When considering metal tin materials for your project, you have important choices to make. Tin is unique because it melts at a low temperature of 232°C and boils at a high temperature of 2590°C. Additionally, tin has ten stable isotopes, more than any other element. Here’s a quick overview:
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Melting point | 232°C |
| Boiling point | 2590°C |
| Stable isotopes | 10 |
Unlike copper, brass, bronze, or aluminium, tin offers strong protection against rust. This makes tin especially valuable in many applications. Understanding these properties of tin and how it compares to other metal tin materials like copper, brass, bronze, and aluminium will help you make the best choice for your needs.
Picture suggestion: Show tin metal, copper, brass, bronze, aluminium, tin’s structure, and how tin prevents rust. Include at least five pictures covering each topic.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Tin melts at a low temperature. It is very soft. This makes tin easy to shape. But tin is not strong for heavy jobs. Tin does not rust easily. It is good for covering other metals. Tin also protects food in cans. Zinc is best for stopping rust outside. Tin is safer for food and electronics. Copper is strong. It is great for electrical wires and plumbing. Copper is often mixed with tin to stop rust. Aluminum is light and strong. It can be recycled. Aluminum is good for building and packaging. It usually costs less than tin.
Overview
Differences
When you look at tin, zinc, copper, and aluminum, you see they are not the same. Each metal has special features that change how you use them. Tin is different because it melts at a lower temperature than copper or aluminum. It is also much softer than the others. Tin melts at 231.9°C, which is lower than copper and aluminum. Tin is very soft, with a hardness of 27, while copper is 301 and aluminum is 271. Because tin is so soft, you can shape it easily. But it is not good for building strong things.
| Property | Tin’s Characteristic | Comparison to Other Metals |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Mohs) | Low (1.5) | Tin is softer than zinc, copper, and aluminum |
| Melting Point | Low (231.9 °C) | Lower than most structural metals |
| Corrosion Resistance | High at room temp due to oxide layer | More resistant than zinc, less than noble metals |
| Alloying Versatility | High; forms bronze, solder | Enhances other metals’ properties |
Tin does not rust as fast as zinc. Zinc wears away over time because it protects other metals. Copper gets stronger and thicker as it gets older. Aluminum is light and has medium strength. Tin is mostly used to cover other metals or to make alloys. You can see how soft tin is in the chart below:
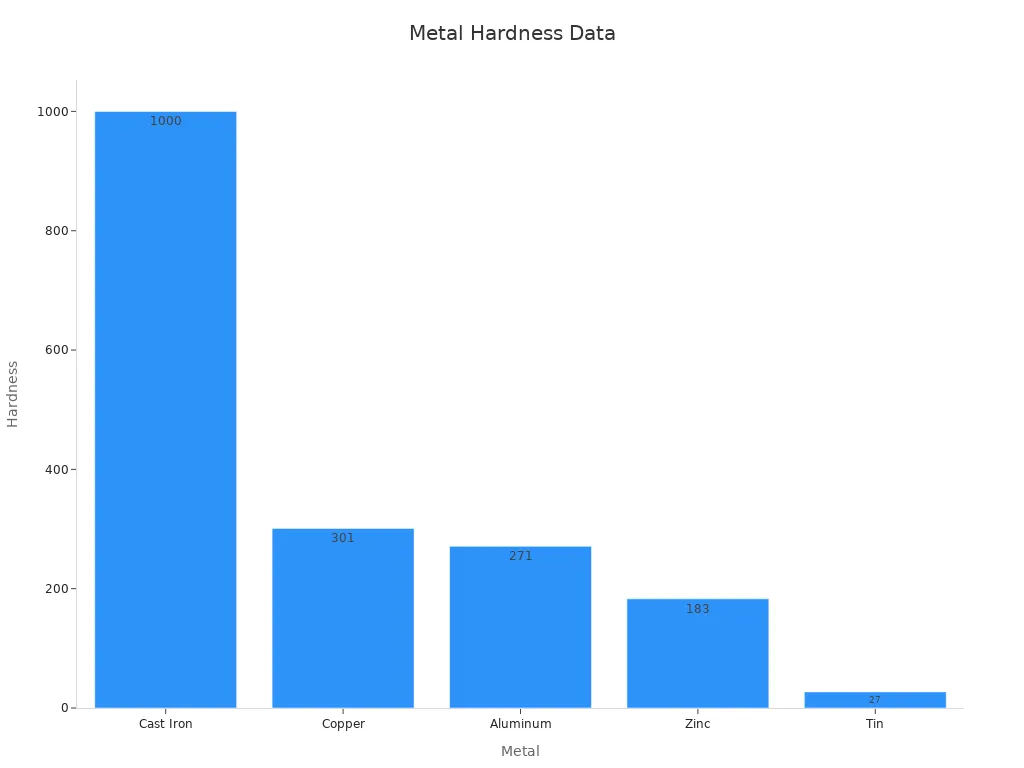
Tin is easy to bend and shape, but it is not strong like other metals.
