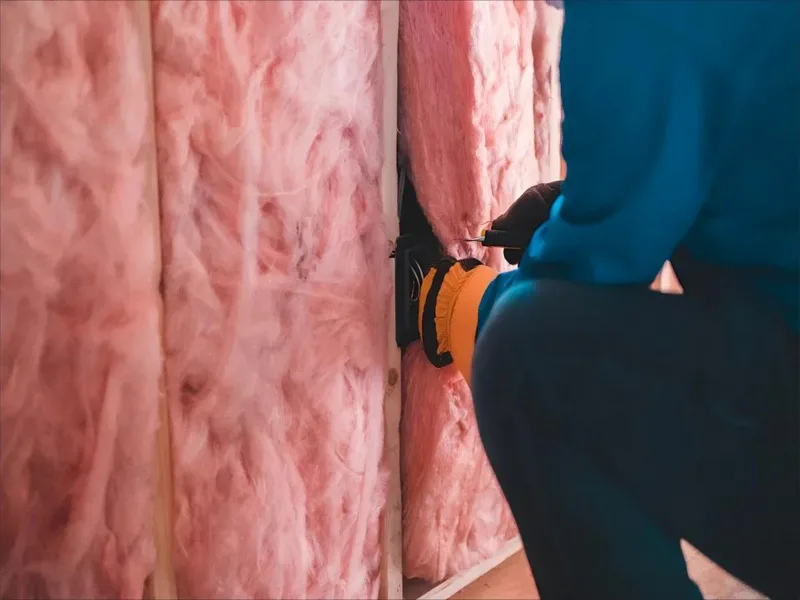
Fiberglass is made from tiny glass fibers. It is used in many industries because it is very useful. Fibreglass is strong but also light. This helps people make new things in cars, buildings, and boats. In 2023, the world market for fiberglass was worth $18.78 billion. Every year, about 5.6 million metric tons of fibreglass insulation are made. This number continues to grow as companies seek to improve energy efficiency and utilize stronger materials.
Fiberglass has special properties like not rusting and being tough. This makes it a top pick for engineers and designers. Fiberglass is now used instead of old materials because it can do more and save money over time. It helps solve new problems, like making buildings greener and travel safer. Many businesses use fiberglass because it lasts in tough places and needs less fixing. Fiberglass lets people make cool new designs in factories. As more people want it, fiberglass stays important for jobs that need to work well and last long.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Fiberglass is strong and light. It is made from tiny glass fibers mixed with resin. People use it in building, cars, planes, boats, and sports gear.
- It is very strong and lasts a long time. It does not rust or get damaged by chemicals, fire, or weather. This helps things last longer and need less fixing.
- Fiberglass is easy to shape into many things. Designers can make complex and special parts with it.
- Fiberglass is lighter than metals. It does not rust like metal. This saves fuel and lowers repair costs for cars and buildings.
- Fiberglass keeps heat and electricity from passing through. This makes it safe and saves energy in many ways.
- You must be careful when handling fibreglass. It can hurt your skin, eyes, and lungs. Wear safety gear and clean up well after using it.
- It is hard to recycle fibreglass. People are working to make it easier to reuse and help the environment.
- Fiberglass can break easily and is hard to install. Still, it is a smart and cheap choice for strong, long-lasting things.
What Is Fiberglass?

Basic Definition
Fiberglass is a fiber-reinforced plastic composite. It mixes glass fibre with a polymer matrix. Many industries use it because it is strong and light. It is also easy to shape. Materials science says fibreglass is a composite. It uses glass fibres in different forms, like chopped strand mats or woven cloth. These are set in a resin such as epoxy or polyester. People sometimes call it glass-reinforced plastic (GRP) or fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP). Fiberglass costs less and bends more than carbon fiber. It is stronger than many metals by weight. It does not attract magnets and does not carry electricity. These features make it useful for many things.
Note: Fiberglass lets electromagnetic radiation pass through. It also resists many chemicals. This makes it even more useful in engineering.
Composition
Fibreglass is made of glass fibre and resin. Glass fibre gives it strength. Resin holds the fibres together. Most fiberglass has 20% to 40% glass fibre. The amount depends on how strong the product needs to be. More glass fibres make it stronger. But too much can make it hard to make.
The raw materials for glass fibre are:
- Silica sand
- Limestone
- Soda ash
- Alumina
- Dolomite
- Boric oxide
- Magnesia
- Potash
- Kaolin clay
- Feldspar
Different types of fibreglass use different mixes. For example, E-glass and S-glass have specialized blends for specific applications. The resin is usually a thermoset like polyester or epoxy. It keeps the glass fibres in place and shapes the product.
