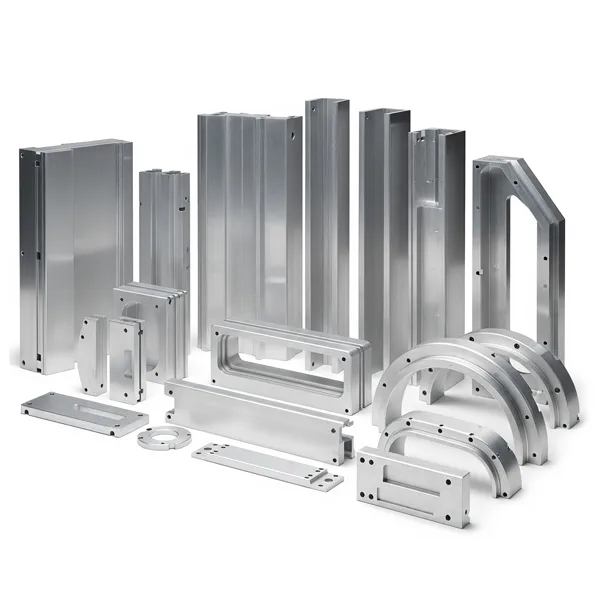
When your project requires metal parts, do you choose die casting or CNC machining? AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. provides expertise in die casting and CNC machining to help you choose the right manufacturing process, taking into account product appearance requirements, cost, raw materials, quantity, part complexity, precision, and delivery cycle.
| Process | Typical Lead Time | Cost Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | 1-2 weeks | No tooling cost; higher cost per single part |
| Die Casting | 3-5 weeks | High upfront tooling cost; more cost-effective for large production runs |
Key Takeaways
- Die casting is suitable for the production of large quantities of parts, which greatly improves production efficiency and can effectively reduce the production cost of products.
- Thin-walled parts and internal components that require high precision standards can be easily produced by die casting.
- Die casting manufactured parts have a good surface finish and low post-processing operation costs.
- Die casting has a limited selection of materials to work with and is not suitable for ferrous metals and metal alloys with very high melting points.
- The cost of casting molds is expensive, the mold production cycle is long, and it is difficult to manufacture large parts.
- CNC machining can produce very precise parts. The ability to start making parts quickly makes it suitable for small to medium sized orders, as well as for making prototypes.
- CNC machining designs can be easily changed without the need for molds. It allows precise control of the cutting tool to produce parts with tight tolerances and excellent repeatability.
- CNC machining requires skilled operators and programmers to operate and maintain the machine, increasing labor costs and additional maintenance costs.
- CNC machining may not be possible for some products with very complex structures.
- Both die casting and CNC machining play an important role in a wide range of applications, from automotive, aerospace, and telecommunications, to medical devices, electronics, and consumer products.
Table of Contents
Appearance
Die Casting Finish
Typical Results
Die casting makes parts by pushing hot metal into a mold. This way, you can get complex shapes fast. The surface of these parts often has fine lines from the mold. You might see small flaws in cooling. There can be a rough feel or seams where the mold joins. These marks are normal for die cast parts.
Post-Processing
You can make the part look better with extra steps. People often use sand or shot blasting, surface grinding, trimming flash, and heat treatment. These steps help remove rough spots and smooth out seams. They also make the part look nicer. Many industries use these methods to meet higher looks standards.
| Surface quality level | Surface roughness Ra(µm) |
| YB1 | 1.6 |
| YB2 | 3.2 |
| YB3 | 6.3 |
| YB4 | 12.5 |
CNC Machining Finish
Surface Quality
CNC machining uses computers to control cutting tools. This gives a very smooth and exact surface. The tools make clean lines and sharp edges. Most CNC-machined parts do not need much extra work. The part looks shiny and neat right away, and some materials can also be processed to produce a mirror effect.
Surface roughness of CNC machining
| Surface finish grade | Ra(µm) | Surface roughness |
| 1 | 50 | very rough |
| 2 | 25 | rough |
| 3 | 12.5 | rougher |
| 4 | 6.3 | medium |
| 5 | 3.2 | smoother |
| 6 | 1.6 | smooth |
| 7 | 0.8 | very smooth |
| 8 | 0.4 | super smooth |
| 9 | 0.2 | smoothest |
Customization
CNC machining lets you pick the surface finish you want. You can choose matte, glossy, or textured looks. This helps you match the part’s look to your project.
