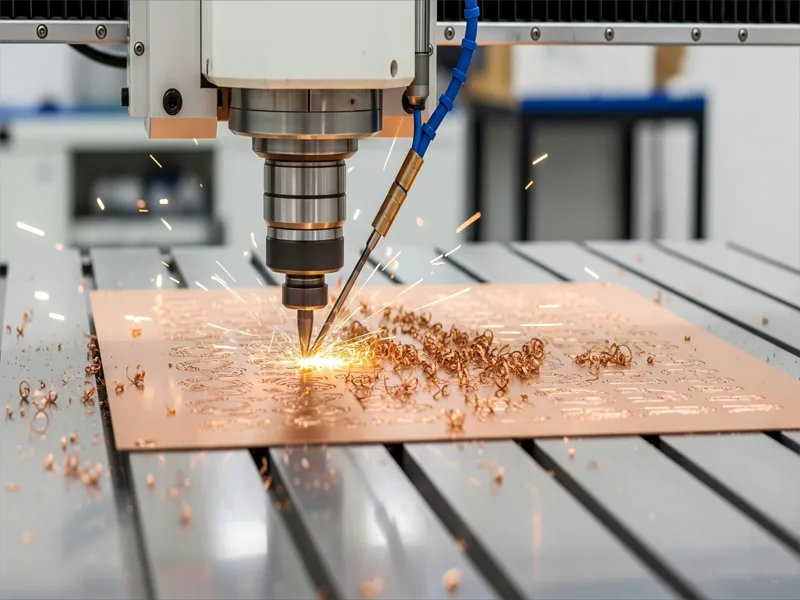
You can get very accurate results with copper CNC machining. Copper is special because it carries electricity and heat very well. This makes it important for electronics, heat exchangers, and connectors. CNC machining copper helps you make complex shapes for springs, non-sparking tools, and aerospace bushings. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. makes custom copper parts using strict quality checks and new technology. Many industries use copper for gears, decorative fittings, and energy storage systems because it is strong and does not rust easily.
Key Takeaways
- Copper CNC machining uses computers to control machines. These machines shape copper parts with great accuracy. The parts also have smooth surfaces.
- Copper is special because it conducts electricity and heat very well. It does not rust easily. Copper is soft. This makes it good for electronics, plumbing, and decorations.
- Picking the right tools and settings is very important. Sharp carbide or high-speed steel tools work best. The right angles and coolant help stop tools from wearing out. They also help make smoother parts.
- There are different copper alloys like pure copper, brass, bronze, and tellurium copper. Each alloy has its benefits. Some are easy to machine. Others are strong or very precise.
- Common CNC processes for copper are turning, milling, sheet metal work, and casting. Each process works best for certain shapes and amounts of parts.
- Using the right lubricant and coolant lowers heat and friction. This helps tools last longer. It also makes the surface of the part better.
- Quality control uses careful measurements and certifications. This makes sure copper parts meet strict rules. These rules are important for the aerospace, medical, and car industries.
- Beginners should watch for tool wear. They need to change feeds and speeds carefully. They should fix problems like built-up edges and overheating. This helps make better parts.
Table of Contents
Copper CNC Machining Basics
What Is Copper CNC Machining?
Copper CNC machining uses computer-controlled (CNC) machine tools to cut and shape copper and copper alloys into various shapes and applications. Because the cutting tool’s trajectory is precisely controlled by computer programming, high-precision copper products are produced.
The usual steps for copper CNC machining are:
- Use CAM software to make CNC code from your design.
- Set up the machine and hold the copper piece in place.
- Run the CNC machine to shape the copper with sharp tools.
- Use coolant and manage chips to stop overheating.
- Check the finished part to make sure it is right.
Why Use Copper
Copper is special because it has unique properties. It carries electricity better than any other metal. This makes it great for electrical parts like connectors and wires. Copper also moves heat very well, so it is used in heatsinks and radiators. It does not rust easily, so it lasts a long time in tough places. Copper is soft and easy to shape into complex forms.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Moves heat fast, good for heatsinks and radiators. |
| Electrical Conductivity | Carries electricity better than other metals, used in electrical parts. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Does not rust easily, lasts longer in harsh places. |
| Machinability | Makes smooth finishes and exact shapes. |
| Dimensional Stability | Keeps its shape when under stress or heat. |
| Density | Heavy and stable, helps reduce vibration during machining. |
Key Benefits
Copper cnc machining gives you many good things:
- Great electrical and thermal performance. Copper C101 is known for its high conductivity, so it is important for electrical parts.
- Kills germs naturally. Copper kills over 99.9% of bacteria in two hours, which is good for medical products.
- Very good at resisting corrosion. Copper parts last longer in most factories, so you do not need to fix them often.