Manufacturing Process
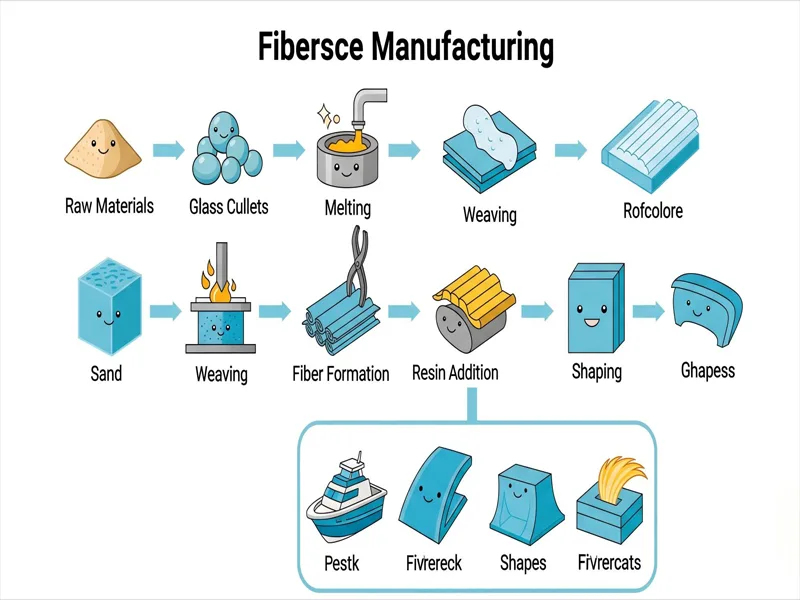
Making fibreglass starts by melting raw materials. These include silica sand, limestone, and soda ash. They melt in a furnace at about 2500°F (1371°C). The melted glass goes to the forming equipment. It passes through spinnerets with tiny holes. This makes fine glass fibres.
There are several ways to form these fibres:
- Continuous-filament process: Glass fibres are pulled fast, coated with binders, and wound onto tubes.
- Staple-fiber process: Fibres are cooled, broken into short pieces, and collected into strands.
- Chopped fiber: Strands are chopped and made into mats.
- Glass wool: Molten glass is spun and blown into wool, then cured for insulation.
After forming, fibres are bundled into rovings or mats. The next step is often fibreglass pultrusion. In this process, glass fibre rovings or mats go through a resin bath. Then they go through a heated die. The resin hardens, making a solid composite. Fibreglass pultrusion makes strong, long-lasting products like utility poles and sports gear. This method helps make lots of fibreglass items with steady quality.
Tip: Fiberglass pultrusion helps make complex shapes and long profiles. This lets many industries use this material in new ways.
Fiberglass Properties

Strength
Strength is one of the most important things about fibreglass. Engineers like fibreglass because it is very strong and has high tensile strength. It can hold heavy things without breaking or stretching. The glass fibre inside gives fibreglass its strength. These fibers make it tough and help it resist pulling.
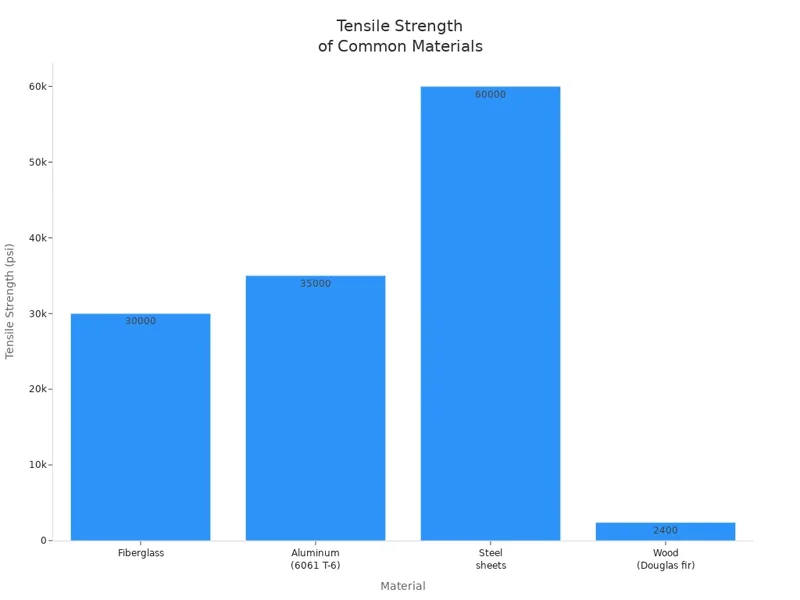
The table below shows how strong fibreglass is compared to other materials:
| Material | Typical Tensile Strength (Yield Strength) |
|---|---|
| Fiberglass | ~30,000 psi |
| Aluminum (6061 T-6) | ~35,000 psi |
| Steel sheets | ~60,000 psi |
| Wood (Douglas fir) | ~2,400 psi |
Fiberglass is not as strong as steel, but it is much stronger than wood. It is almost as strong as aluminum. Fibreglass is light but strong, so many industries use it. Pound-for-pound, Fibreglass is stronger than many metals. Its specific strength is about 1,307 kN·m/kg, while stainless steel is only 63.1 kN·m/kg. This means fibreglass can hold heavy loads without being heavy.