Visual Differences
You can see clear differences between die cast and CNC machined parts.
| Factor | Die Casting | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Often needs extra steps like sand/shot blasting, surface grinding, trimming flash, and heat treatment to look better | Usually looks great right away because of sharp cutting tools, so you do not need much extra work |
| Tolerances | Usually looser, about ±0.1 mm or more, so you may see size changes and surface flaws | Very tight, up to ±0.0002″, so the part looks smoother and more exact |
Die cast parts can look rough and have small marks from the mold. You often need extra steps to make them smooth. CNC machined parts look smoother and more exact from the start. You see fewer flaws and sharper details.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. uses modern machines and skilled workers to make great finishes for both die casting and CNC machining. You can trust their team to help you get the best look for your parts.
Cost & Volume
Die Casting Costs
Tooling
When you pick die casting, you pay a lot at first for the mold. This mold shapes the metal into your part. The tooling can cost $20,000 or even more. The price depends on how big and complex your part is. But this cost gets shared by every part you make. If you make thousands of parts, the cost for each one drops fast.
Per-Part Savings
Die casting saves money when you make lots of parts. After you have the mold, each part is much cheaper to make. For example, one company changed from machining to die casting and saved 83% in total costs. Making better molds and using modular dies can also cut costs. These changes help by making less waste and speeding up work.
| Case Study / Example | Numerical Evidence | Cost Effectiveness Aspect |
|---|---|---|
| Company switching from machining to die casting | 83% cost reduction | Big savings when making many parts with die casting |
| Project Engineering GmbH (HPDC process optimization) | 3% price reduction | Faster cycles and less scrap by changing the process |
| Tooling cost amortization principle | Volume dependent | More parts made means lower cost for each, so die casting is good for big orders |
CNC Machining Costs
Setup
CNC machining costs less to set up. You do not need pricey molds. You only pay to program the machine and set up tools. This makes CNC machining a good pick for samples or small orders.
Unit Price
Each CNC machined part costs more than a die cast part. This is true when you order many parts. The price for each part stays about the same. There is no mold to spread the cost over many pieces. For orders under 1,000 units, CNC machining is often the better choice.
Volume Break-Even
The best process depends on how many parts you want. Die casting is best for making lots of parts. CNC machining works well for small or medium amounts. The break-even point is usually around 1,000 units. At this point, die casting’s lower part cost beats the high tooling price.
| Process Comparison | Tooling/Setup Cost | Per-Part Cost at High Volume | Break-Even Volume | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | $200 | N/A | Below 1,000 units | Best for samples and small orders |
| Die Casting (HPDC) | $20,000 | Much lower | ~1,000 units | Great for making many parts |
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. can help you pick the best way to save money. Their team can handle both small and big orders. They make sure you get the most for your project.
Material
Die Casting Options
Common Alloys
Die casting uses a few main metals. The most used are aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Aluminum alloys are strong but not heavy. Zinc alloys are good for small and detailed parts. Magnesium alloys are even lighter than aluminum. They are used in cars and electronics. These metals melt at lower heat, so they work well for die casting.
| Alloy | Material Grade | Main Ingredients | Melting point (°C) | Very light weight and good castability. Ideal for weight-sensitive applications. Used in aerospace, automotive and electronics (e.g. handheld devices). |
| Aluminum Alloy | A380、A360、A390、A413、ADC12 | Al、Cu 、Si、Mg | 577 – 660 | Lightweight, corrosion resistant, high strength, good processability. Widely used and cost-effective. Used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer products |
| Magnesium Alloy | AZ91D, AM60B, AS41B | Mg、Al、Zn | 632 – 650 | Very light weight and good castability. Ideal for weight-sensitive applications. Used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics (e.g,. handheld devices). |
| Zinc Alloy | Zinc Alloy 2, #3, #5, #7, ZA8, ZA27 | Zn、Al、Cu、 | 381-419 | Excellent castability, low melting point, suitable for complex designs. High cost performance. Used in electronics, hardware, toys and automotive parts. |
| Copper Alloy | C85700, C93200 | Cu、Zn、Sn | 900-1083 | High strength, excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Durable. Used in pipes, electrical connectors, marine components and bearings. |
| Tin alloy | – | Sn、Cu、Pb、Sb | 170-230 | Low melting point, good fluidity, corrosion resistance. Easy to cast. Mainly used for decorations, figurines and jewelry. |
| Lead alloy | – | Pb、Sn | 183-327 | Soft, low melting point, good corrosion resistance. Used in radiation shielding, previously used in batteries (limited by toxicity concerns). |
| Tin-based alloy | – | Sn、Cu、Sb | 232 | Low melting point, good corrosion resistance. Easy to cast at low temperatures. Used in electronics, jewelry and special applications. |
Limits
Die casting is best for metals that melt easily. You cannot use steel or titanium because they need more heat. Some alloys can react with the mold or cause surface problems if you do not pick the right one. You also have to think about rust. Copper alloys can rust faster when it is hot or in tough places. Surface treatments can help protect these parts and make them last longer.
