Metal nickel is very important in 2025 for technology and industry. Nickel metal has special features, including resistance to rust and exceptional strength. These features make it useful in tough places. The car industry needs nickel metal to make electric car batteries better. Airplane companies use nickel for parts that must handle heat and stay strong. People who make electronics use nickel metal because it carries electricity well. Builders use nickel metal to help make stainless steel. All these uses show why metal nickel is still important. Its features help shape our lives and new ideas for the future.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Nickel is a hard, shiny metal. It does not rust. It carries electricity well. This makes it important for many industries in 2025.
- Most nickel is used to make stainless steel. It is also used in electric car batteries. These products last longer and work better with nickel.
- Nickel mostly comes from a few countries. These are Indonesia, Russia, and Canada. Mining methods are changing to meet demand.
- New technology and recycling help make cleaner nickel. This helps lower pollution. It supports a greener future.
- Nickel alloys are used to make strong parts. These parts go in airplanes, ships, and power plants. They can handle heat and stress.
- The nickel market is growing because of electric vehicles and clean energy. But supply chain problems cause price changes and risks.
- Health and safety rules keep workers and consumers safe. They protect people from nickel allergies and dust.
- Environmental efforts try to cut emissions and manage waste. They also restore land to lower nickel mining’s impact.
Metal Nickel Overview
What Is Nickel?
Nickel is found in nature. Its symbol is Ni and its atomic number is 28. Scientists say nickel is hard and silver-white. It does not rust or corrode easily. Nickel metal looks shiny and has a cube-shaped crystal form. It can bend without breaking, so it is ductile. Nickel metal is also magnetic when it is cold enough. In factories, people sort nickel by how pure it is, like Class I or Class II. Nickel metal helps make alloys, batteries, and other things. It is good at handling heat and does not corrode, so it is used in many jobs.
Nickel metal is special because it can be recycled many times. It keeps its good features even after being reused. This makes it important for a greener future.

Nickel Metal Basics
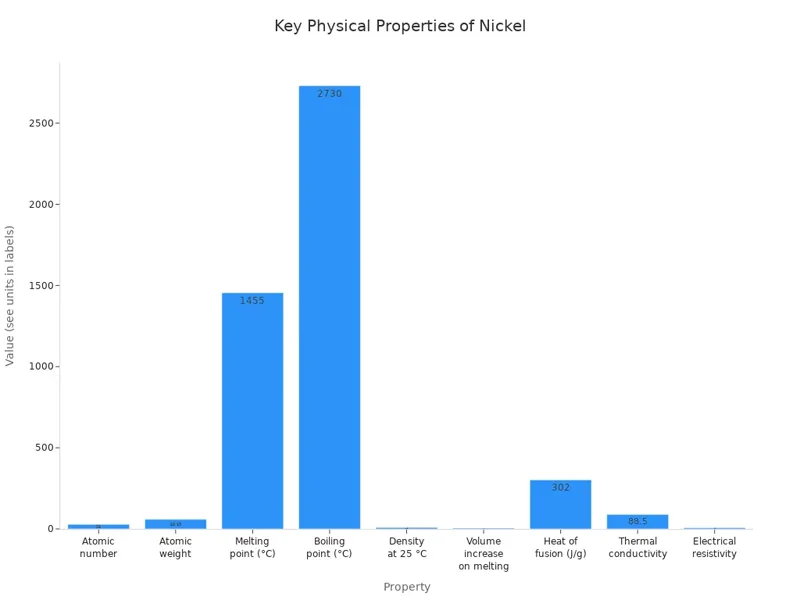
Nickel metal has many useful features. It melts at about 1455 °C. It boils at around 2730 °C. At room temperature, its density is about 8.9 grams per cubic centimeter. Nickel metal moves heat and electricity well. It is strong and can be shaped into wires or sheets. The table below lists some main facts about nickel metal:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Atomic number | 28 |
| Atomic weight | 58.69 |
| Melting point (°C) | About 1455 |
| Boiling point (°C) | About 2730 |
| Density at 25 °C | Approximately 8.9 g/cm³ |
| Heat of fusion (J/g) | 302 |
| Thermal conductivity | 88.5 W m⁻¹ K⁻¹ |
| Electrical resistivity | 6.9 μΩ/cm |
| Appearance | Lustrous, silvery-white |
Nickel metal comes in different forms. These are pure nickel, nickel alloys, and nickel compounds. Each kind is used for special things because of its features.