Here is how copper compares to other metals in CNC machining:
| Metal | Tool Wear | Machining Speed | Surface Finish | Machinability Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Medium | Low | Fair | 4/10 |
| Aluminum | Low | High | Excellent | 9/10 |
| Steel | High | Moderate | Good | 5/10 |
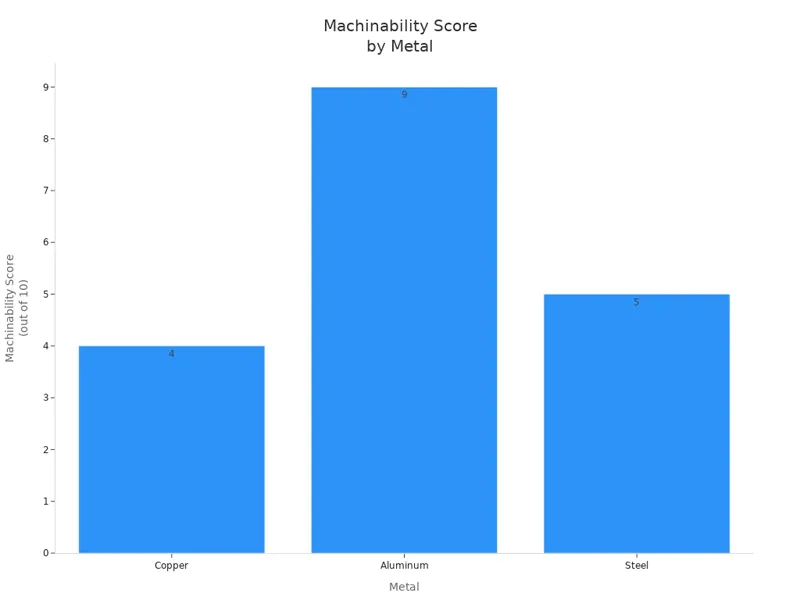
Copper CNC machining needs careful tool choices and slower speeds than aluminum. But you get the best electrical and thermal properties.
Copper Properties

Softness and Ductility
Copper feels soft and bends without much force. This makes it easy to shape during copper CNC machining. You can stretch or bend copper, and it will not break. This is called ductility. Because of this, you can make custom copper parts with tricky shapes. Copper’s softness means you must pick the right tools. High-speed steel (HSS) tools work well because they do not stick as much. Cemented carbide tools are also good, but they must stay sharp. If your tool is dull, copper can stick and cause trouble. Use a cutting-edge angle close to 90° for soft copper. This gives a smooth finish and keeps your tools working well.
- Copper is easy to machine because it is soft and ductile, but you must control how fast you cut. If you go too fast, copper gets hot and wears out your tools.
- Red copper CNC machining uses these properties to make many parts, like copper heatsinks and quick prototypes.
Work Hardening
When you machine copper, it can get harder as you work. This is called work hardening. Cutting or bending copper makes its surface stronger but less bendy. Work hardening can make CNC copper parts machining harder. You might see a shiny, slippery spot on the copper. This means the copper is harder and can wear out your tools faster.
To stop work hardening, use sharp tools and the right settings. Keep your depth of cut above 0.05 mm. Do not stop or pause the tool in one place. If you see rough spots or your tools wear out fast, work hardening may be the reason. Annealing, which means heating copper before machining, can make it softer. This helps you get a better finish and makes your tools last longer.
Tip: Always check your tool’s position and use enough coolant. This helps stop work hardening and keeps your cnc machining for copper smooth.
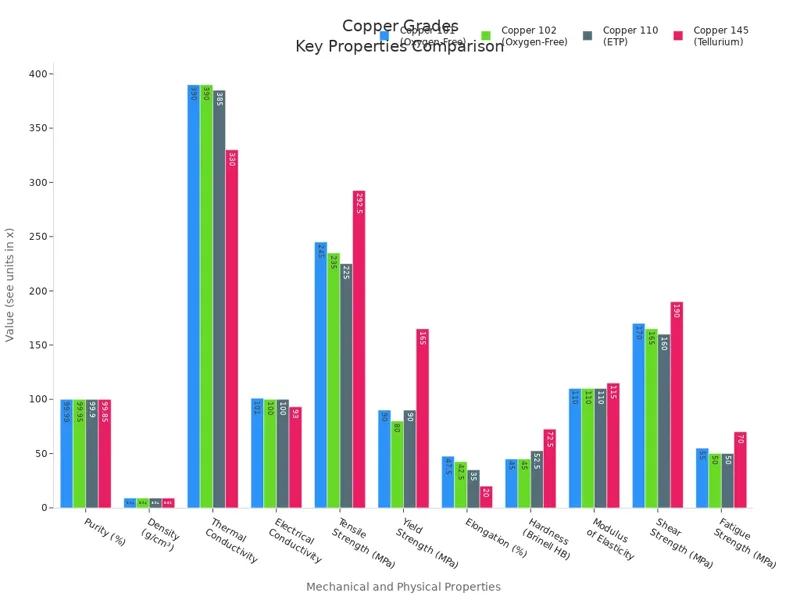
Conductivity
Copper is special because it carries electricity and heat very well. This makes copper the best choice for electrical connectors, wires, and copper heatsinks. When you use copper in brass CNC machining or custom copper parts, you get great results for both electricity and heat.
Here is a table that shows how copper’s conductivity compares to aluminum:
| Property | Aluminum | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | About 61% of copper | 100% (reference) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 210 W/mK | 401 W/mK |
| Density | 2.70 g/cm³ | 8.96 g/cm³ |
You can see copper’s electrical conductivity is much higher than aluminum’s. This is why copper is used in electrical parts and precision copper parts machining. Copper’s high thermal conductivity helps make parts that move heat away fast, like copper heatsinks.
Copper alloys, like Tellurium Copper and Beryllium Copper, keep good conductivity but have different strengths. This lets you pick the best material for your CNC machining for copper project. If you need a copper machining supplier or copper machining manufacturer, find one who knows these properties. They can help you choose the right copper alloy for your job.
Copper Alloys
Pure Copper
Pure copper is used a lot in CNC machining for copper projects. Grades like C101 and C110 are known for carrying electricity and heat very well. You pick pure copper when you need parts that move electricity or heat fast, like custom copper parts for electronics or copper heatsink machining. C101 can look shiny like a mirror, but sometimes you see small smears or marks from shaking. C110 cuts easily and works for most copper mechanical machining jobs.