Note: Surface finishing is very important for die cast metals. Coatings and treatments can protect your parts and make them look better.
CNC Machining Options
Metals
CNC machining lets you use many kinds of metals. You can use aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass, copper, titanium, and more. Aluminum is light and easy to cut. It is used a lot in cars and planes. Steel is strong and tough. Stainless steel does not rust, so it is good for food and medical tools. Brass and copper are easy to cut and carry electricity well. Titanium is strong and light, so it is used for tough jobs.
Plastics
CNC machining also works with many plastics. ABS and polycarbonate are used for test parts because they are easy to shape and cheap. PEEK is a special plastic that can withstand heat and chemicals. It is used in medical and plane parts. CNC machining can also cut composites like carbon fiber and fiberglass. These are strong and light.
- Stainless Steel
- Aluminum Sheet
- Titanium
- Copper
- Brass
- Other Steel Alloys
- Plastic
Choosing by Material
First, think about what your part must do. Think about strength, weight, heat, and price. If you need a light part for a car, aluminum or magnesium is a good pick. If you need a part that does not rust, use stainless steel or coated die cast aluminum. For electric parts, copper or brass is a good choice.
Engineers use tools and software to help pick the right material. You can ask experts, use databases, or try special programs to compare choices. Many companies use these tools to balance price, how well the part works, and how green it is.
| Process | Metals Supported | Plastics Supported | Composites Supported | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | Aluminum, Zinc, Magnesium | No | No | Automotive, electronics, appliances |
| CNC Machining | Aluminum, Steel, Brass, Copper, Titanium, Stainless Steel, and more | Yes | Yes | Aerospace, medical, prototyping |
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. has many materials for both die casting and CNC machining. Their experts can help you pick the best material for your project. They make sure your parts work well, cost less, and last a long time.
Complexity
Die Casting Shapes
Intricate Details
Die casting can make parts with very tricky shapes. You can add thin walls and hollow spots. The hot metal fills every part of the mold. This gives you sharp edges and small details. You can put many features into one part. This means you do not need to put together lots of pieces. Die casting is good for parts that must be light and strong, like in cars or electronics.
Here is a table that shows what die casting can do for complex shapes:
| Design Complexity Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Thin Wall Capability | Makes walls as thin as 0.5mm (0.020 inches) for lightweight, detailed parts |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Holds precision within ±0.005 inches, so parts fit together well |
| Complex Geometries | Forms undercuts, curves, internal passageways, and hollow sections |
| Advanced Tooling Features | Uses slides, lifters, and side-actions for tricky shapes |
| Mold Filling Characteristics | High fluidity fills even the smallest mold cavities |
| Part Consolidation | Combines several components into one strong casting |
| High-Pressure Injection | Up to 20,000 psi ensures complete filling and less porosity |
Cavities
Die casting can make deep holes or channels in parts. Special tools help make these shapes. Vacuum die casting helps stop air bubbles. This makes the part stronger. It is good for parts that carry wires or fluids inside.
CNC Machining Shapes
Precision
CNC machining gives you very exact parts. You can make parts with tight fits. Some machines can cut shapes with just a ±0.0002 inch difference. Multi-axis CNC machines can cut tricky 3D shapes in one go. This gives smooth surfaces and sharp corners. Automated CNC machines and sensors help every part come out the same.
- CNC machines make tight fits and tricky shapes.
- Multi-axis machines need fewer setups and are more exact.
- Automated systems help lower mistakes and make better parts.
- Special CNC types, like EDM and water jet cutters, can cut hard shapes.
Simpler Forms
CNC machining is also good for easy shapes. You can quickly make flat plates or blocks. It is great for test parts or small orders. You can use many kinds of materials. This gives you more choices for your project.