Occurrence and Sources
Nickel metal is found in the Earth’s crust. There are two main types of nickel ores: laterite and magmatic sulfide. Laterite ores form in warm places like Indonesia, the Philippines, Brazil, and New Caledonia. These ores make up about 65% of all nickel in the world. Magmatic sulfide ores are found in Russia, Canada, and South Africa. These ores are deeper and have more nickel in them.
The biggest nickel sources are in Australia, Indonesia, Russia, Canada, South Africa, the Philippines, and New Caledonia. Australia has the most nickel saved up for the future. Most nickel metal is taken from these places and cleaned for use in factories.
Nickel metal is found in many countries, but only a few make most of it. This makes the world nickel market very important for technology and industry.
Metal Nickel Properties
Physical Properties
Appearance
Nickel metal looks shiny and silvery-white. Its surface shines because it reflects light. Even after a long time, it stays bright. Nickel metal is often made into bars, sheets, or wires. This look helps people know it is nickel in factories and products.
Strength and Ductility
Nickel metal is strong and tough. It can bend without breaking. Workers can roll or stretch nickel into thin sheets or wires. This makes nickel useful for many things. Nickel alloys also stay strong and tough. They work well in hard places.
Magnetic Properties
Nickel is magnetic at room temperature. It can attract magnets and become magnetized. This helps when making electronics and shields for magnets. Some nickel alloys, like Permalloy, are even more magnetic. These alloys protect devices from outside magnets.
The table below shows some main physical properties of nickel metal in 2025:
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 1453 – 1455 | °C (1726 K) |
| Density | 8.9 | g/cm³ (at 300 K) |
| Electrical Conductivity | ~1.43 x 10^7 | S/m |
Chemical Properties
Corrosion Resistance
Nickel metal does not rust or corrode in air or water. It forms a thin oxide layer on its surface. This layer keeps the metal safe from harm. Nickel alloys, like stainless steel, use this to last longer. Many industries pick nickel for this reason, especially in ships and chemical plants.
Temperature Stability
Nickel metal keeps its strength at high heat. It does not melt or get weak easily. Nickel alloys, like Nichrome and Nimonic, work well when it is hot. These alloys are used in jet engines, power plants, and heaters. Nickel’s high melting point makes it good for tough jobs.
Nickel’s chemical properties also include:
- Nickel makes a thin oxide layer that keeps it stable.
- It reacts with acids and bases to make salts.
- Nickel mixes with metals like iron and copper to get stronger and resist rust.
- Its crystal shape helps nickel bend and stay tough.
Nickel Alloys
Nickel alloys mix nickel with other metals to get better features. These alloys are strong, resist rust, and stay stable in heat. People use nickel alloys in many ways, like in ships and airplane engines.