Pure copper bends and shapes without breaking. This is called ductility. You need sharp tools and careful settings for precision copper parts machining. Sometimes pure copper sticks to your tools, so you should use lots of coolant and keep your tools sharp. If you want rapid prototyping of copper parts or need a copper machining supplier for high-purity work, pure copper is a good choice.
Tip: Oxygen-free copper, like CW024A, is even better at carrying electricity and bending. You can use it for top-quality electrical parts and vacuum electronics.
Brass

Brass is made by mixing copper with zinc. Brass CNC machining is popular because brass is easy and quick to machine. Grades like C360, called free machining brass, let you cut fast and remove material quickly. Brass rods do not hurt your CNC tools, so you can make many CNC copper parts machining projects without changing tools often.
Here are some reasons to pick brass for your project:
- Brass is easy to machine, especially with leaded grades like C360.
- Brass does not rust easily, so your parts last longer in wet places.
- Brass is easy to shape into tricky forms.
- Brass has a gold color, which looks nice for fancy products.
- Brass costs less and lets you make parts quickly.
You can use brass for gears, musical instruments, and decorations. Brass also works for plumbing parts and some electrical connectors. Some brass grades have lead, which can cause cracks or health problems in medical uses. Brass can react with acids and may need extra care in tough places.
Bronze
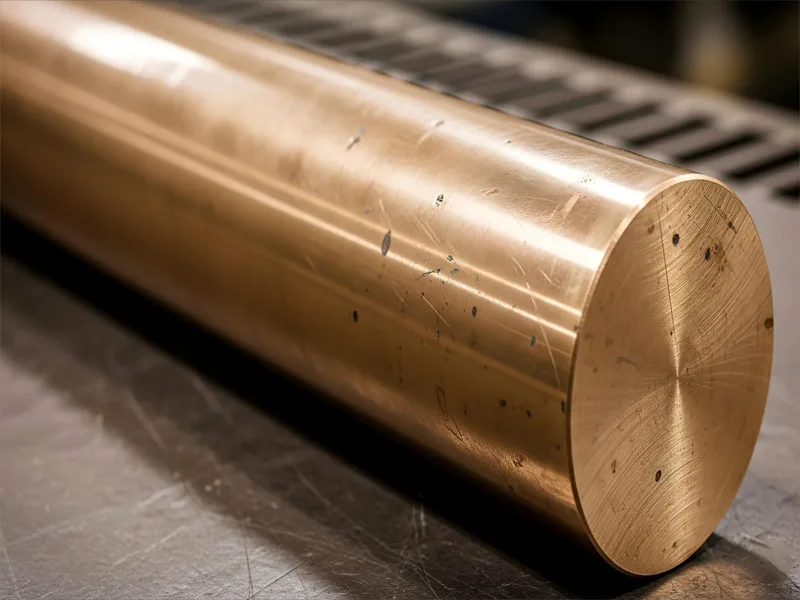

Bronze is another copper alloy. You make bronze by mixing copper with tin. Bronze is strong and lasts a long time, so it is good for heavy-duty jobs. You see bronze used for statues, gears, and bearings. Bronze is stronger and harder than pure copper.
Here is a table comparing bronze and copper:
| Property | Bronze | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength | 125 – 800 MPa | 33.3 MPa |
| Tensile Strength | 350 – 635 MPa | 210 MPa |
| Brinell Hardness | 40 – 420 | 35 |
| Machinability | Moderate to Low | High |
| Formability | Moderate | High |
Bronze can handle more stress and wear than copper, so you use it for parts that need to last. Bronze is harder to machine than copper. You need slower speeds and sharp tools to stop tool wear. Bronze can smear when you cut it, so you should use the right cutting fluids and control your feed rates. If you want strong CNC copper parts machining or need a copper machining manufacturer for gears and bushings, bronze is a good pick.
Note: Bronze moves heat away well during machining, but you should watch for thermal expansion, which can change part size.
Each copper alloy has its own good points. Pure copper is best for carrying electricity, brass is easy to machine and looks nice, and bronze is strong for tough jobs. When you work with a copper machining supplier like AFI Industrial Co., Ltd., you can pick the right alloy for your custom copper parts, whether you need red copper CNC machining, brass CNC machining, or bronze for strong components.
Tellurium Copper

Tellurium copper is a great choice for fast and accurate machining. People also call it C145. This alloy has a little tellurium, about 0.3% to 0.6%. Adding tellurium changes how copper acts. Tellurium copper still carries electricity and heat well. It is much easier to machine than regular copper.
Here is a table that shows why tellurium copper is good for CNC machining:
| Property | Description / Value |
|---|---|
| Tellurium Content | Approximately 0.3-0.6% |
| Machinability | Significantly improved, enabling faster speeds and reduced tool wear |
| Strength and Hardness | Increased compared to pure copper, providing durability |
| Electrical Conductivity | Maintains good conductivity (45-60% IACS) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity (201-234 W/(m·K)) |
| Surface Finish | Improved surface finish achievable via CNC machining |
| Tolerances | Tighter tolerances possible compared to traditional copper machining |
| Tool Life | Longer tool life due to reduced wear |
| Application Examples | Electrical connectors, terminals, switch parts requiring precision and conductivity |
You can use tellurium copper for many CNC machining jobs. It works well for electrical connectors, terminals, and switch parts. These parts need to be very exact and carry electricity well. Tellurium copper lets you machine faster than pure copper. You can get very close tolerances, like ±0.005 mm. This helps you make detailed and tricky shapes with CNC copper parts machining.
Choosing tellurium copper helps your tools last longer. The alloy makes tools wear out more slowly. You do not need to change tools as often. You get smoother surfaces, which is good for custom copper parts and copper heatsink machining. If you need rapid prototyping copper parts, tellurium copper gives you repeatable and steady results. It is smart for both small and large production runs.