Fiberglass rebars in buildings have tensile strengths around 1000 MPa. This is even higher than steel rebars, which are about 550 MPa. Because fibreglass is so strong, it can replace heavier materials. Designers use this to make products that are lighter, safer, and work better.
Durability
Durability is another important thing about fibreglass. This material lasts a long time, even in hard places. Fibreglass does not get damaged by water, chemicals, or sunlight. It does not rust like metal or rot like wood. The glass fibre makes it strong, and the resin keeps it safe from outside things.
- Fiberglass (FRP) does not corrode easily. Metals can corrode, but fibreglass stays strong.
- FRP does not need special coatings or lots of repairs. This saves money on fixing things.
- Marine, chemical, and wastewater jobs use fibreglass because it does not break down in harsh places.
- Fiberglass keeps its shape and strength even after years in the sun or in hot and cold weather.
- High strength and new technology make fibreglass structures last a long time.
But, fibreglass can get weaker over time. Water, heat, and sunlight can lower its strength. Water can get inside and cause small changes. These changes can slowly make it less strong. Still, engineers use tests and new materials to make fibreglass last longer. With good care, fibreglass products stay strong and useful for many years.
Fire Resistance
Fire resistance is very important for many uses. Fiberglass is much better at resisting fire than many plastics and some metals. The glass fibre does not burn. The resin can have special things added to slow down fire.
| Fire Resistance Aspect | Standard/Test | Result/Rating | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Burning Characteristics | ASTM E84 | Flame Spread Index: 25 | Shows low flame spread |
| Rate of Burning of Plastics | ASTM D635 | Self-extinguishing | Material stops burning by itself |
| Flammability of Plastic Materials | UL 94 | V-0 Rating | Highest rating for stopping flames |
| Non-Combustibility Classification | ASTM E136 | Not classified | Not fully non-flammable by strict rules |
Fiberglass reinforced polymer (FRP) passes big fire safety tests. It spreads flames slowly and can stop burning by itself. Some types get the best rating for stopping flames (UL 94 V-0). But, FRP does not meet the hardest rules for being non-flammable. This means it is not fully fireproof, but it is much safer than many plastics.
Many builders pick fibreglass because it can handle heat and fire well. These features help keep buildings, cars, and equipment safe from fire. The physical properties of fibreglass make it a good and safe choice for many things.
Chemical Resistance
Fiberglass is very good at resisting chemicals. This makes it great for places with harsh substances. The glass fibre inside does not react with most acids or bases. PTFE-impregnated fibreglass fabrics work well with chemicals. These fabrics do not get damaged by most acids and bases. This helps them last longer in labs and chemical plants. But they cannot handle hydrofluoric acid or hot phosphoric acid.
Many companies use fibreglass for tanks, pipes, and linings. It keeps its shape and strength with strong chemicals. This helps save money on repairs and makes equipment last longer. Engineers pick fibreglass when they need something tough for chemicals.
Note: Always check which type of fibreglass you need. Some types protect better against certain chemicals.
Electrical Insulation
Fiberglass is great at stopping electricity from passing through. This keeps people and equipment safe from shocks. The glass fibre and resin do not let electricity flow. That is why fibreglass is used in panels, boards, and cable trays.
The table below shows how well fibreglass insulates:
| Material / Thickness | Dielectric Strength (V/mil) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass (NEMA GPO-3) 0.031″ thick | ~750 V/mil | Exceeds NEMA minimum of 300 V/mil |
| Fiberglass (NEMA GPO-3) 0.062″ thick | ~700 V/mil | Exceeds NEMA minimum |
| Fiberglass (NEMA GPO-3) 0.125″ thick | ~550 V/mil | Exceeds NEMA minimum |
Fiberglass laminates keep their strength even after high heat. They work well for up to 300 hours at 270°C. This means they are good for tough electrical jobs. ASTM D-149 is the test for dielectric strength. Fibreglass insulation works better than many other hard materials. This makes it a safe choice for electricity.
Thermal Insulation
Fiberglass insulation does not let heat move through easily. It is made from melted glass spun into thin fibers. These fibers trap air and slow down heat. This makes fibreglass insulation a top pick for buildings.
Low thermal conductivity means heat does not pass through much. This keeps homes warm in winter and cool in summer. People use less energy for heating and cooling. How well fibreglass works depends on fiber size, density, and temperature. Builders use it to save energy and lower bills.
Fiberglass composites also block heat better than metals. The glass fibre and resin stop heat from moving. That is why fibreglass is used for insulation in many places. Its thermal property, plus strength and corrosion resistance, make it popular in construction and industry.
Tip: Putting fibreglass insulation in walls, roofs, and floors saves energy and keeps rooms comfortable.
