You make aluminum extrusion shapes by pushing hot aluminum through a special die. When you ask, “what is aluminum extrusion,” you are referring to a method of shaping aluminum into long pieces that maintain the same cross-section throughout. You can use steps to transform raw aluminum into precise shapes. These shapes are utilized for a variety of applications. This process provides you with strong, lightweight, and practical parts for your projects.
Key Takeaways
- Aluminum extrusion shapes are made by pushing hot aluminum through a die. This makes long pieces with the same shape all the way through. This process creates strong and light parts. These parts are used in many things like buildings, cars, and electronics. Picking the right die material, such as H13 steel, is very important. It helps make smooth and exact aluminum profiles. The aluminum billet must be heated to 400°C to 500°C. This makes it soft enough to shape but not melt. This also stops cracks from forming. The extrusion press uses a lot of pressure to push aluminum through the die. The amount of force needed depends on the profile size and alloy type. Cooling methods, like air or water quenching, change the final properties of aluminum profiles. This affects how strong they are and how well they keep their shape. Surface treatments like anodizing and powder coating make aluminum profiles last longer. They also make them look better and good for outdoor use. Quality control is done during the whole extrusion process. This keeps the standards high and makes sure aluminum products are reliable and exact.
Table of Contents
What Is Aluminum Extrusion
Definition
When you ask, “what is aluminum extrusion,” you want to know how aluminum gets shaped into useful forms. This process makes long pieces that look the same all the way through. In technical terms, what is aluminum extrusion? It is a way to make things by heating aluminum alloy strips. Then, you push them through a shaped die with high pressure. This step gives you profiles with exact shapes and sizes.
You can trust aluminum extrusion standards to help you. These standards show you how to make, test, custom machining,and check aluminum profiles. They make sure every piece is high quality and always the same.
Aluminum extrusion is not just about shaping metal. It helps you make strong, exact, and reliable parts for many uses. You get a process that uses heat and pressure to give you what you need.
Common Applications for Aluminum Extrusions
You might wonder where you see aluminum extrusion in your life. You find these shapes in lots of places because they are strong, light, and flexible. Here is a table that shows some common uses for aluminum extrusions:
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Architecture and Construction | Used for window frames, curtain walls, and railing systems. |
| Automotive | Components like structural frames and chassis for improved fuel efficiency. |
| Aerospace | Structural frames and components for enhanced performance in aircraft. |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and enclosures for thermal management in electronic devices. |
| Consumer Goods | Various products benefiting from lightweight and durable aluminum profiles. |
You see aluminum extrusion in buildings and construction. You find it in window frames, curtain walls, and railings. In cars, you use extruded aluminum for frames and chassis. This helps make cars lighter, so they use less fuel and pollute less. You also see aluminum extrusion in planes, electronics, and everyday products.
- You get strong and flexible building parts for façades and curtain walls.
- You use light support systems that do not weigh down foundations.
- You enjoy windows and doors that do not rust easily.
- You use light battery boxes in electric cars.
- You rely on good energy absorption for crash safety.
What is aluminum extrusion? It is a way to make strong, light, and useful parts. You can count on this process to give you good results for many industries. That is why you see aluminum extrusions used so often in today’s manufacturing.
Aluminum Extrusion Process
Die Preparation

You begin by getting the die ready. The die shapes the aluminum as it goes through. You must pick a strong material for the die. H13 steel is used most because it handles heat and lasts long. Some dies use A2 or D2 tool steel for more strength. Carbide inserts are used when making lots of parts. The die must match the shape you want. A good die gives you smooth and exact aluminum profiles. If the die is not good, the product can have problems and be weak.
| Material Type | Description |
|---|---|
| H13 Steel | Tough, heat-resistant, and durable for repeated use |
| A2 Tool Steel | Good wear and crack resistance |
| D2 Tool Steel | High wear resistance, holds sharp edges |
| Carbide Inserts | Used for high-volume production |
Tip: Always look at the die for damage before you start. This helps you stop problems in your finished aluminum profile.