Here are some reasons to pick tellurium copper for your project:
- You want faster copper CNC machining and less tool wear.
- You need tight tolerances and smooth surfaces for precision copper parts machining.
- You work with electrical parts that must maintain good conductivity.
- You want to make more parts without losing quality.
Tip: If you need a copper machining supplier or copper machining manufacturer, ask if they use tellurium copper. This alloy can help you save time and money on CNC machining for copper, especially for hard or big jobs.
Tellurium copper also works for brass CNC machining and red copper CNC machining when you need easier machining. You can trust this alloy for copper mechanical machining, especially for detailed features or rapid prototyping of copper parts.
CNC Machining Copper Components
CNC Turning
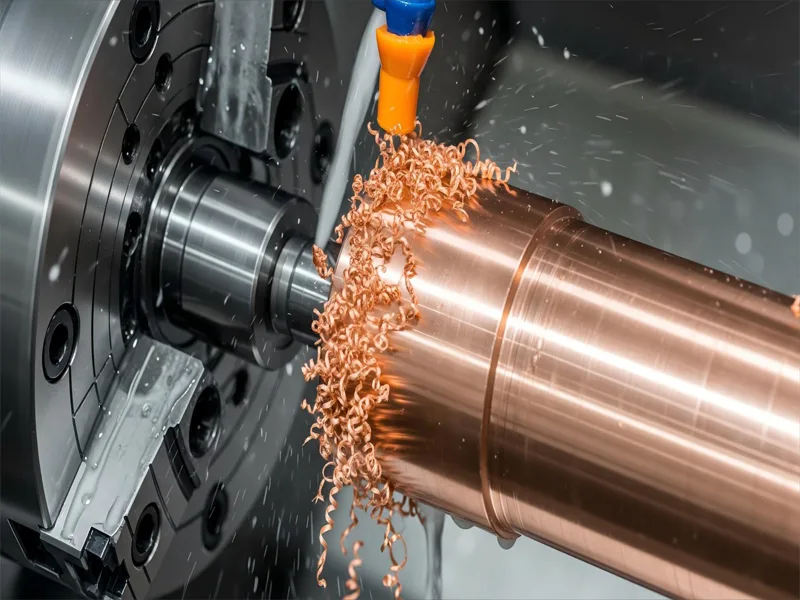

CNC turning changes copper bars or rods into round parts. You put the copper in a CNC lathe. The machine spins the copper fast. A sharp tool cuts away the extra copper. This makes smooth, round shapes that are very exact. You can make many kinds of copper parts with CNC turning. Some examples are gaskets, clamps, ball floats, bearings, and gas welding nozzles. Copper radiators and sprinkler heads are also made this way.
CNC turning can make parts with tight tolerances. The table below shows the usual tolerances and surface finishes for copper parts:
| CNC Turning Tolerance Category | Typical Tolerance Range (inches) | Typical Tolerance Range (mm) | Surface Finish (RA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Precision | ±0.005″ | ±0.13 mm | ~125 RA |
| Premium Precision | Between ±0.005″ and ±0.001″ | Between ±0.13 mm and ±0.025 mm | N/A |
| Ultra Precision | ±0.001″ to ±0.0001″ | ±0.025 mm to ±0.0025 mm | N/A |
After turning, you may see small tool marks on the copper. You can make the surface better by bead blasting or powder coating. These steps help the parts look nice and last longer.
CNC Milling
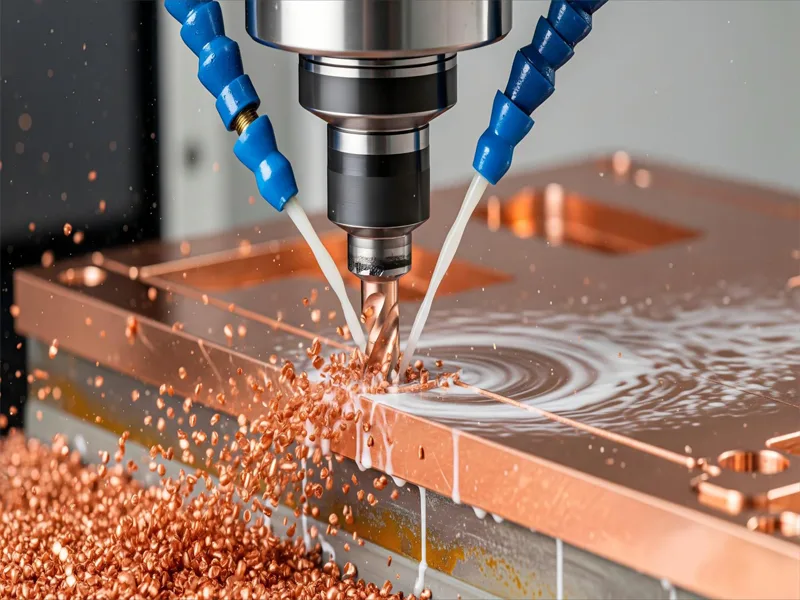

CNC milling uses spinning tools to cut copper into shapes. You start with a solid block or plate of copper. The CNC milling machine moves the tool in different ways to remove copper. This works well for making copper parts with holes, slots, or pockets.
You can make many things with CNC milling, like electrical switches, connectors, vacuum devices, and heat exchangers. Milling also helps make custom copper parts for electronics and energy systems. The process works for both simple and tricky designs.
CNC milling gives you high accuracy and the same results every time. You can get tight tolerances and smooth surfaces.
Tip: Always use sharp tools and enough cooling when milling copper. This keeps your tools from wearing out and makes the surface smooth.