The price of tin is also different from the others. Tin was the third best in yearly returns over 21 years. Copper and aluminum had different results. Tin’s price does not always go up or down with copper. This means tin acts differently in the market.
Similarities

These metals also have things in common. Tin, zinc, copper, and aluminum all fight rust in their own ways. Tin and zinc make a layer on top that keeps the metal safe. People use tin and zinc to cover steel and stop it from rusting. Copper and aluminum also do not rust easily, but copper can turn green after a while.
- All four metals are used to cover other metals and to make alloys.
- You can recycle and use each metal again.
- They are found in electrical work, building, and packaging.
- Tin, zinc, copper, and aluminum all have prices that go up and down, but each one changes in its own way.
A study showed that putting tin over copper and zinc on aluminum made it much harder for the metal to rust. This is why tin is a good choice for covering other metals. Tin coatings last longer than zinc, which needs to be replaced after some years. Copper and aluminum are also strong, but tin is special because it does not react much and protects for a long time.
You can trust these metals to last and protect in many jobs.
Metal Tin Materials
Properties
Metal tin materials have special physical and chemical features. Tin melts at about 231.9°C. This means you can use it when you need low heat. Tin changes how it stretches or grows depending on its crystal direction. The way tin expands can be twice as much in one direction. Its elastic modulus can change up to five times. These things help explain why tin is good for some jobs.
Tin has two allotropic forms. When it is warmer than 13.2°C, tin is in the metallic β-tin form. This form is shiny and stable. When it gets colder, tin can turn into gray α-tin. This form is less stable. This change can make tin get bigger or smaller. Scientists use electron microscopy to study this process. This helps them see why tin changes shape or texture in the cold.
Tin has lower electrical resistivity than lead. It also has higher thermal conductivity. This makes tin good for solder joints in electronics. In real life, tin-plated copper connectors can change if kept cold. Gray powdery bumps can show up on these connectors. This shows how tin’s structure can shift in some conditions.
Tip: Think about temperature and where you use tin to get the best results.
Uses
You can use metal tin materials in many ways. Tin is great for coating other metals. It keeps steel from rusting and keeps food safe in cans. Tin is used in solder to join electronic parts. Its low melting point helps make strong connections without hurting small parts.
People use tin to make alloys like bronze and pewter. These alloys have different strengths and uses. In electronics, tin helps make strong solder joints. In packaging, tin keeps food fresh and safe. Tin is also found in bearings, pipes, and some musical instruments.
Here are some common ways to use metal tin materials:
- Coating for steel cans and food containers
- Solder for electronics
- Alloys such as bronze and pewter
- Bearings and bushings
- Pipes and plumbing parts
- Musical instruments
| Application | Benefit of Tin Use |
|---|---|
| Food cans | Stops rust, keeps food safe |
| Electronics solder | Strong, melts at low heat |
| Alloys | Makes metals stronger |
| Bearings | Less friction |
Note: Metal tin materials give you many safe and useful choices for everyday things.
Zinc
Properties
Zinc is known for being strong and fighting rust. Pure zinc is pretty dense, about 7.13 Mg/m³. Its tensile strength can be from 150 to 320 MPa. This depends on the alloy and how it is made. Some zinc alloys, like Zamak 3 and Zamak 5, are even stronger and harder. If you cool zinc alloys quickly, they get tougher. Zinc melts at a low temperature. This makes it easy to shape and cast.
| Property | Pure Zinc Value | Zinc Alloy Range |
|---|---|---|
| Density (Mg/m³) | 7.13 – 7.15 | 6.6 – 7.2 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 150 – 320 | 230 – 365 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 75 – 160 | 150 – 260 |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 80 – 160 | 80 – 160 |
| Elongation (%) | 2 – 5 | 2 – 5 |
Zinc makes a thin oxide layer on its surface. This layer keeps rust away and helps zinc last longer. Zinc alloys do not rust easily, even in wet air. Mixing zinc with aluminum or copper makes it stronger. But pure zinc cannot bend much and gets tired faster.