The table below shows some main nickel alloys and what they are used for:
| Nickel Alloy Series | Composition Highlights | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Monel | Nickel-copper alloys (~63% Ni) | Marine hardware, pumps, valves, aerospace, chemical industries |
| Hastelloy | Nickel with molybdenum, chromium, iron, cobalt | Chemical processing, pollution control, high-temperature corrosive environments |
| Nimonic | High nickel content with chromium, iron, cobalt | Gas turbines, aerospace engines, power generation, automotive high-temp components |
| Incoloy | Nickel-based with chromium, iron, molybdenum | Heat exchangers, petrochemical processing, furnace components, offshore oil and gas |
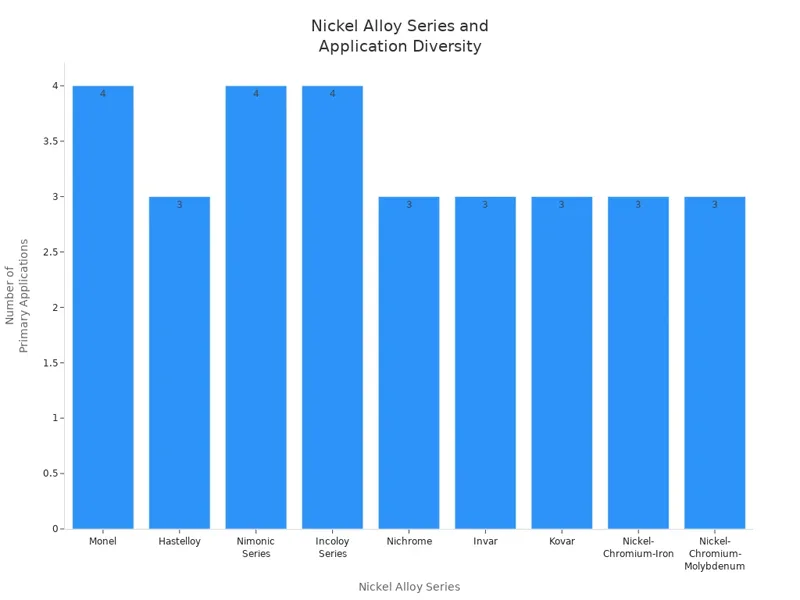
Nickel alloys are important in today’s industry. Their good features help things last longer and work better in hard places. Engineers choose these alloys for their strength and toughness. Nickel alloys help new ideas in planes, energy, electronics, and chemical plants.
Nickel metal and its alloys are still important in 2025. Their special features make them needed for the future.
Nickel Production Process

Nickel Extraction and Processing
The nickel production process starts with getting nickel from the ground. Workers dig up nickel ore and turn it into pure metal. They use many steps to separate nickel from other stuff. Each step makes the nickel cleaner.
The main steps in nickel extraction and processing are:
- Crushing and size separation: Workers break the ore into small pieces. They sort it by size and use magnets to help.
- Flotation: Chemicals make bubbles that lift nickel minerals away from waste rock.
- Smelting: Very high heat changes the mix into a matte with nickel and cobalt.
- Pyrometallurgical refining: Heat helps split metals from the matte.
- Hydrometallurgical refining: Workers use chemicals and pressure to pull out nickel, take away copper, and make nickel solid again.
- Electrowinning: Electricity pulls pure nickel metal out of a solution.
These steps change raw ore into nickel that factories can use. The whole process is important for making things like batteries and stainless steel.
Mining Methods
Nickel is mined in different ways depending on the ore and place. In 2025, Asia is the top nickel producer. Indonesia and China lead the way. Indonesia mines laterite ore using big machines. They use High Pressure Acid Leaching (HPAL) and Rotary Kiln-Electric Furnace (RKEF). These methods turn laterite ores into nickel for batteries and more.
China makes a lot of nickel pig iron (NPI), but this has slowed since 2019. Outside Asia, nickel mining is going down. Many old mines in Europe, Oceania, Africa, and the Americas have closed or slowed. Now, Southeast Asia’s laterite mining is the main source. Sulfide mining is less common in other places.
In 2025, nickel comes from three main sources: magmatic sulfide ores, nickel laterites, and recycled stainless steel scrap. Sulfide ores give very pure nickel. Laterites make lower-purity products like ferronickel and NPI. Indonesia’s export ban on nickel ore made companies build local plants. This makes laterite mining more popular.
Nickel mining uses different ways based on ore, place, and new technology. These things change how nickel is made around the world.
Refining Steps
After mining, nickel goes through more steps to get very pure. Refining uses heat and chemicals. For sulfide ores, workers use smelting and heat-based refining. For laterite ores, they use chemical extraction.
New ideas in nickel refining use better chemical methods. These ways help separate and clean nickel, save energy, and make less waste. Some new plants use magnets and bubbles to get better nickel. Test plants now get over 99% of the nickel out. They use leaching, special chemicals for cobalt, and crystal-making to get battery-grade nickel sulfate.
Better refining technology helps make more battery-grade nickel. These changes also help the environment by making less pollution. Companies now make cleaner nickel with less harm to nature.
Sustainability Innovations
In 2025, the nickel industry cares more about the planet. Companies and governments want to help the environment and local people. They use new ideas to make mining and refining safer and cleaner.
Some top efforts for sustainability are:
- Responsible sourcing programs follow world rules. These programs stop human rights problems and keep conflict minerals out.