Sheet Metal
Sheet metal fabrication shapes thin copper sheets into useful parts. You can cut, bend, stamp, or punch copper sheets to make many shapes. This process works for both easy and hard designs.
You find sheet metal copper parts in circuit boards, heat sinks, pipes, roofing, and decorative panels. Copper moves electricity and heat well, so it is great for these uses. Its germ-killing property helps in medical equipment and kitchen surfaces. Copper is easy to shape without breaking, so you can make detailed parts.
Here are some main reasons to use sheet metal for copper parts:
- Copper bends and forms easily because it is malleable and ductile.
- It does not rust and lasts a long time, even with lots of use.
- Copper’s color and patina look nice in decorations and buildings.
- You can join copper parts with soldering or welding for strong connections.
- Sheet metal fabrication is fast and works for both samples and large orders.
- The process is good for the planet because copper can be recycled and retains its properties.
Note: Sheet metal copper parts need little care and meet many industry rules. This makes them a smart pick for many projects.
Casting

Casting lets you make copper parts with tricky shapes. First, you melt copper until it is liquid. Then, you pour the liquid copper into a mold. The mold has the shape you want for your part. When the copper cools, it gets hard and keeps the mold’s shape. This way, you can make strong parts that are hard to shape by cutting.
There are different ways to do casting for copper CNC machining. Here are some common types:
- Sand Casting: You press sand around a pattern to make a mold. This works well for big or simple parts. You can use it for custom copper parts like bushings or connectors.
- Die Casting: You use a metal mold and push melted copper in with pressure. This gives you smooth parts and tight fits. It is good for making many CNC copper parts machining projects fast.
- Lost Wax Casting: You make a wax copy of your part and cover it with ceramic. Then, you melt out the wax and pour in copper. This helps you make very detailed shapes.
Tip: Casting is good for parts that are hard or expensive to cut from solid copper. You can save time and copper by using this process.
Here is a table to help you see the differences between casting methods for CNC machining for copper:
| Casting Method | Best For | Surface Finish | Precision Level | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Large/simple parts | Fair | Moderate | Bushings, connectors, fittings |
| Die Casting | High-volume, small parts | Excellent | High | Switch parts, housings, terminals |
| Lost Wax Casting | Detailed, complex shapes | Very Good | Very High | Decorative items, precision gears |
You can also use casting for brass CNC machining and red copper CNC machining. This works for both quick samples and big orders. If you need a copper heatsink machining project or want special copper parts, casting gives you many choices.
When you pick a copper machining supplier or copper machining manufacturer, ask if they do casting.
Note: Casting is smart when you need lots of parts at once. You get strong, detailed copper parts that match your design.
Copper CNC Machining Techniques
Tool Selection
Choosing the right cutting tool for copper is the first step to getting a clean, accurate part. Copper is soft and ductile, so it can stick to tools and cause a built-up edge. You want a tool that stays sharp and resists wear. For most jobs, use uncoated carbide or high-speed steel tools. These tools cut copper smoothly and help you avoid rough finishes. Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tipped tools work best for long runs or when you need the sharpest edge. PCD tools last longer and keep their shape, which is important for precision copper parts machining.
You can also use special coatings to help your tools last longer. Some coatings, like TiB2 and ZrN, stop copper from sticking to the tool. Others, like CVD diamond and PCD diamond, give the tool a hard surface that resists wear. The table below shows some common coatings and their benefits:
| Coating | Description | Max Working Temperature | Key Benefits | Recommended Use for Copper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiB2 (Titanium Diboride) | Stops built-up edge, good for non-abrasive copper alloys | 900°F (482°C) | Longer tool life, cleaner cuts | Use with sharp tools |
| ZrN (Zirconium Nitride) | Abrasion resistant, lower cost | 1110°F (600°C) | Hard, smooth, resists wear | Good for brass cnc machining and bronze |
| CVD Diamond | Very hard, grown on carbide | 1100°F (593°C) | High wear resistance | Best for abrasive copper alloys |
| Amorphous Diamond | Good for brass CNC machining and bronze | 750°F (399°C) | Smooth finish, resists wear | Good for plastics and abrasive copper alloys |
| PCD Diamond | Brazed diamond layer, sharp | 1100°F (593°C) | Best wear resistance | Ideal for all copper alloys |
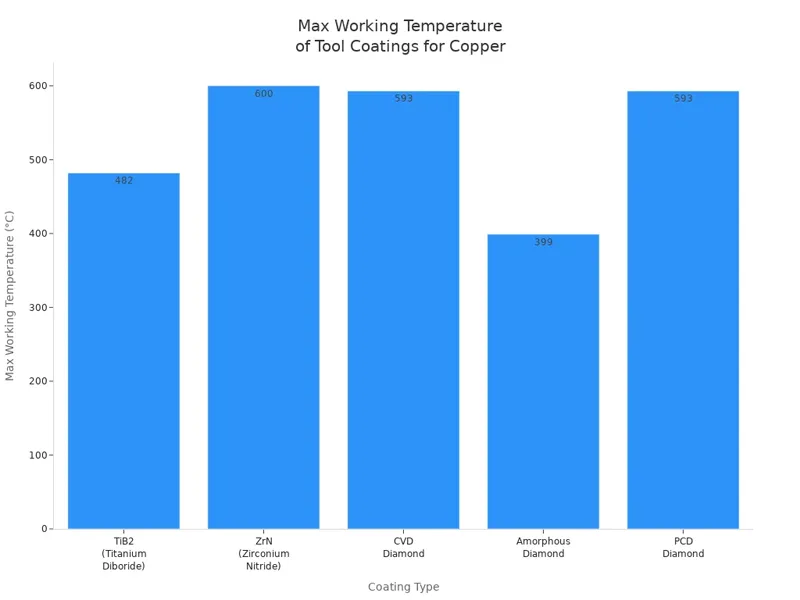
When you pick a cutting tool for copper, always check if it is sharp and clean. Dull tools cause smearing and poor finishes.