Best Fit by Design
The best process depends on your part’s shape. If you need many features, thin walls, or deep holes, die casting is often best. It is good for making lots of tricky parts. If you need very tight fits or custom shapes, CNC machining is better. It is great for making special parts, even if you only need a few.
Here is a table to help you decide:
| Design Type | Best Process | Why It Fits Best |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Design | CNC Machining | Fewer components, easy shapes, high precision |
| Complex Design | Die Casting | Multiple features, thin walls, integrated parts, high volume |
| Custom/Unique | CNC Machining | Custom shapes, tight tolerances, small batches |
| Integrated Parts | Die Casting | Combines many features into one strong part |
Tip: Think about how many parts you need and how tricky your design is. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. can help you pick the best way, whether you need simple test parts or lots of complex ones.
Lead Time
Die Casting Setup
Mold Time
When you choose die casting, you need to plan for mold creation first. Making a mold takes time because it must be strong and precise. The mold must reach the right temperature before you start. For example, the fixed mold temperature should be 200 °C, and the moving mold temperature should be 220 °C. The casting temperature for liquid aluminum is about 670 °C. These settings help you get high-quality parts every time.
| Parameter | Value | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed mold temperature | 200 °C | Keeps mold stable and ready for casting |
| Moving mold temperature | 220 °C | Ensures proper mold conditions |
| Casting temperature | 670 °C | Helps metal flow and solidify correctly |
| Die time | 30 s | Maintains pressure for strong, accurate parts |
Simulation software, like MAGMAsoft, helps you test and adjust these settings before real production starts. This digital approach lets you avoid mistakes and get the mold right the first time.
Production Speed
Once the mold is ready, die casting moves fast. You can make many parts in a short time. The process uses both slow and fast injection speeds. For example, the slow injection velocity is 0.18 m/s, and the fast injection velocity is 4.5 m/s. The inner runner injection velocity can reach 48 m/s. These speeds fill the mold quickly and reduce defects. Each cycle takes about 30 seconds, so you can produce hundreds or thousands of parts every day. Die casting is a great choice for high-volume production.
CNC Machining Speed
Rapid Prototyping
CNC machining gives you a quick start. You do not need to wait for a mold. You can send your design file, and the machine can start cutting right away. This makes CNC machining perfect for rapid prototyping. You can see your first part in just a few days. If you need to change the design, you can update the file and start again without delay.
Fast Turnaround
CNC machining also works well for small or medium production runs. The setup is simple, and you can switch between jobs quickly. You get a fast turnaround, especially when you need custom parts or changes. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. responds quickly to your requests and provides quotes within hours. Their team uses advanced machines to keep your project moving forward.
Project Timeline
You want your project to stay on track. Both die casting and CNC machining offer ways to meet your deadlines. Die casting takes longer at the start because of mold setup, but it speeds up for large production runs. CNC machining starts faster and is flexible for changes.
Modern project timelines use real-time updates and drag-and-drop editing. You can shift due dates and tasks if something changes. Milestone tracking helps you see progress and spot any delays. If a vendor is not available, you can adjust the timeline right away. This flexibility keeps your production on schedule and helps you avoid bottlenecks.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. supports your project with fast responses and flexible scheduling. Their team helps you adjust plans quickly, so you always meet your goals.
Precision
Die Casting Tolerances
Standard Accuracy
Die casting makes pretty accurate parts. Most small features can be made within ±0.1 mm. This happens because the mold, metal, and process are controlled well. Aluminum die casting uses special molds and checks for shrinkage. This helps keep parts close to the right size. If you follow industry rules and design smart, you get steady results. Die casting is good for parts that do not need super tight tolerances but still need to be the same every time.
Secondary Finishing
Sometimes, you want even better accuracy or a smoother look. You can use extra steps like machining, grinding, or polishing after die casting. These steps help you get tighter tolerances or a nicer surface. Many companies do this when they want fast die casting and also need the precision of machining.
CNC Machining Tolerances
High Precision
CNC machining is known for being very exact. You can get tolerances as tight as ±0.025 mm or even better with special machines. CNC machines use computers to control speed, tool position, and feed rate. This helps make parts that fit together perfectly. Industries like aerospace and medical need this level of accuracy for safety and performance.
