Electroplating
Electroplating process, give new life to metal! AFI Industries’ plating services give your products a bright coat that enhances durability and beauty.
Electroplating Process
Electroplating is an electrochemical process used to coat a metal film on a metal or non-metal surface. This process involves using the part to be plated (usually metal) as the cathode and the metal to be plated as the anode, both of which are immersed in a plating solution containing the same metal ions. By applying direct current, the metal on the anode will dissolve into ions into the plating solution, while the metal ions on the cathode will be reduced into metal atoms and deposited on the surface of the plated part to form a uniform, dense metal film. The basic steps of its process are as follows:
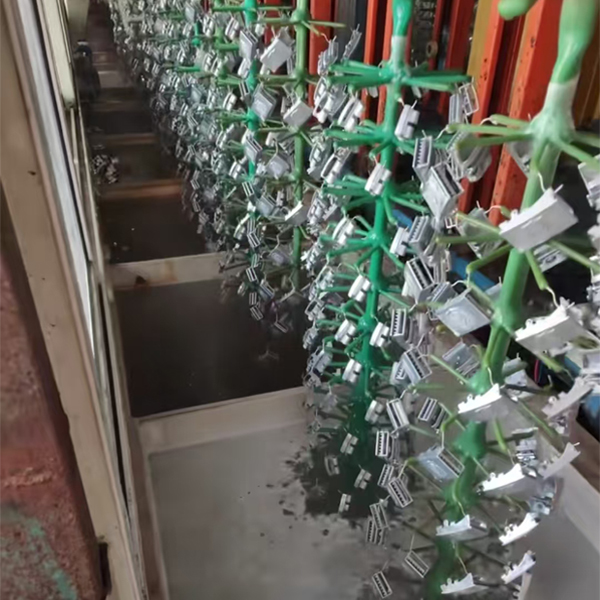

Pretreatment
The pretreatment stage of electroplating process is the key step to ensure the quality of the final coating. The purpose of pretreatment is to remove various pollutants on the surface of the substrate through a series of physical and chemical treatment means, so that it can achieve a good activation state, laying the foundation for the smooth progress of the plating process, including cleaning and degreasing, alkaline cleaning, pickling and passivation.
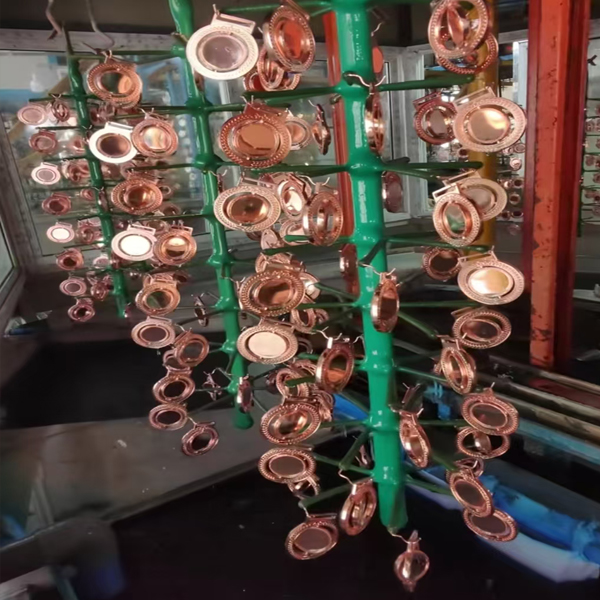
Electroplate
We put the products to be electroplated into the electroplating tank filled with special liquid, and then by adjusting parameters such as the current size, liquid temperature and electroplating time, a metal coating of just the right thickness is formed on the surface of the products. After electroplating is completed.
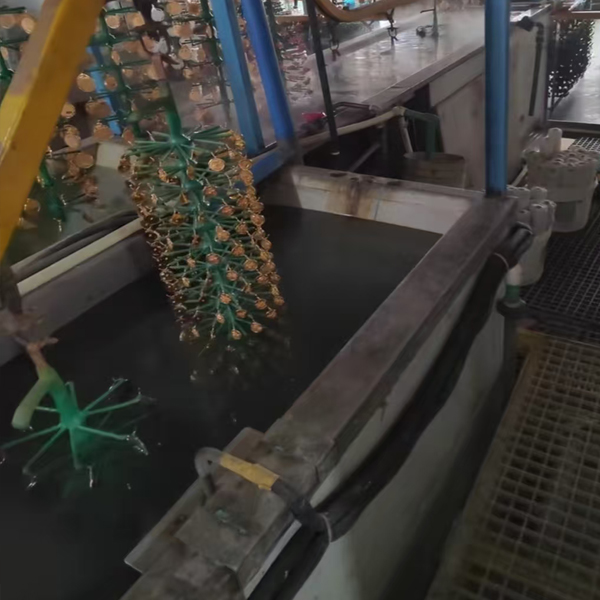