Tip: For rapid prototyping copper parts or high-speed machining on copper, use PCD or coated carbide tools to keep your tools sharp and your parts precise.
Feeds and Speeds
Setting the best feeds and speeds is key to good CNC machining for copper. If you go too fast, copper gets hot and tools wear out quickly. If you go too slow, you waste time and may get rough surfaces. The best feeds and speeds depend on your tool, the copper alloy, and the part shape.
For most copper jobs, use a cutting speed between 200 and 300 surface feet per minute (SFM). This range helps you balance heat and surface finish. Carbide tools let you use higher speeds, while high-speed steel tools work better at lower speeds. Always use coolant to keep the part and tool cool. Coolant also helps remove chips and stops copper from sticking to the tool.
Here is a table to help you set the right parameters:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Cutting Speed (SFM) | 200-300 for copper; helps balance heat and finish |
| Feed Rate Calculation | Feed Rate (IPM) = RPM × Number of Flutes × Chip Load per Tooth |
| Tool Material | HSS for slower speeds; Carbide for higher speeds; PCD for best wear resistance |
| Coolant Use | Always use coolant to control heat and improve finish |
| Tool Selection | Positive rake angles, sharp edges, and proper coatings for copper alloys |
To find the optimal feed rate, use the formula above. You need to know your tool’s RPM, the number of flutes, and the chip load per tooth. For example, if your tool spins at 2,000 RPM, has 2 flutes, and a chip load of 0.002 inches, your feed rate is 8 IPM (inches per minute).
Note: The best feeds and speeds change if you switch from red copper cnc machining to brass cnc machining or bronze. Always check your settings for each alloy.
Tool Angles
Tool angles play a big role in copper mechanical machining. The right angles help you get a smooth cut and avoid tool wear. For copper, use a high rake angle and a sharp edge. This helps the tool slice through copper cleanly and keeps the surface smooth. Carbide tools with sharp edges work well for CNC machining for copper because they reduce heat and tool wear.
A positive rake angle lowers cutting forces and helps you get a better finish. Too much rake can make the tool edge weak, so balance is important. Relief angles give the tool clearance and stop rubbing. If the relief angle is too big, the tool wears out faster. If it is too small, the tool rubs and heats up.
You want your cutting edge angle between 70° and 95°. This range works well for most copper alloys. Sharper edges give cleaner cuts but may wear out faster. For long runs, use a slightly honed edge to keep the tool strong.
Tip: Always check your tool angles before starting a job. Good angles help you avoid smearing and get the best results for custom copper parts and copper heatsink machining.
Tool angles, feeds, and speeds all work together. When you set them right, you get the best finish and longest tool life. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. uses these techniques for every copper machining project, from precision copper parts machining to large batch runs.
Coolant
When you cut copper, it gets hot fast. Too much heat can hurt your cutting tool for copper. It can also make the part’s surface rough. The right lubricant keeps tools sharp and parts smooth.
There are different cutting fluids you can use. Each one helps in its own way:
- Water-based coolants cool the tool and part quickly. They remove heat well, but do not always give the best lubrication.
- Oil-based coolants give strong lubrication. They lower the friction between the tool and copper, so tools last longer.
- Synthetic coolants cool and lubricate at the same time. These are good for precision copper parts machining.
- Semi-synthetic coolants mix water and oil features. They balance cooling and lubrication for CNC copper parts machining.
Using the right Coolant makes your tools last longer. Lubricants make a thin layer between the chip and the tool. This layer cuts down friction and heat. It also helps move chips away and stops rust. You get smoother parts and more exact custom copper parts.
Here is a table to help you compare cutting fluids:
| Type of Coolant | Cooling Power | Lubrication | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water-based | High | Moderate | General cooling, chip removal |
| Oil-based | Low | High | Red copper CNC machining, tool life |
| Synthetic | High | High | Precision copper parts machining |
| Semi-synthetic | Moderate | Moderate | Brass CNC machining, versatility |
If you want the best results for copper mechanical machining or copper heatsink machining, always use the right lubricant. This helps stop tool wear and keeps CNC copper parts machining working well. Coolant is very important, especially if you work with a copper machining supplier or copper machining manufacturer for big orders or rapid prototyping copper parts.
Note: Good lubrication is needed for custom copper parts. It gives you the best finish and helps your tools last longer.
Precision-Machined Copper Parts
Quality Control
You want every part to be just right. Quality control is very important for precision-machined copper parts. At AFI Industrial Co., Ltd., they use a strict process to check each step. Here is how you can make sure your parts are high quality:
- Check the first part in each batch. This helps you see if the CNC copper parts machining process is working well.
- Look at the parts while making them. You check for problems with size, shape, or the surface.
- Use samples to find problems early and fix them.
- Watch machines as they work. This lets you spot changes fast.
- Write down all the data for each part. You can find where the problem started.
- Teach your team often. Skilled workers find mistakes quickly.
- Work with other groups. Good teamwork helps fix problems fast.
- Look at your results. You praise good work and fix weak spots.
- Listen to customers. Their ideas help you get better.
- Always try to improve. Use data and new ideas to raise your standards.
You also check the surface by feeling and looking. You measure roughness to keep the finish the same. You test for cracks and check what the copper is made of. You do strength tests to make sure your high-precision copper parts last long.
