Maintenance | Equipment repair, cutting bolts | Steel, iron |
Pros
Oxy-acetylene welding gives you several advantages:
- Portability: You can move the gas tanks and torch almost anywhere. This helps you work in the shop or out in the field.
- Versatility: You can weld, cut, braze, and heat metal with one tool. This saves you time and money.
- No Electricity Needed: You do not need a power source. This makes it perfect for remote locations.
- Good for Thin Metals: You can control the flame and heat. This helps you avoid burning through thin sheets.
- Simple Equipment: The setup is easy to use and maintain. You can learn the basics quickly.
Note: If you want a flexible and portable way to weld or cut metal, oxy-acetylene welding is a smart choice. You can handle many repair and fabrication jobs with just one torch.
AFI Welding Services

Precision & Quality
You want your welds to be strong and neat. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. gives you this kind of quality. Their team uses modern welding machines and checks every weld carefully. The welds are made with tight tolerances, as close as ±0.1mm. This means your parts fit together just right each time. AFI checks every weld three times during the process. These careful checks keep mistakes very low, under 0.5%. You can trust AFI to make welds that last a long time. They have ISO9001 certification, which shows they care about quality. You see this care in every job, from small fixes to big builds.
Tip: If you need welds that meet tough rules, AFI’s welding services help you feel sure about your project.
Materials & Capabilities

AFI is special because they can weld many kinds of metals. You can bring them carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, or zirconium alloys. Their team knows how to change the welding process for each metal. This helps stop problems like bending or weak spots. AFI can work on tiny parts for electronics or huge steel pieces up to 60 tons. You get custom help for both small and big jobs. Their machines can do fusion welding, pressure welding, and brazing. You can also ask for special coatings to make your parts stronger or look better.
- You can get one part or many made at once.
- You can ask for special welding for odd shapes or rare metals.
- AFI uses new technology to keep your welds strong and neat.
Industry Applications
You see AFI’s welding in many industries. Their work helps factories, builders, transport, and energy companies. You might need strong welds for machines, building frames, or train parts. AFI also works on planes, where welds must be very safe. Artists and designers use AFI for metal art and decorations. The company’s experience means you get the right solution for your job. You can count on AFI for both normal and special projects.

| Industry | Example Applications |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Equipment, machine parts |
| Industrial | Heavy machinery, steel structures |
| Construction | Building frames, bridges |
| Transportation | Rail, ship, and aerospace components |
| Energy | New energy equipment, pipelines |
| Art & Design | Metal art, custom decorations |
Note: AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. gives you smart welding solutions for any tough job.
Welding Processes Pros Comparison
Quick Reference Table
It is helpful to see welding processes side by side. This makes it easier to choose the best one for your job. You should check what each process does best and where it works well. The table below lets you quickly compare the welding processes pros for the top 10 methods. Use this table to find which welding process fits your project.
| Welding Process | Main Pros | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Shielded Metal Arc (Stick) | Portable, works outdoors, low cost | Construction, repairs, heavy equipment |
| Gas Metal Arc (MIG) | Fast, easy to learn, clean welds | Automotive, fabrication, production lines |
| Gas Tungsten Arc (TIG) | High precision, clean, strong welds | Aerospace, food industry, thin metals |
| Flux Cored Arc | High deposition, good for thick/dirty metals | Bridges, shipbuilding, field repairs |
| Submerged Arc | Deep welds, high speed, automated | Shipbuilding, tanks, heavy structures |
| Plasma Arc | Precise, handles thin and thick metals | Aerospace, electronics, medical devices |
| Laser Beam | Very precise, fast, small heat zone | Automotive, electronics, medical tools |
| Electron Beam | Deep, clean welds, joins hard metals | Aerospace, nuclear, high-precision parts |
| Resistance | Fast, repeatable, no filler needed | Automotive, appliances, electronics |
| Oxy-Acetylene | Portable, no electricity, versatile | Repairs, plumbing, art, field work |
Tip: Look at this table to compare welding processes pros for your project. If you want fast work and easy cleanup, MIG welding is a good pick. For fixing things outside, stick welding works best. If you need very neat welds, TIG or laser welding are great choices.
Think about the metal type, how thick it is, and where you will weld. Some welding process pros are good for outdoor jobs or thick metal. Others make clean welds for special projects. If you need to weld many parts fast, resistance welding or submerged arc welding can help you save time.
Every process has its strong points. The welding processes pros table helps you choose wisely. You get the best results when you pick the right process for your needs. If you are not sure, you can ask a welding expert for help.
Understanding the top 10 welding processes helps you choose the right method for your project. Each process has special strengths. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. gives you access to expert welders and advanced technology. You get strong, clean welds for any job. Think about your needs and ask AFI for advice.
Ready to start your next project? Contact AFI for custom welding solutions and expert support.
FAQ
You should use submerged arc welding or flux cored arc welding. These methods work best for thick steel plates. They give you strong, deep welds and save you time on large projects.
Yes, you can weld aluminum with both MIG and TIG welding. TIG welding gives you cleaner, more precise welds. MIG welding works faster and is easier to learn.
You can check your weld by looking for cracks, holes, or uneven spots. You can also use tests like X-rays or ultrasonic scans. AFI uses three-level inspections to make sure your welds are strong and safe.
Welding is safe if you follow the right steps. You must wear safety gear like gloves, goggles, and jackets. Always work in a well-ventilated area. AFI trains workers to follow strict safety rules.
AFI can weld many metals. You can bring carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, copper alloys, and zirconium alloys. AFI adjusts the welding process for each metal to get the best results.
Shielding gas protects the weld from air. This keeps the weld clean and strong. Without shielding gas, the weld can get weak or have holes. You use gases like argon or carbon dioxide for this purpose.
Yes, AFI can help you with custom projects or small batches. You can get one part or many. AFI uses advanced machines to meet your needs, no matter the project size.
You can contact AFI through their website or by phone. Give details about your project, such as the metal type, size, and quantity. AFI will respond quickly with a custom quote.