Zinc’s oxide layer helps protect it outside and in factories.
Uses
Zinc is used in many jobs and products. Builders use zinc-coated steel for roofs and bridges. This keeps buildings safe from rust and helps them last longer. Car makers use zinc for galvanized steel and car parts. Zinc alloys make car parts that are strong but not heavy.
| Zinc Usage Metric / Application | Percentage Share | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Galvanized Zinc Consumption | ~60% | Used for steel galvanization in construction and automotive sectors. |
| Alloyed Zinc | ~25% | Used in die casting for automotive, electronics, and medical devices. |
| Zinc Oxide | ~15% | Used in rubber, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. |
Zinc is also important in electronics. You can find zinc in batteries, circuit boards, and semiconductors. Asia-Pacific uses the most zinc because cities are growing fast. North America and Europe recycle zinc to help the planet.
Zinc is very useful and helps make things last longer.
Copper
Properties
Copper is a metal that people use for many things. You can find copper in nature. After refining, copper is over 99% pure. This high purity helps copper carry electricity and heat very well. Copper is easy to bend and stretch. You can make copper into wires or sheets without breaking it.
Copper can mix with other metals to make alloys like bronze and brass. These alloys change how hard or strong copper is.
The EBSCO Research Starters article “Copper (Cu)” (2025) says copper’s ductility and conductivity are great for electrical work. You can use copper as wires, pipes, or sheets. Copper does not rust easily, so it lasts a long time.
| Property | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Purity (refined) | Over 99% |
| Electrical Conductivity | Very high |
| Thermal Conductivity | Very high |
| Ductility | Easy to bend and stretch |
| Common Alloys | Bronze, brass, Monel metal |
Uses
You see copper in many places every day. Most copper is used in building things. People use copper for wires, pipes, and roofs. A house can have about 440 pounds of copper, mostly in wires and pipes.
- Building and construction use the most copper, with 26.4% in 2024.
- Big projects use copper for power lines, trains, and smart grids.
- Wind turbines and solar panels need copper to move power well.
- Car makers use copper in electric cars and charging stations.
- Electronics and phones need copper for circuit boards and cables.
Asia Pacific uses more copper than any other place because of big building and energy projects.
A new study says people will need more copper soon. This is because more people use electric cars and green energy. Recycling copper helps meet this need and keeps the planet cleaner.
| Application Area | Main Use of Copper |
|---|---|
| Construction | Wiring, plumbing, roofing |
| Energy | Wind, solar, storage |
| Automotive | Electric vehicles, wiring |
| Electronics | Circuit boards, connectors |
| Infrastructure | Power lines, telecom |
Copper is safe, reliable, and lasts a long time in many jobs.
Aluminum
Properties
Aluminum is a very light metal. You can pick it up without much effort. It does not rust easily and does not react fast with air or water. You can bend or shape aluminum into many things. Builders and engineers like this because it makes their jobs easier.
You can look at the table to see how aluminum alloys are different in strength and other features:
| Aluminum Alloy | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5052 | ~220 | Lowest | High toughness, easy to form, welds well |
| 6061 | ~310 | Moderate | Balanced strength, welds well, versatile |
| 7075 | ~572 | Highest | Very strong, used in planes, less formable |
| Alloy | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (HBW) | Key Property Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6061-T651 | 276 | 17 | 95 | Good corrosion resistance, welds easily |
| 7075-T651 | 572 | 11 | 85 | High strength, used in aerospace |
| 5052-H32 | 228 | 12 | 60 | Easy to shape, resists rust |
Aluminum stays strong even though it is light. This makes it good for places where weight is important.
Uses
You can find aluminum in many places. Builders use it for windows, doors, and roofs. You also see it in cans, foil, and packaging. Aluminum helps keep food safe and fresh. The metal is used in cars, planes, and trains because it is both light and strong.