- Many companies try to lower their carbon footprint. They save energy and work to cut down pollution.
- Environmental steps like land reclamation and reforestation fix land after mining. Good waste management keeps water and soil safe.
- More recycled metals are used now. Companies recycle old batteries, scrap steel, and stainless steel. This helps a circular economy and means less new mining.
- Community engagement and safety steps protect workers and local people. Companies also make plans to respect rights and help social sustainability.
New technology is important for these changes. Many nickel producers use hydrometallurgy now. This uses water-based solutions, not high heat. It uses less energy and makes fewer greenhouse gases. Some plants use electric furnaces with renewable energy. This helps lower carbon emissions even more.
Automation and digital tools help too. Companies use drones and sensors to check mines. Big data and machine learning help them plan and save money. These tools make work safer and more efficient.
Hydrogen-based reduction is a new process with promise. It uses hydrogen and argon gas to turn ore into high-grade ferronickel. The only byproduct is water. This makes much less carbon dioxide than old smelting. As sulfide ores get harder to find, hydrogen-based reduction helps process laterite ores in a cleaner way. It helps the nickel industry move toward a low-carbon future.
Note: Even with these changes, some problems remain. Water use, land restoration, and protecting nature are still big challenges for the industry.
These new ideas show the nickel sector is trying to grow while caring for people and the planet.
Nickel Uses
Stainless Steel

Stainless steel uses more nickel than anything else in 2025. Factories need nickel to make stainless steel strong and shiny. Nickel also helps it not rust. About 69% of all nickel goes into making stainless steel. This number stays the same, even though batteries need more nickel now. Stainless steel is used in buildings, bridges, and kitchen tools. It is also found in medical equipment. Nickel makes stainless steel last longer and look nice. Many companies pick stainless steel because it does not stain or rust easily. Nickel gives stainless steel more strength, a longer life, and makes it easy to clean.
Stainless steel with nickel is needed in hospitals, food factories, and water pipes. These places need things that stay clean and safe.
Batteries and Electronics
Nickel is very important for batteries and electronics. More nickel is needed for batteries every year. Electric vehicles and new gadgets use more nickel now. Battery makers pick nickel because it helps batteries hold more energy. It also lets them charge faster. Most lithium-ion batteries, like NCA and NMC, have 60-90% nickel. These batteries power electric cars, laptops, and phones. In 2025, about 18% of cars sold are electric. This number keeps going up. Experts think over 30% of cars sold will be electric by the end of the year. Most of these cars use batteries with lots of nickel.
- Nickel lets batteries store more energy, so cars go farther.
- Electronics makers use nickel because it conducts electricity well and is strong.
- The growing electric car market means more nickel is used in batteries and electronics.
- Battery makers now pay more and see prices change because so many people want nickel.
Nickel is also found in wires, connectors, and circuit boards. These parts need metals that carry electricity well and do not rust. Nickel is good for this, so it is used a lot in electronics.
Industrial Applications

Nickel is used in many other ways besides stainless steel and batteries. Factories use nickel and its alloys in heating parts and engine pieces. Nickel alloys work well in irons, toasters, and thermostats. They do not break from heat or air. Nickel plating covers machine parts to stop rust and wear. This helps them last longer and look better.
Copper-nickel alloys are used in ships and seawater pipes. They are also used in desalination plants. These alloys do not rust in salty water and stop sea life from sticking. Power plants use nickel alloys for turbine blades and boiler tubes. These parts must handle high heat and stress. Nickel alloys are also used in car, airplane, and ship parts that need to be strong.
Hospitals use nickel in surgical tools and implants. Nickel is safe for the body and does not rust, so it is good for medical devices. The food industry uses nickel alloys for machines that must stay clean and last long. Water treatment plants and paper factories also use nickel alloys because they are tough.
Here is a table that shows some main industrial uses for nickel:
| Application Area | Example Uses | Why Nickel Is Used |
|---|---|---|
| Marine | Seawater pipes, ship parts | Corrosion resistance |
| Energy & Power | Turbine blades, boiler tubes | High-temperature strength |
| Electronics | Circuit boards, connectors | Conductivity, corrosion resistance |
| Medical | Surgical instruments and implants | Biocompatibility, durability |
| Food & Water | Processing equipment, water systems | Hygiene, long life |
| Manufacturing | Heating elements, plating, mechanical parts | Heat resistance, wear protection |
Nickel is used in many ways to help make products safer, stronger, and last longer.