After treatment
we will also carry out post-treatment processes such as passivation, sealing or polishing on the product. This can make the product more corrosion-resistant or look more beautiful. Finally, thoroughly dry them, and the electroplating surface treatment of the product is completed.
Custom Plating Service
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. provides electroplating processing services for customers. Whether it’s hardware, electronic components or handicrafts, we can customize electroplating solutions according to your specific needs. We adopt different processes for different materials to ensure that each product is both beautiful and durable. By cooperating with us, not only will the quality of your products be guaranteed, but they will also stand out among similar products, making your brand more upscale.
About Electroplating
Before electroplating, the product has a rough appearance, a monotonous color, poor corrosion resistance and wear resistance, a short service life, and a low added value. After electroplating, the surface of the products becomes smooth and flat, with a bright luster. Their corrosion resistance and wear resistance are significantly enhanced, their service life is greatly prolonged, and their added value is also greatly increased, which can better meet the needs of various application scenarios.
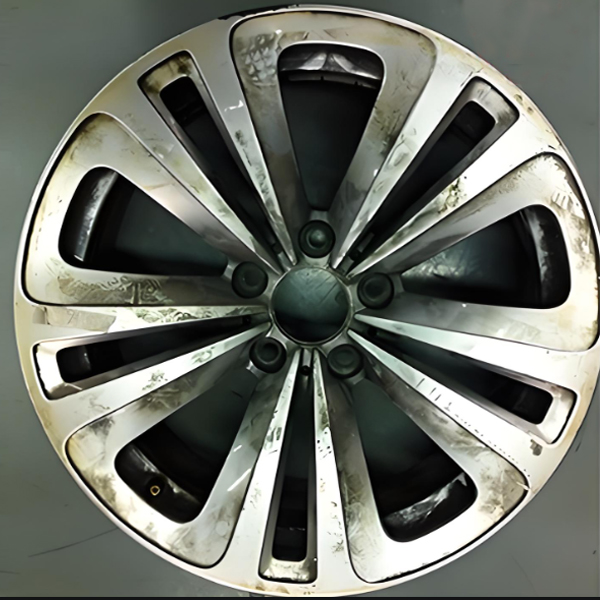

Before Plating
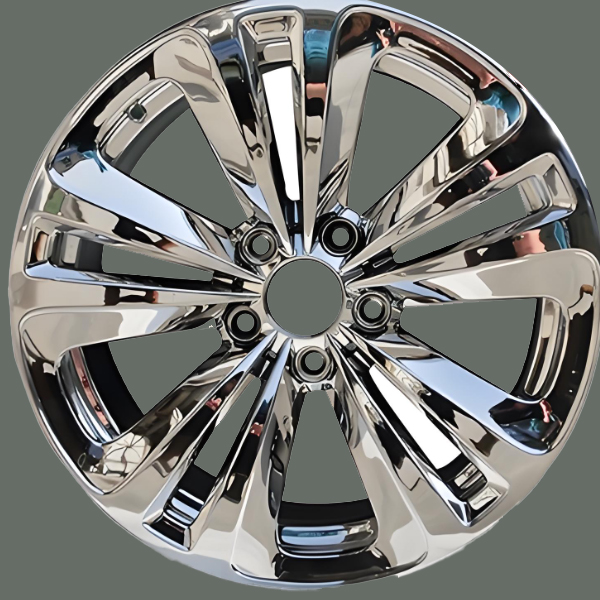

After Plating
Electroplating Equipment
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. has a complete range of automatic electroplating equipment, which makes metals such as copper, nickel, chromium, zinc, silver and other metals into films or improve the physical and chemical properties of metal surfaces through electrochemical reactions. equipment usually includes the following key parts:
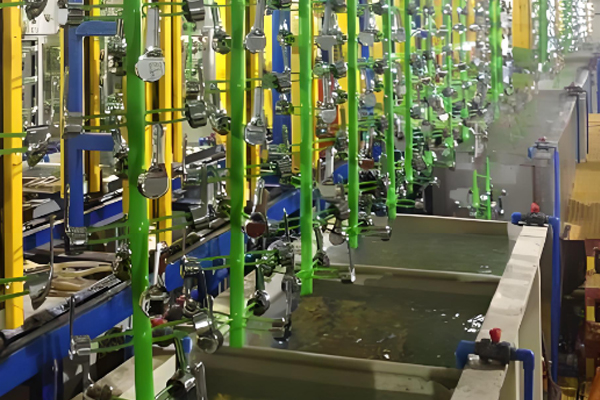

Automatic Plating Production Line
The automatic electroplating production line is an efficient and automated electroplating equipment, which can realize the automated production of multiple processes.
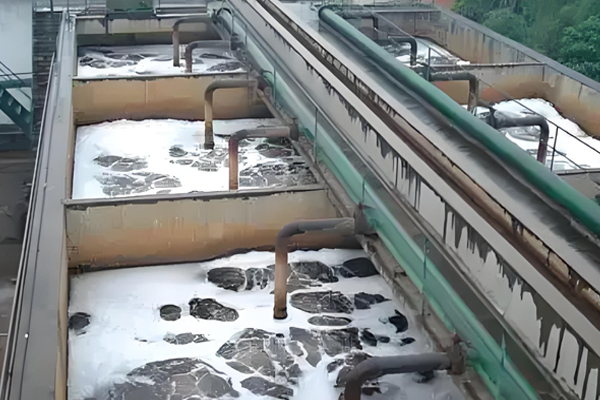