Consistency
CNC machining gives you the same result every time. Machines use sensors and check each part as they work. Tools like Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) measure parts down to 0.0035 mm. This makes sure every piece matches your design. This is important when every part must be exactly the same.
| Process/Material Aspect | Tolerance/Accuracy Statistic | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| High precision CNC machining tolerance | ±0.025 mm (±0.001″) or tighter | Needs special machines and a controlled workspace |
| ISO 2768 Fine class tolerance | ±0.05 mm for dimensions ≤ 30 mm | Used for high precision machined parts |
| Typical CNC machining tolerances | ±0.13 mm (±0.005″) | Common for metals like aluminum and steel |
| Aluminum alloys (machined) | ±0.05 mm | Shows how easy and stable the material is to machine |
| Advanced machining capabilities | ±0.013 mm (±0.0005″) | Reached with top machines and stable temperatures |
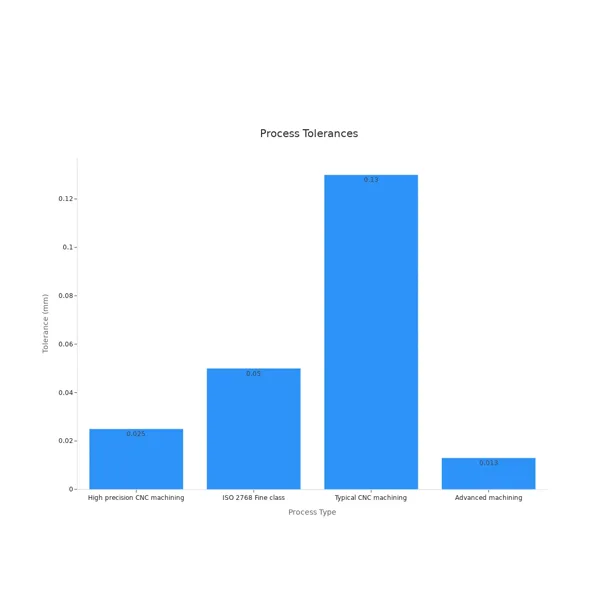
When Precision Matters
Pick CNC machining if your project needs very tight tolerances. This process gives you the best control over size and shape. Medical, defense, and car companies need these tight tolerances for safety and function. Quality certifications, like ISO 9001-2015, show a company can meet strict rules. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. has these certifications and uses advanced checks at every step. Their team uses CMMs, regular machine checks, and skilled workers to make sure every part is right.
Tip: Tight tolerances help your parts fit well, work better, and last longer. AFI Industrial’s quality system makes sure you get reliable, high-precision parts for any project.
Sustainability
Die Casting Waste
Scrap Reduction
You can make less scrap in die casting by using good molds and careful steps. High-quality molds mean fewer mistakes and less wasted metal. Many factories melt down leftover metal to use again. This means they do not need as much new metal. Reusing scrap helps save natural resources and produces less trash.
Energy Use
Die casting melts metals like aluminum and zinc with heat. This takes a lot of energy, mostly when melting and injecting metal. New die casting machines use less power because they have better insulation and smart controls. These features help save energy during work. Recycling metal also saves energy because it uses less power than making new metal from rocks.
| Environmental Impact / Energy Usage Metric | Statistic / Data Point | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Global temperature status in 2024 | Hottest year on record, exceeding 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels | Reuters |
| Increase in global greenhouse gas emissions over 30 years | 50% increase | Statista |
| Economic reliance on nature | Over 50% of global GDP depends on nature | World Economic Forum |
Note: Saving energy and making less scrap in die casting helps lower pollution and keeps the planet healthier.
CNC Machining Waste
Material Loss
CNC machining cuts parts from a solid block. This makes a lot of metal chips and shavings. You can use special tricks to waste less. Nesting and part planning help us use more of each block. Adaptive machining and lean steps also help cut down on extra waste.
- CNC machining can waste up to 30% less material than the old ways.
- New energy systems can use up to 25% less power.
- Some places cut carbon emissions by 40% by using green energy.
- Nesting and part planning help us use more material.
- Lean steps and checking work all the time help stop waste.
Recycling
Most metal chips and shavings from CNC machining can be collected and reused. Many factories use recycling systems that turn scrap into new raw material. Recycling metal uses less energy than making new metal, so it helps lower pollution. By reusing materials, you help the earth and support a system where nothing is wasted.
Eco-Friendly Choice
Both die casting and CNC machining can help the environment if you use smart steps. You can check your results against industry rules to see where to get better. Many companies now use boxes that can be reused and add green steps to their supply chains. These actions help reduce trash and lower carbon emissions.