Billet Heating
Next, you heat the aluminum billet. The billet is a solid round piece of aluminum. You need to make it soft but not melt it. The usual heat range is 400°C to 500°C. This keeps the aluminum easy to shape but still solid. Heating right stops cracks and keeps the shape good. When you heat the billet well, the inside grain and strength get better. Higher heat can make the aluminum stronger, but you must watch the process to stop mistakes.
| Temperature Range (°C) | Description |
|---|---|
| 400-480 | Aluminum is malleable but remains solid |
| 400-500 | Standard heating range for extrusion billets |
| 420-500 | Reduces flow stress and prevents defects |
- Heating changes the grain size and the way grains meet.
- You see changes in how much the metal stretches as it gets hotter.
- Good heating makes welds and the final aluminum profile stronger.
Extrusion Press
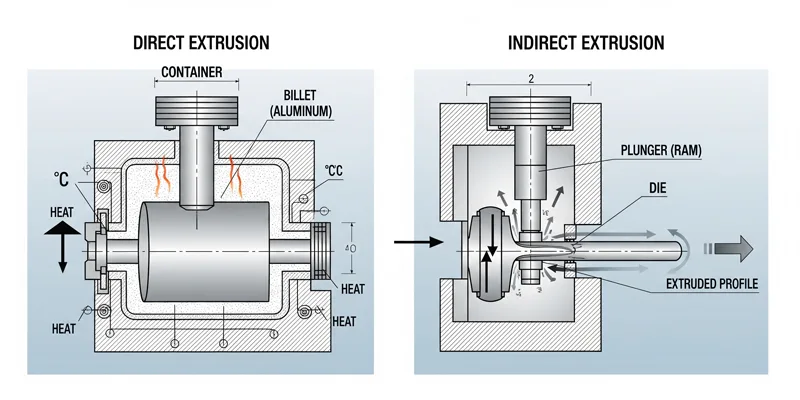
Now you move the hot billet to the extrusion press. The press is the main machine in this process. There are direct and indirect presses. In direct extrusion, a ram pushes the aluminum through the die. This works well for big shapes and high force. In indirect extrusion, the die stays still and the billet moves with the container. This helps control heat and gives steady quality.
- Hydraulic presses use force from 100 to 15,000 tons.
- You need a lot of pressure to push the aluminum through the die.
- The press makes sure the aluminum fills the die shape evenly.
Note: The kind of press you use changes how fast, good, and steady your aluminum profiles turn out.
These steps help you shape aluminum into strong and exact parts. Each part of the process helps you make the right aluminum profile for your needs.
Ram Action
When you use an extrusion press, the ram pushes the hot aluminum billet through the die. The ram moves forward with a set speed and force. You change the ram speed to help shape the aluminum. The speed also affects how good the final product is. If you make the ram go faster, the way aluminum flows and welds inside the die changes.
- If the ram goes too fast, the seam-welded quality can get worse, especially for alloys like AA6063.
- When you speed up the ram, the normal pressure and stress on the aluminum go up.
- The ratio of pressure to stress gets lower as the ram moves faster, which can make welds weaker.
- Welded aluminum parts can lose strength if you use high ram speeds.
You need to balance the ram speed to make strong and well-shaped aluminum pieces. Going too fast can cause weak welds and bad shapes. Going too slow wastes time and energy. You have to find the best speed for your project.
Tip: Always watch the ram speed while you work. This helps you make good aluminum profiles and avoid mistakes.
Pressure
You need a lot of pressure to push aluminum through the die and get the shape you want. The extrusion press gives this pressure, and it is measured in tons. You pick a press based on the size and type of aluminum profile you want.
- Small presses use less than 1,000 tons for simple shapes.
- Most presses for regular profiles use 1,100 to 5,000 tons.