Lightweight

Fiberglass is known for being very light. This is because it has low density. Most fibreglass products have a density close to 2.54 g/cm³. The mix of glass fiber and resin makes it light. Makers can change how dense it is by using different fibers or resins.
- Fiberglass is much lighter than metals like steel or aluminum.
- Engineers pick light fibreglass to make parts easy to move and put in place.
- In cars, trucks, planes, and boats, light fibreglass helps lower the total weight.
Lighter vehicles use less fuel and can carry more stuff. This means better fuel use and more space for cargo. Even though it is light, fibreglass stays strong and lasts long. This makes it great for car and plane parts. Being light also helps shape and move fibreglass in factories.
Tip: Using light fibreglass can cut shipping costs and make setup faster.
Corrosion Resistance
Fiberglass does not rust or corrode, even in tough places. This makes it a top pick for harsh jobs. Metal parts in these places need new coatings every year or two. Fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP) needs less care and lasts longer.
Sometimes, FRP needs a UV sealant for outdoor use. This sealant is just for extra safety and does not need much work. Fiberglass resists rust, so it costs less to keep up. In boats and ships, rust causes lots of damage and costs. Using fibreglass helps stop these problems and keeps the gear safe.
Fiberglass also stands up to many chemicals, so it lasts longer. This is why it works well for tanks, pipes, and things that touch saltwater or chemicals. Its strength and rust resistance help fibreglass last and work well in hard jobs.
Dimensional Stability
Dimensional stability means a material keeps its shape and size. Fiberglass does this well, even with changes in heat or wetness. The glass fiber inside helps stop swelling and shrinking.
- Water can get into fibreglass, especially with some plastics.
- Water moves in slowly, which is called Fickian diffusion.
- When more water gets in, strength and stiffness go down.
- Swelling depends on the way the fibers go, so shape changes are not the same everywhere.
- After drying, fibreglass can get some strength and stiffness back because the matrix gets more crystals.
Heat and time can also change how stable fibreglass is. High heat and long use can lower its strength. But after drying again, it often gets most of its strength back. This makes fiberglass a good pick for things like building panels, car parts, and factory gear.
Note: Fiberglass keeps its shape and strength in normal use, but lots of water or heat can cause small changes.
Fibreglass Uses Advantages
Fiberglass has many good points, but it also has some problems. These problems can change how it is used in different jobs. Knowing about these issues helps builders and engineers pick the right material.
- Anisotropic Behavior: Fiberglass is not strong in the same way in every direction. The glass fiber inside gives it strength in certain ways. This makes designing with it harder than with steel, which is strong all over.
- Brittleness: Fiberglass can crack or snap if hit hard or if the temperature changes fast. It does not bend much before it breaks. This means it can fail suddenly in some cases.
- Low Modulus of Elasticity: Fiberglass can bend or bulge when heavy things press on it. It does not go back to its old shape as well as steel. This can be a problem for pipes underground or tanks under pressure.
- Connection Challenges: Making strong joints with fibreglass takes extra care. Bolts or screws can make weak spots. Glue works well, but the surfaces must be clean and the work must be done carefully.
- Chemical Sensitivity: The resin in fibreglass must match the chemicals it will touch. If the wrong resin is used, the fibreglass can break down. Some resins let chemicals or gases get through, which can hurt the inside or make it weaker.
- Heat Sensitivity: High heat can make fibreglass soft or weak. The resin gets softer when it gets hot, so it loses strength. This means it cannot be used in very hot places.
- Poor Alkali Resistance: In places with lots of alkali, like concrete, fibreglass can wear away. This makes it not stick as well and not last as long.
- Lower Shear Strength: Fiberglass is not as good as steel at handling sliding or twisting forces. This means it cannot be used for some parts that need to resist these forces.
- Poor Ductility: Fiberglass does not stretch or bend much before it breaks. This makes it not a good choice for places with earthquakes or where things move a lot.
- Thermal Expansion Issues: Fiberglass and other materials grow at different rates when they get hot. This can cause leaks or problems where they join together.
- Installation Complexity: Workers need special skills to put fibreglass in the right way. If they make mistakes, the fibreglass can have weak spots or break.
- Standardization and Cost: There are not as many rules for using fibreglass as there are for steel or concrete. This can make projects less certain. Sometimes, fiberglass costs more to buy and put in than other materials.
Note: Engineers use bigger safety margins with fibreglass because we do not have as much long-term data. Good planning and skilled workers help lower the risks from these problems.
Benefits of Fiberglass
Cost-Effectiveness
Fiberglass gives good value to many businesses. The starting price for fibreglass hulls can be more than aluminum. But the total cost often evens out over time. Aluminum hulls are cheaper at first, but custom shapes can make them cost more. Fiberglass is easy to shape and looks fancy, which adds value later. Many builders pick fibreglass because it can be made into cool shapes and smooth surfaces. These things attract people who want nice looks and good use.
It is hard to compare fibreglass and steel costs because there is not much data. But fiberglass does not rust, so you do not pay for rust fixes. This saves money in the long run. Fiberglass needs less care and lasts longer. These things help balance out the higher starting price.