Almost 75% of all aluminum ever made is still being used. You can recycle aluminum over and over without losing quality. This saves energy and helps the earth. Aluminum helps builders meet green building rules. In the U.S., people use more aluminum every year. In 2022, the country brought in about 66 million metric tons to meet what people need.
The packaging business uses more aluminum each year. In 2024, the world aluminum foil packaging market was worth $38.2 billion. Experts think it will grow to $53.3 billion by 2033. Food, drink, and medicine companies trust aluminum to keep their products safe.
- Construction: windows, doors, siding, roofing
- Packaging: cans, foil, trays
- Transportation: car parts, airplane frames, train bodies
- Electronics: phone cases, computer parts
- Household: cookware, ladders, furniture
Aluminum gives you a choice that is strong, light, and lasts a long time.
Tin vs. Zinc

Physical
Tin and zinc are not the same when you look at how they act. Tin melts at a lower temperature than zinc. This means tin is easier to melt and shape. Tin is also much softer than zinc. You can bend and stretch tin without it breaking. Zinc is harder and stronger, but it does not bend well. Tin’s softness makes it good for coatings and mixing with other metals.
Corrosion
Both tin and zinc help stop rust, but they do it in different ways. Tests show that galvanized zinc keeps metal safe from rust the best. This is true even in tough places. Tin coatings also protect steel, but not as much as zinc. You can see how they compare in the table below:
| Coating Type | Corrosion Resistance (Trend) | Test Methods Used |
|---|---|---|
| Galvanized Zinc (CRS) | Highest corrosion resistance | Accelerated Corrosion Test (ASTM G109), Half Cell Potential (ASTM C876), Linear and Tafel Polarization |
| Tin Coated CRS | Better than untreated CRS but less than zinc | Same as above |
| Untreated CRS | Lower than galvanized zinc | Same as above |
Tip: Pick zinc if you want the best rust protection outside. Choose tin if you need a safe coating for food.
Cost
Tin costs a lot more than zinc. The price of tin is much higher than zinc’s price. This is because tin is needed for electronics and green energy. The table below shows what they cost now:
| Metal | Current Price (USD/MT) | Recent Price Change | 12-Month Forecast (USD/MT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tin | ~33,749 (June 26, 2025) | +3.56% (1 month), +4.78% (1 year) | ~36,860 |
| Zinc | ~2,772.60 (June 30, 2025) | -0.36% (1 month), -5.32% (1 year) | N/A |
Tin’s high price is because there is not much of it and many people want it for new technology.

Recyclability
You can recycle both tin and zinc from things like electronics and building parts. Studies show both metals can be taken from waste, like old circuit boards. Tin has a bigger effect on the environment for each kilogram recycled, but both metals help save resources. Recycling helps use less new metal and cuts down on trash.
Note: Recycling tin and zinc saves energy and helps the planet.
Uses
Tin and zinc are used in many jobs. Tin is found in food cans, solder for electronics, and as a coating for other metals. Zinc is used to cover steel, make batteries, and in car parts. In electronics, tin and zinc sometimes work together. For example, zinc–tin oxide films help solar cells and sensors work better. Tin also works better than zinc in cold spray coatings because it sticks at lower speeds.
- Tin: food cans, solder, coatings, alloys
- Zinc: galvanized steel, batteries, die-casting, alloys
Pick tin for safe coatings and electronics. Use zinc for strong, rust-proof building.
Tin vs. Copper
Physical
Tin and copper are very different metals. Tin is much softer than copper. Tin melts at a lower temperature. Copper is stronger than tin. Copper also carries electricity better. Tin oxide and copper oxide are not the same. They have different bandgap energies and conductance. This changes how they work in electronics and coatings.
| Property | Tin Oxide (SnO) | Copper Oxide (CuO, Cu₂O) |
|---|---|---|
| Indirect Bandgap (eV) | ~0.68–0.75 | ~1.4 |
| Direct Bandgap (eV) | ~2.8–3.0 | ~2.4 |
| Photoconductance (eV) | 3.5 | 2.4 |
Tin is easy to shape because it is soft. Copper is strong and good for heavy jobs.