- Special presses can go up to 12,000 tons for big or tricky shapes.
If you use hard aluminum alloys, you need even more pressure. These alloys are harder to move and have rougher surfaces. You must use the highest pressure to push hard aluminum through the die. If you make the extrusion ratio bigger, the job gets harder because the aluminum faces more resistance.
You check the pressure to make sure the aluminum fills the die all the way. If you use too little pressure, the aluminum might not form the right shape. If you use too much, you could break the die or the press.
Note: Always match the press force to your aluminum alloy and profile size. This helps you get the best results and keeps your equipment safe.
Quenching and Cooling
Quenching Methods
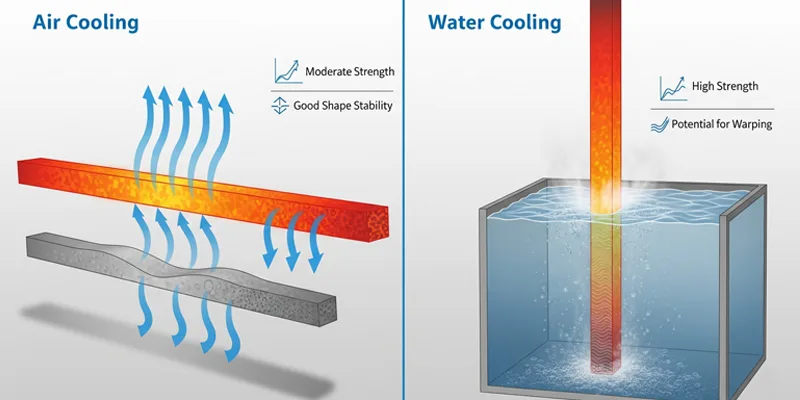
After you shape the aluminum, you must cool it quickly to lock in the right properties. This step is called quenching. You have two main choices: air cooling and water cooling. Each method gives you different results, and you must pick the best one for your project.
- Air cooling works well for 6063 aluminum profiles. You let the hot aluminum cool in the open air. This method costs less and does not need special equipment. You do not see much risk of cracking or distortion. After air cooling, you age the profiles to make them stronger.
- Water cooling is the top choice for high-strength alloys. You move the hot aluminum into water right after extrusion. Water pulls heat away fast, so the metal cools quickly. This method helps you keep the best metallurgical properties, like strength and ductility. You must handle water-cooled profiles with care, because they can bend or twist if you do not support them well.
- T5 profiles use air cooling and stay straight. T6 profiles use water cooling, but they may deform if you do not control the process.
- Water quenching can cause distortion, but air quenching keeps the shape better and costs less.
Tip: You must match your quenching method to the alloy and the shape you want. If you use water cooling, watch for bending. If you use air cooling, check that the strength meets your needs.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Quenching Method | Best For | Risks | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Cooling | 6063, simple profiles | Lower strength | Low |
| Water Cooling | High-strength alloys | Distortion, bending | Higher |
Material Properties
The way you cool aluminum changes its inside structure and how it behaves. Fast cooling with water gives you a strong and tough profile. Slow cooling with air makes the metal softer, but you see less risk of warping.
- Water quenching improves strength and ductility. You get better metallurgical properties because the metal cools fast.
- Air quenching lowers the risk of distortion. You spend less money and keep the shape steady.
- The choice of quenching method affects the microstructure. If you use water, you see smaller grains and tighter bonds. If you use air, the grains grow bigger and the metal becomes less strong.
Researchers use tools like transmission electron microscopy and tensile tests to study these changes. They find that different cooling rates lead to big differences in how the metal stretches and bends. You must think about these results when you pick your quenching method.
Note: If you want the strongest aluminum, use water quenching. If you need a stable shape and lower cost, choose air cooling.
You control the final properties of your aluminum profile by choosing the right quenching method. This step helps you get the strength, shape, and quality you need for your project.