Low Maintenance
Fiberglass items need less care than most other materials. Outdoor fibreglass things like doors and fabrics only need simple cleaning. Wash them with mild soap and water to keep them clean. Do not use rough tools. Use soft cloths or sponges instead. Put on a topcoat every few years to protect from the sun and water.
Here are some tips for fiberglass care:
- Check every month for cracks, chips, or color changes.
- Clean every season and look for mold or water spots.
- Add UV-protective coats every 2–3 years.
- Keep fibreglass in cool, dry places away from the sun.
- Use shades or awnings to block direct sunlight.
These easy steps help fiberglass stay nice and work well. People like that it does not need much work. Needing fewer repairs and coatings is another reason fiberglass is a smart pick for busy places.
Longevity
Fiberglass stays strong for many years, even in tough places. It does not rust, rot, or get hurt by chemicals. This means it works where other materials do not. Builders and engineers use fiberglass for jobs that need to last a long time. Things made from fiberglass keep their shape and strength for years.
Because fiberglass lasts so long, you do not have to replace it often. This means less waste and more savings over time. Many businesses trust fiberglass because it works well in hard jobs. Its strength, stability, and low care needs make it a good choice year after year.
Tip: Using fiberglass outside or in busy places helps things last longer and saves money and time.
Design Flexibility
Fiberglass gives engineers and makers lots of design choices. It can be shaped into many forms and sizes. Makers can mold it into curves, angles, or flat pieces. They can make thin sheets or thick beams. This helps designers build things that fit just right.
Fiberglass works for simple or tricky parts. It can have smooth or bumpy surfaces. Makers use it to add special colors and patterns. This lets products match brands or blend in. Fiberglass can also have details like grooves or raised logos.
Many jobs use fibreglass because it is easy to shape. Car makers use it for cool car bodies. Boat builders make hulls that move well in water. Architects use it for bold building fronts and light panels. Sports gear makers design equipment that is strong and light.
Fiberglass can mix with other materials for more choices. Makers add foam for warmth or extra strength. They can layer it with carbon fiber for tough jobs. This mix gives the right balance of weight, strength, and bend.
Tip: Fiberglass lets designers try new ideas without spending a lot. They can make test models fast and change designs when needed.
The design freedom of fiberglass is a big plus. It helps companies keep up with new needs and stay ahead.
Environmental Impact
Making and throwing away fiberglass affects the environment in many ways. The industry has problems, but is working on fixes.
- Fiberglass and other composites are tough to recycle. Their mix of parts makes recycling hard and costly.
- The industry is trying to reuse materials again and again. This is called a circular economy.
- Using plant-based resins and fibers can make fiberglass greener.
- New ways to make fiberglass, like saving energy and reusing scraps, help cut waste.
- Fixing and making products last longer means less need for new stuff.
- Better recycling, like chemical recycling, could help with waste in the future.
A scientific study looked at fiberglass and carbon fiber. It found that carbon fiber takes more energy to make. But new recycling, plant-based materials, and microwave tech could help carbon fiber be better for the earth than fiberglass one day. Recycling that saves the fibers is the best way to lower the impact of these materials.
Fiberglass lasts a long time, so there is less waste. Its strength means fewer replacements and less trash. The industry keeps working to make fiberglass better for the planet. As recycling gets better, fiberglass could become even more earth-friendly.
Types of Fiberglass Material
Mats
Fiberglass mats are a very common type of fiberglass. Makers use short glass fibers and stick them together with resin. The fibers point in many directions, so mats are strong everywhere but not as strong as other types. Mats let resin move through them easily. This helps when making shapes with curves or corners. Mats are good for making tricky shapes and covering tight spots.
Many companies use mats as the first layer when building things. Mats stop the texture from showing on the outside. They are also the cheapest kind of fiberglass. Builders often use mats with woven fabrics to make things thicker and help layers stick together. People use mats for car panels, boat bottoms, and making molds.
Tip: Mats work best with polyester and vinyl ester resins because of how the binder works.
Cloth
Fiberglass cloth is made by weaving glass fibers together. There are different ways to weave the cloth, like plain, 4-harness satin, and 8-harness satin. Each weave has its good points. Satin weaves are stronger and bend more than plain weaves. This makes them easier to wrap around curves.
Cloth is stronger and lighter than mats. People pick clothes when they need both strength and bending. It is used in airplanes, sports gear, and light panels. Cloth lets resin move in, so it sticks well during making. Designers use cloth for strong, light parts that need to bend or handle stress.
Here is a table that compares mats and cloth:
| Fiberglass Form | Structure Description | Mechanical Properties | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mats | Random short fibers with binder | Uniform, lower strength | Complex shapes, automotive, boats |
| Cloth | Woven fabric, various weaves | Higher strength, flexible | Lightweight parts, curved surfaces |
Chopped Strand
Chopped strand is another key type of fiberglass material. Makers cut long glass fibers into short pieces to make it. These short fibers are pressed into mats or mixed with resin. Chopped strand mat has fibers pointing in all directions and held by a binder. This makes it act the same no matter which way you pull it.