Corrosion
Tin does a great job stopping rust, especially as a coating. In electrical work, tin-silver alloys on copper slow down rust. This helps parts last longer. Copper makes a patina that protects it in air. But in salty or rough places, copper can rust faster. Adding tin to copper alloys helps them fight rust, even in the ocean.
Tinned copper wires work well in soil with unknown or harsh pH. They keep connections working for a long time.
Cost
Copper usually costs less than tin. Copper’s price goes up and down with building and electronics needs. Tin costs more because people use it in electronics and coatings. Think about your budget and what your project needs before you pick one.

Recyclability
You can recycle both tin and copper very well. Recycling copper is easy and works fast. About one-third of copper comes from recycling. Tin recycling also works, but it can be harder. Getting tin out of electronics is more complex. Both metals help save resources and cut down on waste.
| Metal | Recovery Rate (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Tin | Up to 100 | More complex recovery from electronics |
| Copper | Up to 100 | Simple process, widely recycled |
Uses
Copper is used in wires, pipes, and roofs. This is because it is strong and carries electricity well. Tin is often put on copper to stop rust, especially in wires and grounding. Tinned copper does not rust in tough soils or outside. Tin is also used in bronze, which mixes both metals’ strengths.
- Copper: wiring, plumbing, roofing, electronics
- Tin: coatings for copper, solder, bronze, food-safe containers
Pick tinned copper if you want it to last in tough places.
Tin vs. Aluminum
Physical
Tin and aluminum are different in how they feel and act. Tin is soft and bends with little force. Aluminum is much harder and stronger than tin. If you add aluminum to tin alloys, the material gets tougher. The table shows that more aluminum means higher hardness and shear stress. This makes tin-aluminum alloys stronger than plain tin.
| Alloy Composition | Hardness (HV, Kg/mm²) | Minimum Shear Stress (Kg/µµ²) |
|---|---|---|
| Sn87Sb13 (base alloy) | ~23 | 7.6 |
| Sn82Sb13Al5 | ~33 | 11.01 |
| Sn77Sb13Al10 | ~34.5 | 11.38 |
| Sn72Sb13Al15 | ~39 | 12.66 |
| Sn67Sb13Al20 | 43 | 14.32 |
Aluminum has a Mohs hardness of 2 to 2.9. Tin’s Mohs hardness is only 1.5 to 1.8. Tin melts at a lower temperature than aluminum. This makes tin easier to use when you need less heat.
Corrosion
Both metals can fight rust, but they do it differently. Aluminum makes a thin oxide layer that keeps it safe from rust. Tin also stops rust and does not react with food or drinks. This is why tin is good for food packaging. Both metals last a long time, but tin is extra safe for food.
Cost
Aluminum usually costs less than tin. In late 2023, aluminum was about $3,657 per metric ton. Making tin cans costs more because of materials, machines, and work. Tin packaging is more expensive, but it protects products well.
Aluminum is cheaper and light, so many companies use it.

Recyclability
Aluminum is great for recycling. You can recycle aluminum cans many times without losing quality. About half of all aluminum cans get recycled. Tinplate, which is steel with tin on it, is recycled about 60% in the EU. Tin cans break down faster after burning, but aluminum keeps its value after many recycling cycles.
Aluminum’s recycling helps keep the earth clean.
Uses
You see tin and aluminum in lots of things, but they are used for different reasons. Tin is best for food and drink packaging. It keeps food safe from air, water, and light. Tin containers are also used in medicine and makeup because they are airtight and clean. Aluminum is light and strong, so it is used for cans, foil, car parts, and buildings.
- Tin containers keep food, drinks, and medicine safe.
- Aluminum is used in packaging, cars, and buildings.
- Tin is better for food safety and protection.
- Aluminum is strong and easy to recycle.
Pick tin if you want safe packaging. Choose aluminum if you need something light and strong.
Applications

Tin Advantages
Tin is used in many industries because it has special features. In electronics, tin-rich solders help lower lead pollution. This makes devices safer and work better. Tin coatings keep steel cans and food containers safe. They help food stay fresh for a long time. Tin-based white metals in bearings are soft and fight rust. Heavy machines, like ships and turbines, use these alloys to run smoothly.