Consumer Products
Nickel is found in many things people use daily. Companies pick nickel because it is strong and shiny. It also does not rust easily. In 2025, more people want nickel in their products. This is because new technology and green ideas are changing what people buy.
Nickel is important in electronics. Many phones, laptops, and home gadgets have nickel parts. These parts include connectors and switches. Nickel helps them carry electricity and handle heat. Cars also need nickel. It is used in batteries and strong car parts. Nickel silver is a favorite for car parts. It is strong and does not rust.
Jewelry makers like nickel for its bright look. It helps jewelry stay shiny and new. Musical instruments and decorations use nickel too. Nickel makes them last longer. In building, nickel helps pipes and other parts stay strong.

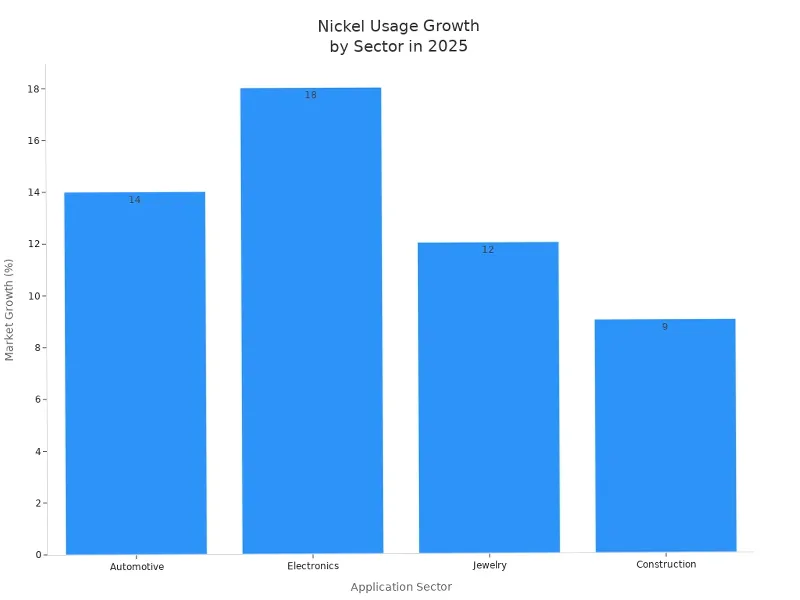
The table below shows how different jobs use nickel. It also shows how the market is changing in 2025:
| Application Sector | Usage Description | Market Growth / Share |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Use of nickel silver for durable, corrosion-resistant automotive parts and decorative items; favored for strength-to-weight ratio and environmental compliance | 14% increase in adoption; 22% market share |
| Electronics | Use in connectors, switches, terminals due to conductivity and thermal resistance; supports growing electronics demand including EVs | 18% growth; 26% market share |
| Jewelry | Use in fine jewelry and musical instruments for aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance | 12% growth; 10% market share |
| Construction | Use in plumbing and structural components for durability and corrosion resistance | 9% growth; N/A market share |
- More nickel-plated plastics in health tools, plane parts, and smart gadgets.
- More cars use nickel, especially electric cars and fancy trims.
- New needs for EMI shielding in electric and self-driving cars.
- Factories use AI and robots to plate nickel faster and better.
- Companies use safer ways to plate nickel, like closed water systems and safe chemicals.
- North America is first to use new materials and green designs.
Nickel is used in many products. It helps things last longer, look nice, and work well.

Nickel is used more in products as technology and green ideas grow.
Chemical Uses
Nickel has many chemical uses in 2025. The biggest change is that more nickel sulphate goes into batteries. Most nickel sulphate is now used for electric car batteries. About 75% is for this. Only about 10% is for stainless steel. About 12% is for plating and other factory uses.
Other chemical uses are in engineering, metal goods, transport, pipes, electronics, and building. The chemical industry likes nickel because it makes strong, rust-proof alloys. It also helps make good chemicals.