Chopped strand lets resin move through it well. It fits into molds and fills small spaces easily. But it is not as strong as woven types. Builders use chopped strand as a base or to make things thicker. It works for car parts, boat bottoms, and places where shape matters more than strength.
Note: Chopped strand mat is cheap and simple to use. It is best when mixed with other fiberglass types to make things stronger.
Roving
Roving is a main type of fiberglass used in many jobs. It is made of long, unbroken glass fibers bundled together. These bundles look like thick yarn or rope. Factories use roving when they need strength in one direction. This makes it different from mats or chopped strand forms.
Roving is good for making strong, light parts. Factories use it in filament winding and pultrusion. In filament winding, machines wrap roving around a mold to make pipes or tanks. Pultrusion pulls roving through resin and a hot die to make beams or rods. These ways help make parts that are strong but not heavy.
Builders pick roving for boat hulls, wind turbine blades, and panels. The long fibers make these things tougher. Roving also helps make big parts fast. It can be used with other fiberglass types to make things work better.
Tip: Roving is simple to use and can be mixed with mats or cloth for special strength and bending.
The different kinds of fiberglass, like roving, let engineers choose what works best. Roving is great when a job needs straight, strong fibers and quick making.
Specialty Forms
Specialty forms of fiberglass are made for special jobs in advanced fields. These include woven tapes, braided sleeves, and 3D fabrics. Each one has features for certain uses.
- Woven tapes are thin strips of fiberglass. They make edges, seams, or joints stronger in composite parts.
- Braided sleeves stretch to fit over pipes or rods. They give even strength around tricky shapes.
- 3D fabrics have fibers woven in three ways. This makes them extra strong and steady for tough jobs.
Some specialty types use special glass mixes or coatings. For example, E-glass stops electricity, while S-glass is stronger. Other forms are surfacing veils, which make smooth finishes, and mesh, which adds support in building panels.
Engineers use specialty forms when regular fiberglass does not work for the job. Makers of planes, cars, and sports gear use these advanced materials. Specialty forms help make things lighter, stronger, and longer-lasting.
Note: The many types of fiberglass give designers lots of choices. They can pick the right material for any job, from small fixes to high-tech making.
Applications of Fiberglass

Construction
Builders use fiberglass more than any other group. They pick it because it is strong, lasts long, and can bend without breaking. Fiberglass helps make buildings, bridges, and roads stronger and last longer.
- Fiberglass fabric goes into concrete for bridges, buildings, and roads. It makes them stronger and helps stop cracks.
- Workers put fiberglass in walls, roofs, and floors for insulation. This keeps buildings warm or cool and quiet inside.
- Old buildings get fixed with fiberglass. It makes them stronger and helps them last longer.
- Big projects like highways, tunnels, and airports use fiberglass. It is strong, does not rust, and is easy to put in.
- Mesh made from fiberglass stops walls from cracking and keeps water out.
Most fiberglass is used in building things. Builders use it in panels, roof plates, and wall covers. These keep water and heat away from wood, steel, and concrete. Fiberglass also makes buildings look better and last longer. Cities are growing fast, so more fiberglass is needed. New rules for green buildings mean more fiberglass is used. Building codes now allow fiber-reinforced polymer, so fiberglass is even more popular.
Note: Fiberglass is great for building because it does not rust, lasts a long time, and helps make green buildings.
Automotive
Car makers use fiberglass for many car parts. It is better than steel and aluminum in many ways.

- Fiberglass is used for hoods, bumpers, doors, and belts. It is also in brake pads, clutches, tires, trains, and trams.
- Fiberglass is much lighter than steel. This helps cars use less gas and go faster.
- Fiberglass does not rust, so car parts last longer and need less fixing.
- It stands up to chemicals and does not wear out fast.
- It does not burn easily, which makes cars safer in crashes.
- Fiberglass parts are smooth, so cars move through the air better.
- It is strong but not heavy, so cars are safer and lighter.
- Fiberglass can be shaped into many forms for cool car designs.
Fiberglass needs less care than steel and does not break down as fast. Tires with fiberglass give a smoother ride and last longer. Its fire safety and smooth finish are good for fast trains and buses. Fiberglass is cheap and good for the Earth. It lasts 30–50 years and does not need much work. These things make it a top pick for trailers, car bodies, and many other car uses.
Aerospace
Airplane makers use fiberglass for many parts inside and outside. They like it because it is light, strong, and tough.
- Airplane bodies use fiberglass to weigh less. This helps planes use less fuel and go farther.
- Wings are stronger with fiberglass, so planes are safer.
- Seats and panels inside planes are light and last long with fiberglass.