Tip: Check your machines often. This helps you stop breakdowns and keeps your copper mechanical machining running well.
Dimensional Accuracy
You need precision-machined copper parts to fit just right. Dimensional accuracy means your parts match the design exactly. AFI Industrial uses Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) for this job. CMMs can measure with errors as small as 0.005 mm. This accuracy is needed for aerospace and medical jobs. You can trust your custom copper parts will fit and work as planned.
Industry rules say size should not change more than 0.5%. You can do this by checking every step of the CNC machining for the copper process. You also follow ISO rules for measuring and checking machines. This helps you keep the finish the same and hold tight sizes.
Certifications
You want proof that your copper machining supplier follows world rules. Certifications show a company uses strict rules for quality and safety. AFI Industrial has ISO 9001:2015 and SGS certifications. These show every step in their precision copper parts machining meets top rules.
Here are some certifications you might see:
- ISO 9001:2015 for quality management
- IATF 16949:2016 for car parts
- ISO 13485 for medical devices
- AS9100D for airplanes
- ISO 14001:2015 for caring for the environment
| Certification | What It Means |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001:2015 | Quality management for all industries |
| IATF 16949:2016 | Automotive quality management |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device quality management |
| AS9100D | Aerospace quality management |
| ISO 14001:2015 | Environmental management |
You can trust AFI Industrial for fast work and strong quality checks. Their certifications and full checks give you confidence in every order of precision-machined copper parts.
Applications
Electronics
Copper is used a lot in electronics. If you open a phone or computer, you will see copper inside. It is found in circuit boards, connectors, and heat sinks. CNC machining helps make these copper parts very exact. Copper is needed because it carries electricity better than other metals. This is why it is used for printed circuit boards. The copper makes thin lines that connect all the parts.
CNC copper parts machining makes small connectors and contacts. These must fit perfectly, so machines cut them to the right size. Copper is also used in antennas. Its conductivity and ability not to rust help antennas work well. When devices get hot, copper heatsink machining makes parts that move heat away fast. This keeps electronics cool and working.
Manufacturers use CNC machining for copper to add detailed marks on parts. These marks help with tracking and checking quality. Copper mechanical machining gives you strong and reliable electrical parts. If you need custom copper parts for a new device, rapid prototyping copper parts help you test ideas fast. Many companies pick a copper machining supplier like AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. for these jobs.
Tip: Copper is very important in electronics. It helps your devices work faster, stay cool, and last longer.
Plumbing
Copper is a great choice for plumbing. You see copper pipes, fittings, and valves in many buildings. Copper does not rust, so water stays clean and pipes last a long time. CNC machining for copper makes these parts with the right shapes and sizes. This makes sure every piece fits together and does not leak.
Copper can handle hot water without getting damaged. CNC copper parts machining makes many parts quickly. This saves time and money. The process also makes less waste than the old ways.
Copper mechanical machining gives you smooth and strong parts. You do not need extra coatings. Copper is soft, so you can bend pipes without breaking them. Its germ-killing property helps keep water safe. If you want special copper parts, a copper machining manufacturer can make them for you.
- Copper’s resistance to rust keeps plumbing working for many years.
- CNC machining makes it easy to make tricky shapes for valves and joints.
- Automation in CNC machining for copper lowers mistakes and makes parts faster.
Automotive
Copper is found in many car parts. Modern cars use copper for both electrical and mechanical jobs. Copper CNC machining makes connectors, terminals, and wiring parts that carry electricity in the car. These parts must be exact to keep the car safe.
CNC copper parts machining also makes heat exchangers and radiators. Copper moves heat away from engines and batteries, so cars stay cool. Brass CNC machining and red copper CNC machining are used for gears, bushings, and other moving parts. These parts last a long time and do not wear out fast.
Precision copper parts machining makes sure every part meets strict rules. If you need a new design, rapid prototyping copper parts help you test it before making many. A copper machining supplier can send big orders quickly. This helps car factories keep working.
Note: Copper is strong, carries electricity well, and does not rust. This makes it very important in cars.
Decorative
You can find copper in many things used for decoration. People like copper for art, jewelry, and home items because it is shiny and changes color as it gets older. Copper CNC machining helps you make custom parts for lamps, handles, and wall panels. This process lets you make cool shapes and patterns that look nice and last a long time.
Copper heatsink machining is not only for electronics. You can use these skills to make cooling fins for sculptures or lights. Brass CNC machining helps you make gold-colored parts for furniture and musical instruments. If you want a special look, red copper cnc machining gives a warm, reddish color that stands out in any room.
You can work with a copper machining supplier to make your designs. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. can make rapid prototyping of copper parts, so you can see your ideas before making a lot. You get to pick the finish, like shiny, matte, or a green patina. CNC copper parts machining lets you add small details, like engravings or logos, to your pieces.
Tip: Ask your copper machining manufacturer to make matching sets for your home or business. This helps you keep the same style in every room.
Some popular decorative uses for copper are:
- Wall art and sculptures
- Door handles and knobs
- Light fixtures and lamp bases
- Kitchen backsplashes and sinks
- Table edges and furniture accents
- Musical instrument parts
Copper mechanical machining makes strong and smooth surfaces. This means your decorative items will not scratch or wear out fast. Precision copper parts machining helps you get the exact size and shape you want. You can also mix copper with other metals, like brass, for a two-tone look.
| Decorative Item | CNC Machining Process | Finish Options | Customization Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wall Panels | CNC Milling, Sheet Metal | Shiny, Matte, Patina | High |
| Lamp Bases | CNC Turning, Milling | Polished, Brushed | Medium |
| Door Handles | CNC Milling, Brass Machining | Gold, Red Copper | High |
| Sculptures | Casting, CNC Milling | Patina, Textured | Very High |
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. can help you from the first idea to the finished product. They use cnc machining for copper to make sure your decorative pieces look good and last long. If you want to try new ideas, rapid prototyping copper parts let you test shapes and finishes before you choose.