Waste Water Treatment Equipment
Specially designed to treat the wastewater produced in the electroplating process, which usually contains heavy metal ions, organic pollutants and other harmful substances, to achieve sustainable development.
Electroplating Material
Most metal materials (such as iron, steel, copper, aluminum, zinc, etc.) are suitable for electroplating because they have good electrical conductivity by themselves.
Non-metallic materials such as plastic, ceramics and glass are not suitable for direct electroplating by themselves, but they can also be electroplated after special surface treatment.
Electroplating Testing Equipment
The quality inspection of the plating process involves many aspects of the testing equipment. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. ensures the quality and stability of the plating process through the testing equipment, and accurately measures the thickness of the coating, adhesion, plating solution composition and other key parameters to meet the product quality requirements.

microscope
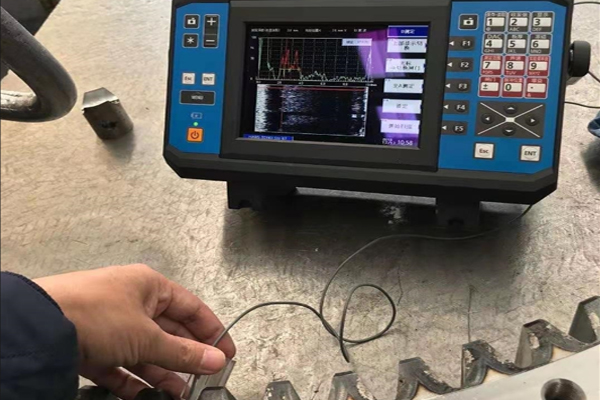

Hardness testing equipment
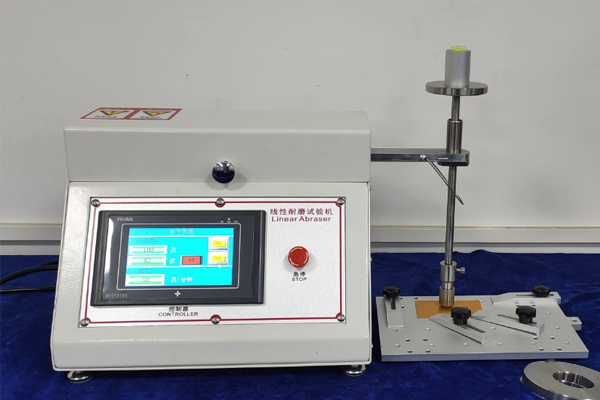

Falling sand abrasion tester
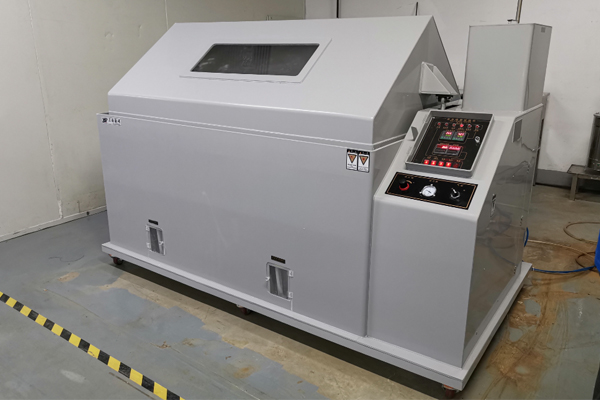

Salt spray testing machine
How to Start Your Order
Your satisfaction and trust are our eternal pursuits. Let us work together to create excellent quality and service, and witness every moment of success.

Frequent Asked Questions
It can significantly enhance the performance of CNC parts, including: corrosion resistance, wear resistance, electrical conductivity and aesthetics. We will recommend the appropriate process for you based on your application scenarios.
We control the thickness of the coating in the following ways:
Process standardization and real-time monitoring (using ultrasonic thickness gauges or X-ray fluorescence meters for detection).
Customers can specify the thickness range (such as 5-20μm), and we ensure strict compliance.
Common problems we encounter include bubbling, peeling, color difference or porosity. The possible causes are: incomplete pretreatment (residual oil or oxide layer), out-of-control electroplating parameters (improper current density, temperature), and substrate impurities (such as residual chips from CNC processing).
Our solution: Strict pretreatment (acid washing, ultrasonic cleaning), process quality inspection (random inspection of adhesion and salt spray test per batch), material screening (avoiding the use of sulfur/lead substrates that are prone to corrosion).
Our prioritizes environmentally friendly solutions: cyanide-free (such as alkaline zinc and trivalent chromium replacing hexavalent chromium), wastewater treatment (neutralizing heavy metals and discharging up to standard), and compliance certification.
Some high-anti-corrosion coatings (such as cadmium plating) may be restricted. We will inform you of the alternative solutions in advance.