Cutting and Stretching
Cutting

You must cut aluminum profiles to the right length. It is important to be exact. First, measure and mark the aluminum carefully. Use a square to make sure your lines are straight. Clamp the aluminum down before you cut it. This keeps it from moving and helps you stay safe.
You can use different tools to cut aluminum extrusions:
- A miter saw lets you cut at any angle. It gives you smooth and clean edges.
- A chop saw makes straight cuts. It may not work well for big pieces.
- A circular saw also makes clean cuts. It is not as exact as a miter saw.
Pick a blade made for non-ferrous metals like aluminum. These blades have special teeth. They help stop rough edges and keep the cut smooth. Use a thin cutting oil to help the blade move through the metal. This also keeps the blade cool.
Safety Tip: Always wear safety goggles and a face shield. Protect your eyes and face from flying pieces. Clamp the aluminum so it does not slip or move.
After you cut, check the ends for rough spots. You might need to file or sand them to remove burrs. This helps your aluminum pieces fit together well when you build with them.
Alignment
After cutting, you need to make sure the profiles are straight. Sometimes, the extrusion process leaves them bent or twisted. You fix this by stretching the aluminum. Aluminum bends easily, so you can straighten it without breaking it.
Put the aluminum on a flat surface. Press down to stretch out any bends. For long or tricky shapes, use a stretching machine. This machine grabs both ends and pulls gently. The force makes the profile straight again.
Note: Straight profiles fit together better and look nicer. They also work better in the final product.
Always check if the profile is straight after stretching. Use a straightedge or a laser tool to check. If you see any bends, stretch the aluminum again until it is straight.
By doing these steps, you make sure your aluminum is the right length and straight. This careful work gives you good parts for finishing and building.
Finishing
Surface Treatment
You want your aluminum profiles to look nice and last long. Surface treatment helps you do this. You can pick from different ways to protect and improve your aluminum. Here are some common surface treatments you can use:
- Anodising
- Bright Anodising
- Colour Anodising
- Hard Anodising
- Mechanical Surface Treatment
- Painting
- Powder Coating
Anodising is a popular choice for many people. You put the aluminum in a chemical bath. This makes a strong oxide layer on the outside. The layer keeps the aluminum safe from rust and damage. You can add color during anodising to make your profiles look special.
Anodising makes the oxide layer thicker. This helps stop rust and keeps the surface from getting scratched. It works well for things used outside, where weather can hurt untreated aluminum.
Powder coating is another good way to protect aluminum. You spray dry powder on the aluminum and bake it in an oven. The powder melts and makes a hard cover. This cover does not chip or scratch easily. You can choose many colors and textures, so powder coating is very useful.
Surface treatments help more than just looks. You make the surface harder and tougher. You help your aluminum last longer. Anodised aluminum can last up to 20 years, even with strong chemicals or sunlight.
Tip: Pick the surface treatment that fits your project. If you want strong protection and lots of color choices, try anodising or powder coating.
Quality Control
You need to make sure every aluminum profile is high quality. Quality control starts before you shape the aluminum and goes until the last check. You follow steps to get the best results:
- Raw Material Inspection: You check aluminum billets for problems and make sure they are good.
- Process Monitoring and Control: You watch temperature and pressure while shaping aluminum. This helps keep things working right.
- tight tolerances Checks: Machines look at profiles as they are made. You find mistakes early.
- Post-Extrusion Inspection: You measure each profile for size and strength. You look for problems that could cause trouble.
- Quality Documentation and Traceability: You write down every step. This helps you fix problems fast.
You keep your good name by using strong quality control. You give customers products they can trust.
Quality control helps you get aluminum extrusions that are always good. You avoid big mistakes and make customers happy. By using careful surface treatment and checking everything, you make aluminum profiles that work well and look nice.