Note: Decorative copper items add style and value to any space. You can use cnc copper parts machining to make pieces that fit your taste and needs.
Tips for Beginners
Tool Wear
When you start CNC machining for copper, you will notice that tool wear can happen quickly. Copper is soft and sticky, which means it can build up on your cutting tools and make them dull. You need to pay close attention to managing tool wear so your parts stay accurate and your tools last longer.
Here are some best practices for managing tool wear when working with copper:
- Use a larger stepover and deeper cuts during roughing passes. This helps you remove material quickly, but you must watch for heat and tool stress.
- Switch to a smaller stepover and shallower cuts for finishing passes. This reduces tool wear and gives you a smoother surface.
- Balance your stepover settings. If you go too fast or too deep, you create more heat and wear out your tools faster.
- Always check your tool condition. Adjust your cutting parameters if you see signs of wear or if the copper starts to stick to the tool.
You should also choose the right cutting tools for copper mechanical machining. High-speed steel (HSS) tools work well because they handle copper’s softness. Cemented carbide tools are strong and resist wear. Diamond-coated tools last even longer, especially for precision copper parts machining. Make sure your tools are always sharp. Dull tools cause more wear and rough finishes.
Here is a simple table to help you pick the best tool for CNC copper parts machining:
| Tool Type | Best Use Case | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
| HSS | Soft copper, roughing passes | Medium |
| Carbide | Brass CNC machining, finishing | Long |
| Diamond-coated | Red copper CNC machining, high precision | Very Long |
You need to optimize your cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. If you set these too high, you will see more heat and faster tool wear. If you set them too low, you waste time and may not get a good finish. Always use coolant to keep your tools and copper cool. This helps prevent heat buildup and keeps your tools sharp.
Managing tool wear is one of the biggest challenges for beginners in copper CNC machining. You must learn how copper behaves and adjust your techniques. Use chip breakers and coolant systems to control chips. Hold your copper workpiece tightly with collets or chucks to stop vibrations. This keeps your tools safe and your parts accurate.
Tip: Set your cutting tool edge angle between 70° and 95°, close to 90° for softer copper. This helps reduce wear from heat and gives you a better finish.
If you follow these steps, you will get better results in CNC machining for copper. You will make custom copper parts that fit well and look good. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. can help you with rapid prototyping of copper parts and give advice on tool selection. A good copper machining supplier or copper machining manufacturer will always check tool wear and help you solve problems.
Troubleshooting
When you start copper CNC machining, you may face problems that affect your parts or your tools. You need to know how to spot these issues and fix them quickly. Troubleshooting helps you keep your CNC copper parts machining smooth and your results accurate.
Common Problems in CNC Machining for Copper:
| Problem | What You See | How to Fix It |
|---|---|---|
| Tool Wear | Dull edges, rough finish | Use sharper tools, adjust speeds |
| Built-Up Edge | Copper sticks to tool | Use coated tools, increase coolant |
| Poor Surface Finish | Scratches, smears | Lower feed rate, check tool angles |
| Overheating | Burn marks, warped parts | Use more coolant, reduce speed |
| Chip Packing | Chips clog tool area | Improve chip removal, use chip breakers |
| Dimensional Errors | Parts do not fit | Calibrate machine, check setup |
You may see copper sticking to your cutting tool. This is called a built-up edge. You can fix this by using a coated tool or increasing the amount of coolant. If your part looks rough or has scratches, check your feed rate and tool angle. Lowering the feed rate and using a sharper tool often helps.
Sometimes, your copper mechanical machining may cause overheating. You will notice burn marks or warped parts. You can solve this by using more coolant and reducing your cutting speed. If chips pack around your tool, use chip breakers or adjust your chip removal system.
Dimensional errors happen when your parts do not match the design. You should calibrate your CNC machine and check your setup. Always measure your custom copper parts after machining. This helps you catch mistakes early.
Tip: If you see the same problem many times, keep a log. Write down what you changed and what worked. This helps you solve issues faster next time.
You may also face problems with brass CNC machining or red copper CNC machining. Each alloy acts differently. You should adjust your settings for each type. For copper heatsink machining, watch for heat buildup. Use extra coolant and check your tool often.
If you need help, ask your copper machining supplier or copper machining manufacturer. They can give advice or help with the rapid prototyping of copper parts. You can also join online forums or read guides about precision copper parts machining. Sharing your experience helps you learn new solutions.
Troubleshooting is a skill you build over time. You will get better at spotting problems and fixing them. Stay patient and keep learning. Your CNC copper parts machining will improve with practice.
FAQ
Copper is soft and can stick to tools. You need sharp tools and the right speed for CNC copper parts machining. Using good lubrication helps stop tool wear. These steps help you get clean cuts and exact shapes.
Yes, you can use CNC machines for brass and bronze. Brass is easy to cut and looks gold. Bronze is strong and lasts a long time. You can choose the best alloy for your project.
You check every part with special tools like CMMs. You measure the size and how smooth the surface is. A copper machining supplier like AFI Industrial uses strict checks and has ISO 9001 certification.
Pick a supplier with experience in CNC machining for copper. They should check quality, work fast, and offer many machining choices. AFI Industrial gives you all these things.
Yes, red copper CNC machining works well for heatsinks. Red copper moves heat fast. You get smooth, custom shapes for cooling electronics with copper heatsink machining.