Key facts about chemical uses of nickel in 2025:
- Making battery materials uses most nickel sulphate, mostly for electric cars.
- Less nickel sulphate is used for stainless steel and plating now.
- Factories want purer and better nickel chemicals for batteries.
- New ways and digital tools help make better nickel chemicals with less waste.
- Safety and green rules make companies use cleaner chemicals and work better.
Nickel’s chemical uses change as new tech and markets grow. Nickel is needed more for batteries and new materials as clean energy and electronics get bigger.
Nickel Pros and Cons
Advantages
Nickel is helpful in many industries and technologies. It makes stainless steel strong and bendy. This metal stays strong when made into thin wires or sheets. Nickel helps stainless steel not rust, so things last longer and look shiny. Factories use nickel because it does not rust, even in tough places like chemical plants or near the sea.
Nickel alloys like Inconel and Monel are used in wind turbines and solar panels. These alloys stay strong in high heat and bad weather. Jet engines use nickel superalloys because they do not break under heat or stress. Nickel also makes ceramics and composites stronger for cars and planes.
Nickel can be recycled many times. Most stainless steel has about 60% recycled nickel. Recycling nickel saves energy and produces less pollution. The nickel industry tries to be safer and better for the planet. Nickel is also important for new things like electric car batteries and smart medical devices.
Nickel’s special features help make products stronger, last longer, and work better.
Disadvantages
Nickel has some problems that limit its use. Nickel alloys cost more than many other metals. This means they are not used in things that do not need special features. It is hard to cut and shape nickel alloys because they are very tough. Workers need special tools and more time to work with them.
Welding nickel alloys is also hard. They melt at high heat, which can cause bending or stress in the finished part. Some nickel alloys mixed with copper can lose their shine in air and water. This makes them look dull after a while.
Nickel can cause allergies. People who wear jewelry or use things with nickel may get skin problems. These allergies mean nickel is not good for some medical and wearable items.
- Nickel alloys cost a lot.
- Cutting and welding are hard.
- Some alloys lose their shine.
- Nickel can cause skin allergies.
Health and Safety
Nickel can affect health in different ways. Touching nickel for a long time, like from jewelry or watches, can cause skin problems. This can make skin red, itchy, or even blister. Many people become allergic to nickel after touching it many times.
People who work where nickel is mined or cleaned have higher risks. Breathing nickel dust or fumes can cause serious health problems. These include bronchitis, asthma, and some cancers like lung or nose cancer. Nickel compounds that dissolve in water are very bad for the lungs. Rules in places like the European Union help lower skin and air contact with nickel. This helps stop allergies and other health problems.
Most people do not have big risks from nickel in daily life. But people who work with nickel or wear nickel items should follow safety rules. Using safety gear and following work rules can help stop health problems.
Good safety rules and laws help keep workers and people safe from nickel risks.
Environmental Impact
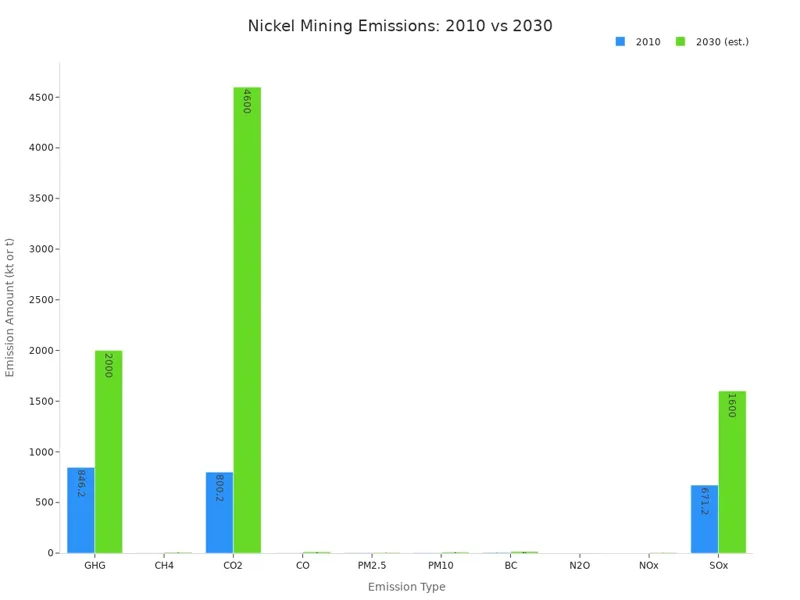
Nickel mining and making nickel can hurt the environment. These steps make a lot of pollution and waste. Mining uses lots of energy. This makes greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. These gases trap heat and make climate change worse. The table below shows some main types of pollution and waste from nickel production. It compares amounts from 2010 and what is expected in 2030.