Benefits of Extrusion
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
You get great strength when you use aluminum extrusion. The process uses heat treatments like overheating and soft annealing. Overheating means heating the billet very hot before cooling it fast. This makes the metal stronger. Soft annealing makes the billet easier to shape by making Mg₂Si particles form. This lets you push the aluminum faster through the die. Alloys like HyperAl 6061 show these benefits. They move quickly and form small grains inside. Small grains make your extruded profiles even stronger.
Aluminum extrusion fabrication is better than other ways to shape metal. Here are some main mechanical benefits you get:
- Precision: You can make shapes that are exact and detailed.
- Versatility: You can make solid, hollow, or partly hollow profiles.
- Scalability: You can make just a few or many parts.
You can count on extruded aluminum to give you strong and dependable parts for tough jobs.
Flexibility
You get lots of design choices with aluminum extrusion. This process lets you make shapes that are hard to make with other methods. You can change designs fast if your project needs change. The table below shows how aluminum extrusion is different from casting or rolling:
| Feature | Aluminum Extrusion | Casting/Rolling |
|---|---|---|
| custom profile design | High – lets you make tricky shapes | Limited – hard to make complex shapes |
| Dimensional Accuracy | High – keeps sizes exact and steady | Variable – not always as exact |
| Production Flexibility | High – easy to change profiles | Low – takes more time to set up |
| Cost Efficiency for Complex Parts | Small cost change for tricky shapes | Higher costs for complex shapes |
You can design special profiles for windows, doors, car parts, or electronics. You do not pay much more for tricky shapes. You also keep sizes exact, so your parts fit well.
You get to be creative and fix problems with aluminum extrusion.
Sustainability
You help the planet when you pick aluminum extrusion. Aluminum is easy to recycle, and most profiles use recycled material. In big markets like cars and buildings, recycling rates can reach 90%. Almost 75% of all aluminum ever made is still being used. Recycling aluminum saves 95% of the energy needed to make new aluminum.
Here is a quick look at recycling rates:
| Metal | Energy Savings in Recycling | Recyclability Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Up to 95% | High |
| Copper | Up to 85% | High |
- You help nature by choosing aluminum extrusion.
- You use less energy and make less pollution.
- You support recycling because aluminum can be reused forever.
Sustainability is a big plus for aluminum extrusions. You help make the world greener every time you use extruded aluminum.
You make aluminum extrusion shapes by following simple steps. First, you get the die ready. Next, you heat the billet. Then, you press and shape the aluminum. After that, you cool it down. You cut the aluminum to the right size. Last, you finish the surface. Aluminum extrusions are strong and light. They let you design many shapes. You save money when you use this process.
- Aluminum extrusions do not rust easily and are simple to recycle. You can make special shapes for different jobs.
- You can pick finishes like anodizing or powder coating. These finishes help protect the aluminum.
- You check the quality by inspecting and using good machines.
Aluminum extrusion gives you parts that last a long time. You can trust them to work well for your project.
FAQ
You get shapes that are strong and light. The sizes are exact. Aluminum extrusion lets you make custom profiles. You use these for many things. You save money and time over other metal forming ways.
You can recycle aluminum extrusions without trouble. Most profiles use recycled aluminum. Recycling saves energy. It helps keep the environment safe.
You pick a finish that fits your project. Anodizing helps stop rust. Powder coating gives color and more protection. You can ask your supplier for help.
You can make solid, hollow, or semi-hollow shapes. You can design tricky shapes. You use profiles for windows, doors, cars, or electronics.
You get very accurate profiles with aluminum extrusion. The process keeps sizes steady. Shapes stay exact. You can trust profiles to fit your project.
You can use aluminum extrusions outside. Surface treatments like anodizing stop rust and weather damage. Profiles last for years outdoors.
You wait about two to six weeks for custom extrusions. Lead time depends on die design, order size, and finish.
You can make profiles up to 60 feet long. Most projects use shorter lengths. Shorter pieces are easier to move and handle.