Tin bronzes have 5–12% tin and are good for the sea and chemicals. These alloys do not wear out fast and do not rust easily. That is why they are picked for valves and fittings. Tin coatings, like tin-nickel and tin-zinc, are easy to solder and last a long time. Pure tin is also used to make flat glass for windows and mirrors.
| Application Area | Tin’s Role and Advantages | Performance Metrics / Industry Data Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics (Soldering) | Tin-rich solders reduce lead contamination and improve strength | Growing use in automotive and plumbing electronics |
| Bearings | Tin-based white metals provide softness and corrosion resistance | Preferred in heavy machinery for conformability and repairability |
| Tin Bronzes | 5–12% tin in bronze castings for corrosion and wear resistance | Used in marine and chemical processing valves |
| Tin Coatings | Tin and tin alloys offer solderability, wear resistance, and corrosion protection | Widely used in electronics and automotive industries |
| Float Glass Process | Pure tin creates optical flatness in glass casting | Adopted for windows, mirrors, and windshields |
Tip: Pick metal tin materials if you want safe coatings, strong solder, or tough bearings.
Zinc Advantages
Zinc is great at stopping rust. Builders use zinc to cover steel for roofs, bridges, and fences. This is called galvanizing and helps things last longer in bad weather. Zinc alloys are used in die casting to make car parts and electronics strong but light. Zinc is also found in batteries to help store energy safely.
Zinc works well in brass and bronze alloys too. These alloys are used in coins, musical instruments, and plumbing. Zinc makes a shield on its surface, so it is trusted outside and in factories.
- Galvanized steel for building and car parts
- Die-cast zinc alloys for electronics and machines
- Zinc batteries for storing energy
- Brass and bronze for coins, valves, and musical instruments
Zinc is a good choice for stopping rust and making strong, light parts.
Copper Advantages
Copper is very good at carrying electricity and heat. You can find copper wires in homes, cars, and power lines. Copper pipes move water in plumbing. Copper bends and stretches, so you can shape it for many jobs.
Copper alloys, like bronze and brass, are stronger and do not rust fast. Bronze, made from copper and tin, is used in bearings, bushings, and boat parts. Brass, made from copper and zinc, is used for coins and decorations. If you need safe wiring, plumbing, or strong parts, copper is a smart pick.
- Electrical wires and power lines
- Plumbing pipes and fittings
- Bronze for bearings, boat parts, and statues
- Brass for coins, valves, and musical instruments
Copper is a top pick for safe wiring, plumbing, and strong alloys.
Aluminum Advantages
Aluminum is special because it is light and strong. You see aluminum in cars, planes, and trains. Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it great for moving things and building. Aluminum makes a shield that stops rust in many places.
You can recycle aluminum many times and it stays good. This saves energy and helps the earth. Aluminum cans and foil keep food and drinks fresh. Builders use aluminum for windows, doors, and siding because it is easy to shape and put in place.
| Aspect | Aluminum Advantages |
|---|---|
| Recyclability | Can be recycled indefinitely, saving up to 95% energy |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High strength and hardness, good for aerospace and automotive |
| Corrosion Resistance | Forms a self-healing oxide layer, effective in many environments |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Abundant, lightweight, and stable market prices |
| Application Suitability | Used in packaging, construction, aerospace, automotive, and electronics |
Aluminum is a smart pick for things that need to be light, strong, and good for the planet.
There are lots of metals you can pick from. Tin is a good choice if you want to stop rust, shape things easily, or keep food safe. Zinc works well for things outside or for making strong parts. Copper is best for wires or pipes. Aluminum is great if you need something light for building or packing. Always think about what your project needs before you choose. Tin is known for being safe and dependable in many jobs.
FAQ
Tin keeps food safe by stopping rust and blocking air. You can trust tin cans to protect food from spoilage. Tin does not react with most foods.
You can recycle tin from cans and electronics. Recycling tin saves resources and energy. Many recycling centers accept tin products.
Tin works well for food and medicine containers. Tin does not react with food or drinks. Aluminum is safe for many uses, but tin offers extra protection for sensitive products.
You find tin in solder for joining wires and parts. Tin coatings protect connectors from rust. Tin helps electronics last longer.
Builders use tin coatings to stop rust on steel and copper. Tin coatings help pipes, wires, and roofs last longer in tough conditions.