| Emission/Waste Type | Major Stage(s) | 2010 Amount | 2030 Estimate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse Gases (GHG) | Mining | 846.2 kt | 2 mt | Mining is the largest GHG source |
| Methane (CH4) | Mining (energy use) | 1.4 kt | 7.9 kt | Comes from coal, oil, and gas use |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Mining | 800.2 kt | 4.6 mt | Main CO2 emissions from mining |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Primary extraction | 1.5 kt | 12.8 kt | Highest CO emissions at this stage |
| Particulate Matter PM2.5 | Primary extraction | 2.9 kt | 6.7 kt | Fine dust harmful to lungs |
| Sulfur Oxides (SOx) | Primary extraction | 671.2 kt | 1.6 mt | Causes acid rain |
| Solid Wastes | Smelting, leaching | Large | N/A | Toxic heavy metals, risk to soil and water |
Making nickel also makes solid waste like smelter slags and leaching leftovers. These wastes can have toxic metals in them. If not handled right, they can get into soil and water. This can hurt plants, animals, and people who live close by. Some wastes are not well studied, so we do not know all the risks.
Air pollution is a big problem too. Mining and making nickel send out dust and gases like sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides. These can cause breathing problems and make acid rain. Acid rain can damage forests, rivers, and buildings.
Recycling nickel helps cut down on pollution and waste. Using recycled nickel in batteries and steel saves energy and lowers emissions.
Many companies now try to use better ways. They recycle more metal and use less energy. Some use life cycle assessment (LCA) to check and lower their impact. But as more nickel is needed, pollution and waste could go up unless new technology is used.
Sustainable steps like waste valorization and better recycling are important for the future. These actions help protect nature and keep people safe. The nickel industry is under pressure to do better, but things change slowly without strong rules and new ideas.
Nickel Trends 2025
Market Demand
Experts think people will need more nickel in 2025. This is mostly because of stainless steel and electric car batteries. In 2022, the nickel market was worth over $20 billion. It is expected to grow about 5% each year. By 2030, it could reach almost $30 billion. Asia Pacific uses the most nickel. China is the biggest user in that area. Stainless steel still uses most of the world’s nickel. Cars and buildings need a lot of stainless steel.
Key points about market demand:
- More than 60% of nickel goes into stainless steel.
- Electric car batteries use more nickel every year.
- Companies like Samsung SDI and General Motors spend billions on new battery factories in the U.S.
- New chemical plants in Saudi Arabia help make more battery materials.
- Some places, like Europe, use less nickel because of energy and supply problems. Still, the overall need for nickel keeps going up.
More electric cars and clean energy mean more nickel is needed. This is likely to keep happening for years.
Supply Chain
The nickel supply chain has many problems in 2025. Battery makers want more pure nickel than before. Only about half of all nickel is pure enough for batteries. This pure nickel comes mostly from sulfide ores. These ores are hard to find and process. Most nickel refining happens in China and Russia. This can be risky for other countries.
Main supply chain issues include:
- Indonesia has much of the world’s nickel ore. Indonesia and the Philippines work together to control supply and prices.
- The Philippines may stop selling ore to other countries in five years. This could make it harder for China to get nickel and change the world market.
- Chinese companies own many nickel projects in Indonesia. This makes it tough for Western countries to get their own nickel.
- Western governments spend money on new projects in safer countries. They do not want to depend on China and Russia.
- Fights between countries and trade bans make the supply chain less safe.
- Things like COVID-19 and worker strikes have closed mines and stopped work.
- Nickel prices go up and down quickly because of these problems.
Many countries now try to make their nickel supply chains safer and stronger. They want to stop sudden shortages and big price changes.