- Radomes, which cover radar, use fiberglass. It lets radar waves go through with no problem.
Fiberglass weighs less than metal, so planes can carry more people or things. Its strength helps planes handle flying stress. Fiberglass does not rust or wear out fast, so parts last longer. It can be shaped into smooth, fast shapes for better flying. It also protects planes from bird hits, hail, or flying bits.
Tip: Using fiberglass in planes makes them safer, better, and last longer.
Marine
Fiberglass is very important for boats. Boat makers like fiberglass because it is strong and light. These features help boats last longer in the ocean. Fiberglass keeps boats safe from saltwater and sun. It does not break or crack easily in bad weather. The material stops water from getting inside the boat. This helps stop rot and keeps wires safe. Fiberglass also blocks salt, sunlight, and sea animals. This makes boats last longer and look good. The smooth surface helps boats move fast in water. Boat makers can shape fiberglass into many cool designs.
Different resins and fiberglass types are used for boats. Polyester resin is common and strong. Vinylester resin keeps out water better. Epoxy resin is the best, butit costs more. E-glass is the usual fiberglass cloth. S-glass is stronger for hard jobs. Picking the right resin and fiber makes boats safer or faster.
Fixing damage fast keeps boats safe and strong. Repairs to the outside or inside are important. Fiberglass boats are a good mix of price, strength, and how well they work. This is why many people pick them for the sea.
Tip: Check your fiberglass boat often and fix problems quickly. This helps your boat last longer and stay safe.
Consumer Goods

Fiberglass is used in many things we use every day. Its special features make it popular with makers and buyers.
- Sports gear like surfboards and skis uses fiberglass. It makes them strong and light. These things need to handle bumps without breaking.
- Furniture makers use fiberglass for cool chairs and tables. The material lets them make bold shapes and smooth surfaces.
- Many home devices have fiberglass parts inside. It keeps them safe from heat and electricity.
- Fiberglass does not rust, so things last longer even if they get wet.
People like fiberglass products because they are easy to use. They are light, so you can carry them easily. They do not break fast, even if you use them a lot. Fiberglass keeps you safe from heat and shocks. This makes it a good choice for many products.
Note: Fiberglass lets designers make things that look good and work well.
Industrial Equipment
Factories use fiberglass for many machines and tools. Fiberglass is strong, safe, and easy to shape.
Fiberglass stops electricity from passing through. This keeps workers and machines safe. It does not soak up much water, so it does not get moldy. It stands up to most chemicals and does not rust. Fiberglass is lighter than steel but still very strong. This makes it easy to move big machines.
Makers can shape fiberglass into many forms and sizes. They put glass fibers and resin together to make tough parts. This lets them make special shapes for each job. Fiberglass stays strong even when it gets hot or cold. Some products mix fiberglass with other things to stop fires.
Factories can be wet or full of chemicals. Wood can rot and steel can rust, but fiberglass does not. This keeps machines safe and lowers repair costs. Water plants, oil rigs, and chemical factories all use fiberglass.
Tip: Using fiberglass in factories means safer, stronger, and better machines.
Sports Equipment

Fiberglass is very important in sports gear. Makers pick fiberglass because it is strong and light. This helps athletes do better and use their gear longer. Fiberglass has a high strength-to-weight ratio. Sports gear can take hard use, but does not get heavy.
Many sports use fiberglass to help players do well. In water sports like surfing and kayaking, fiberglass makes boards and boats lighter. This makes them easier to move and control. Athletes can go faster and turn more easily. Fiberglass bends, so makers can make cool shapes and smooth designs. These things help people go faster and steer better on water.
Winter sports use fiberglass, too. Skis and snowboards have fiberglass layers for more energy and control. Skiers and snowboarders feel steadier and can turn better. Fiberglass helps these things last longer, even in tough weather.
Racket sports like tennis and badminton use fiberglass to cut down on shaking. Players feel less shock in their hands, so it is more comfortable. Fiberglass lets racquets have bigger sweet spots without getting heavy. This helps players hit better and have more fun.
Fiberglass lets makers try new ideas in sports gear. They can make special shapes and custom gear for athletes. New fiberglass mixes let them add smart things, like sensors that track how you play. Some companies use green fiberglass to help the planet. Now, athletes can get gear made just for them.
Tip: Fiberglass makes sports gear last longer, work better, and feel nicer to use. Its special features make it a favorite for many sports.
More sports gear uses fiberglass every year. Its mix of strength, lightness, and bending makes it great for new ideas and better play. As tech gets better, fiberglass will stay important in sports gear.
Why Choose Fiberglass?
Versus Metals
Many companies look at fiberglass and metals before picking a material. Steel and aluminum are strong, but they are heavy. Fiberglass is much lighter. This helps cars and planes use less fuel. Lighter parts are easier to move and ship. This saves time and money when putting things together. Fiberglass does not rust or break down in bad weather. Metals need paint or care to stop rust. Fiberglass needs less work to finish, so it is faster to make. It also blocks noise better than metal. This helps keep buildings and cars quieter. Fiberglass can be shaped into tricky forms more easily than metals. This lets people make new and cool designs.