A world study showed that companies that care about the environment and use less energy get more investors. This means being eco-friendly helps the planet and makes your business look better and stronger.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. works hard to use green steps in every part of making things. Their team recycles, saves energy, and always looks for ways to do better so you can reach your green goals.
Die casting vs CNC machining

Process Comparison
Key Differences
When you compare die casting vs CNC machining, you see that each manufacturing process has its own strengths. Die casting works best when you need many parts with complex shapes. You get lower costs per part when you make large batches. This process uses molds to shape hot metal quickly. You often see die casting in the automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries. Sometimes, you need extra steps like grinding to get a smoother finish or tighter fit.
CNC machining gives you high precision and flexibility. You can use many types of metals and plastics. This process cuts parts from solid blocks using computer-controlled tools. You get very tight tolerances, sometimes as low as 0.005 mm. CNC machining is great for prototypes, custom parts, or small to medium production runs. You can change designs quickly and start production fast.
Here is a table to help you see the main differences:
| Factor | Die Casting | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower cost for high-volume production | Higher setup costs, cost-effective for low to medium volumes |
| Precision | Good, may need post-machining for tight tolerances | High precision with tight tolerances (as low as 0.005 mm) |
| Material Options | Limited to metals like zinc, aluminum, magnesium | Broad range of materials available |
| Production Speed | Fast for large volumes | Slower, suitable for prototyping and small batches |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste due to casting process | More material waste due to subtractive process |
| Post-Processing | Often needed for surface finish or tighter tolerances | Extensive post-processing for surface finish |
| Suitable Volume | Best for large production volumes | Best for low to medium volumes or prototyping |
You should choose die casting if you want to make thousands of parts with complex shapes and strong features. You should choose CNC machining if you need high accuracy, special materials, or only a few parts.
Decision Factors
You need to think about several things before you pick a manufacturing process. Ask yourself these questions:
- How many parts do you need?
- What material do you want to use?
- Do you need very tight tolerances?
- How fast do you need your parts?
- What is your budget for setup and production?
- Do you want to change your design later?
Die casting vs CNC machining is not just about cost. It is about matching your project needs to the right process. If you need a fast start and flexible changes, CNC machining is a good choice. If you want to save money on big orders, die casting is the way to go.
Quick Guide
Checklist
You can use this checklist to help you decide between die casting vs CNC machining:
- Decide how many parts you need for your project.
- Choose the material that fits your part’s function.
- Check if your design needs tight tolerances or special shapes.
- Think about how soon you need the finished parts.
- Set your budget for both setup and per-part costs.
- Plan for any changes or updates to your design.
- Review if you need post-processing for surface finish or accuracy.
- Make sure your supplier can handle your order size and timeline.
- Ask for sample parts or prototypes if you are unsure.
- Talk to experts to confirm your choice before you start production.
Tip: A clear checklist helps you avoid mistakes and keeps your project on track.
When to Consult Experts
Sometimes, you may not know which process fits your needs best. You might have a complex design or a tight deadline. You may want to test your part in real-world conditions before full production. In these cases, you should talk to manufacturing experts.
AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. offers both die casting and CNC machining. Their team can review your design, suggest the best manufacturing process, and help you save time and money. You get fast quotes, expert advice, and support at every step. If you want to make sure your parts meet quality standards, reach out to AFI Industrial for guidance.
When picking between die casting and CNC machining, you should look at some main things. These include how the part looks, how much it costs, what it is made of, how many you need, how tricky the shape is, how fast you need them, how exact they must be, and how green the process is.
Need help? You can reach out to AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. for expert help and special answers for your next project.
FAQ
Die casting uses molds to shape melted metal into parts. CNC machining cuts parts from solid blocks using computer-controlled tools. You choose die casting for high volumes and CNC machining for precision or small batches.
Pick die casting when you need thousands of parts with complex shapes. This process lowers your cost per part for large orders. You get fast production once the mold is ready.
CNC machining can meet your higher requirements for surface smoothness.
Yes, you can. Many companies use die casting for the main shape and CNC machining for tight features or holes. This gives you both speed and high accuracy.
Die casting works best with aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys. CNC machining supports a wide range of metals and plastics, including steel, brass, titanium, and engineering plastics.
Both processes can be eco-friendly. Die casting creates less scrap, while CNC machining recycles chips and uses efficient planning. AFI Industrial uses green practices for both methods.
List your needs: quantity, material, shape, precision, and timeline. Use the checklist above or ask AFI Industrial’s experts for advice. They help you match your project to the best process.