Technology Advances
New technology helps the nickel industry keep up with demand and fix supply problems. Companies use better ways to get and clean nickel. Atlas Materials made a new way to treat low-grade ore. This method makes almost no waste or pollution. It lets more types of ore be used for electric car batteries.
Other important advances:
- Bioleaching uses tiny living things to get nickel from ore. This is cleaner and uses less energy.
- New flotation methods help separate nickel minerals better.
- High-pressure acid leaching (HPAL) gets up to 90% of nickel from ore. It uses less energy and makes less pollution than old ways.
- Many factories now use renewable energy and recycle water to help the environment.
- Better machines and controls save energy and cut down on waste.
| Technology | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Bioleaching | Lower environmental impact |
| HPAL | Higher recovery, less energy use |
| Renewable energy use | Fewer emissions, cleaner production |
| Advanced flotation | Better mineral separation |
These new ideas help the nickel industry make more metal with less harm to nature. They also help meet the growing need for battery-grade nickel.
Regulatory Changes
In 2025, new rules change how companies make and use nickel. Governments want the nickel industry to be safer for people and nature. These new laws affect mining, refining, and selling nickel everywhere. In the United States, lawmakers work on new updates. They want to change the Federal Power Act. This gives the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission more control. The group checks if the power system is safe and steady. Nickel mines and refineries use lots of electricity. Now, they must follow stricter rules to keep the power grid strong.
Lawmakers also look at the National Environmental Policy Act. They want stricter environmental checks. Companies must prove their projects do not hurt land, water, or air. Nickel mines and plants need better plans to protect nature. They must share more details and fix problems faster.
There are talks about changing rules for using public land. Lawmakers may limit how much land companies can use for mining. They might also make it cost more to use public land. Nickel companies must plan for these changes and try to help the environment.
Trade rules do not focus on nickel in 2025. But new energy and environmental rules make moving nickel between countries harder. Companies have more paperwork and higher costs to follow these rules.
Key trends in 2025 are:
- Tougher checks for new mining and refining projects
- More reports about pollution and land use
- Higher costs for using public land
- Stricter rules for energy use and power safety
Companies that follow these rules can earn trust from customers and governments. They also help protect the earth for the future.
These new rules make nickel companies use cleaner and safer ways. Companies that change fast can find new chances and stay ahead in the market.
Industry experts think metal nickel is very important in 2025. The table below gives key facts for this year:
| Key Aspect | 2025 Details |
|---|---|
| Global Production | 3.735 million tons |
| EV Battery Nickel Demand | 450,000 tons needed |
| Recycling Contribution | 12% of supply, rising to 18% by 2030 |
| Market Share | China-Indonesia: over 60% of global supply |
| Stainless Steel Demand | ~72% of total nickel use |
Nickel is strong and does not rust. It also carries electricity well. These features make it good for batteries, stainless steel, and electronics.
Key points:
- Nickel production is growing for electric cars and green technology.
- Recycling and new ways to process nickel bring new chances.
- There are still problems with supply and changing prices.
Investors should look for smart projects, pay attention to new rules, and think about future needs.
FAQ
Nickel is needed for batteries in electric cars. It also helps make stainless steel strong. Many new technologies use nickel. Nickel does not rust and is very tough. This makes it useful in lots of products.
Most nickel comes from Indonesia and the Philippines. Russia and Canada also mine a lot of nickel. These countries have big mines. Australia keeps a lot of nickel for the future.
Nickel is safe in most things we use. Some people get skin rashes from nickel in jewelry. Workers in nickel mines wear safety gear. This helps them not breathe in nickel dust.
Yes, nickel can be used again and again. Factories use old nickel to make new steel and batteries. Recycling nickel saves energy and helps the planet.
Nickel lets batteries store more energy. Cars with nickel batteries can go farther. They also charge faster. Car makers use more nickel to make better batteries.
Nickel mining can pollute air and water. It makes waste and uses lots of energy. Companies now try new ways to make less pollution. They also recycle more nickel.
Nickel is in coins, kitchen tools, and car parts. Phones and medical tools also use nickel. Nickel helps these things not rust and carry electricity.
Tip: If you have a nickel allergy, look for nickel-free labels.