Note: Picking fiberglass instead of metals can mean less pollution, fewer repairs, and faster setup.
Versus Plastics
Plastics are used a lot because they are light and easy to shape. But fiberglass is stronger than most plastics. This makes it better for heavy or tough jobs. Plastics are lighter, but they may not last as long outside or with chemicals. Fiberglass stands up to bad weather and harsh stuff better. It keeps its shape and strength for a long time. Plastics can be made fast in large amounts. Fiberglass takes longer and needs more skill to make. Fiberglass costs more than plastics, but it lasts longer and works better for hard jobs. New plastics are getting stronger, but fiberglass is still best for strong parts.
| Feature | Fiberglass | Plastics |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Higher | Lower (improving) |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Good |
| Moldability | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Production Speed | Slower | Faster |

When to Use Fiberglass
The best material depends on what the job needs. Fiberglass is great when you need strength and shapes that do not rust. It works well in building cars, boats, and planes. Use fiberglass if you want to make things lighter and save fuel. It is also good for jobs that need to last a long time and need little fixing. If you need lots of cheap parts, plastics might be better. For tough jobs with bad weather or chemicals, fiberglass is often the best pick.
Tip: Pick fiberglass if you want strong, long-lasting, and flexible designs. It is a smart choice for many new projects.
Fiberglass Safety and Handling
Health Considerations
Fiberglass is helpful, but it can be risky if not handled correctly. When you cut or sand it, tiny glass fibers can come off. These fibers can bother your skin, eyes, and lungs. People sometimes get itchy or get rashes after touching fiberglass. Breathing in the fibers can make you cough or have a sore throat. It can also make it hard to breathe. The risk is higher if you work in small spaces with little fresh air.
The table below lists health problems and signs:
| Exposure Area | Possible Effects | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Skin | Irritation, rash | Itching, redness |
| Eyes | Irritation | Redness, watering |
| Lungs | Respiratory discomfort | Coughing, sore throat |
Note: Most health groups say fiberglass does not cause cancer in people. Still, you should not breathe in dust for a long time.
Safe Use Tips
Handling fiberglass the right way keeps people safe. Experts say to wear personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with it. These steps help lower the risk:
- Wear long sleeves, gloves, and pants to cover your skin.
- Use safety goggles or glasses to protect your eyes.
- Wear a dust mask or respirator so you do not breathe in fibers.
- Work where there is fresh air or use fans to move air out.
- Clean up dust with a vacuum that has a HEPA filter.
- Wash your hands and skin with cool water after touching fiberglass.
- Change your clothes and take a shower after work to get rid of fibers.
Tip: Do not rub your skin or eyes if they itch. Rinse with water first to wash away fibers.
Disposal and Recycling
Throwing away fiberglass needs care to keep people and nature safe. Most places say fiberglass is not dangerous waste, but do not put it in normal recycling bins. Put scraps and dust in sealed bags before throwing them out. This stops fibers from getting into the air.
Some companies recycle fiberglass by grinding it up for cement or asphalt. Special recycling centers take old fiberglass boats, panels, or insulation. They use the material to make new things, which helps keep trash out of landfills.
♻️ Callout: Always check your local rules before throwing away fiberglass. Safe disposal helps protect people and the environment.
Fiberglass is special because it is strong and light. It also lasts a long time. Engineers like that it does not burn or get hurt by chemicals. It does not rust either. Many jobs use fiberglass, like building, cars, and sports. People need to be careful when working with it. There are safety steps to help keep everyone safe. Fiberglass has some problems, but the good things are more important.
Tip: Fiberglass is a smart pick for projects that need tough, lasting materials.
FAQ
Fiberglass is used most in building, cars, and boats. Builders use it for insulation and panels. It is also used to make things stronger. Makers pick it because it is strong and light. It does not rust or break down easily
Fiberglass can bother your skin, eyes, and lungs. You should wear gloves, long sleeves, and a mask. Wash your skin with cool water if you touch it. Wearing safety gear helps keep you safe.
It is hard to recycle fiberglass. Some special places grind it up for cement or roads. Most local recycling centers do not take it. Always check your local rules before throwing it away.
Fiberglass can last for 30 years or more. It does not rust, rot, or get hurt by chemicals. Checking it often and fixing small problems helps it last longer.
Fiberglass does not catch fire like many plastics. The glass fibers do not burn at all. Some resins might burn, but special additives help stop fire. Always look at the fire rating for each product.
Fiberglass can crack if hit hard. It does not bend much before it breaks. High heat can make it weaker. You need skilled workers to put it in. Recycling is still not easy.
Makers can add color when they make fiberglass. You can also paint or coat it after it is made. The surface must be prepared well for the paint to stick and look smooth.





