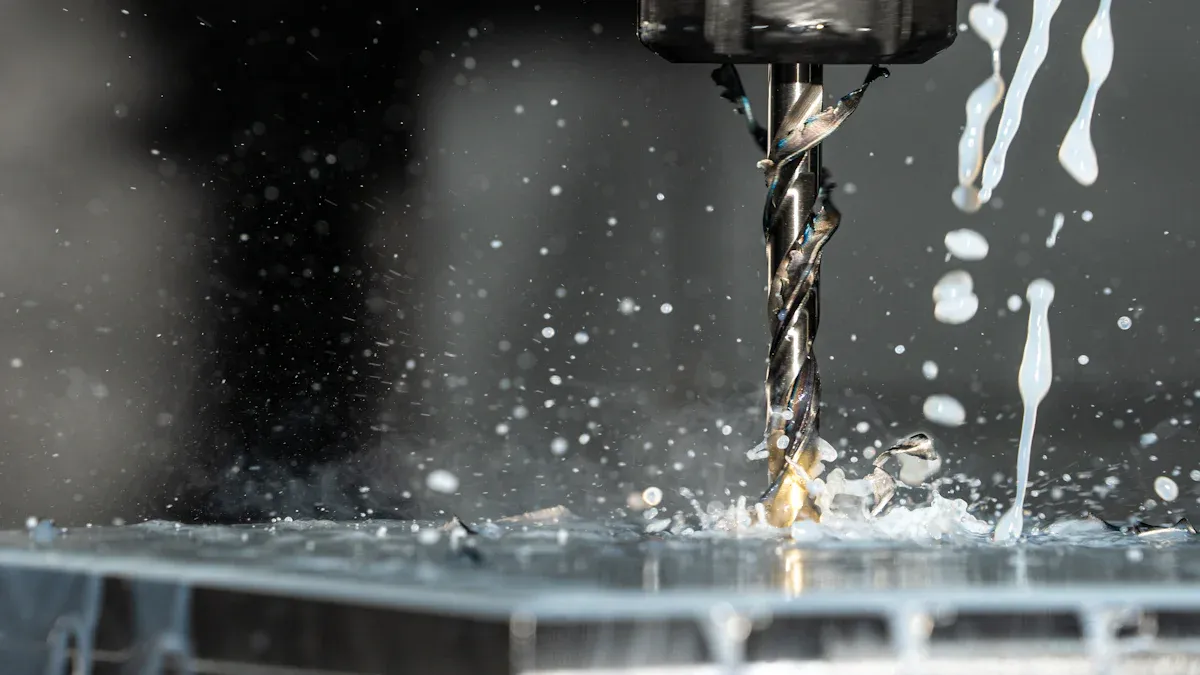
CNC turning spins a workpiece while a cutting tool cuts it. CNC milling keeps the workpiece still and uses spinning tools to cut it. Picking the right process affects how good and fast the work is. Companies using better control methods have made over 5% more good parts. They have also saved millions of dollars. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. offers both CNC turning and CNC milling. Their Precision Machining Services give customers accurate, dependable, and affordable parts.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- CNC turning spins the part while a tool stays still and cuts. This works best for round things like shafts and bushings.
- CNC milling holds the part in place and moves a spinning tool. It makes hard shapes and is good for flat or detailed parts.
- Turning is quicker and uses less power for simple round parts. Milling can make hard shapes but costs more and takes longer to set up.
- You should pick the right process based on the part’s shape, material, how many you need, and what the machine can do. This helps save time and money.
- AFI Industrial gives expert help and uses advanced machines. They help customers get exact, high-quality parts using the best way.
CNC Turning Process
How It Works
CNC turning shapes a workpiece by spinning it fast. A cutting tool stays still and removes material. The computer controls how the workpiece spins and how the tool moves. This makes parts with exact cylindrical shapes, tapers, threads, and grooves. The machine follows a CAD file to match the design. CNC turning can make many identical parts with high accuracy.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Workpiece Rotation | The workpiece spins on a spindle. This lets the tool cut all around it. |
| Tool Movement | The cutting tool moves in straight lines. It goes along and across the workpiece to shape it. |
| Main Movements | 1. The workpiece spins. 2. The tool moves along the axis. 3. The tool cuts into the workpiece. |
| Mechanical Components | Spindles, chucks, carriages, and tool turrets work together for accurate machining. |
| CNC Control | Computer programs guide every movement. This gives the same results each time. |
Machines and Tools
Modern CNC turning centers can be horizontal or vertical. Some machines have two to six or more axes. This lets them do hard jobs in one setup. Main parts are spindles that spin the workpiece, chucks that hold it, and turrets that carry tools. Carbide inserts and special coatings help tools last longer. AFI Industrial uses advanced CNC lathes with fast spindles and automatic material handling. This helps them make parts with tight tolerances and high productivity.
- CNC turning machines use spindles, turrets, and chucks with 3 or 4 jaws.
- Cutting tools are carbide inserts in tool holders.
- Tool turrets switch tools by themselves for different jobs.
- Machines can do roughing, finishing, drilling, threading, and more.
Operations
The CNC turning process has several main steps:
- Change the part design into CNC code with CAD/CAM software.
- Set spindle speed, feed rate, and depth of cut for best quality and energy savings.
- Hold the workpiece on the spindle.
- Do turning jobs like straight turning, taper turning, threading, grooving, knurling, parting, and drilling.
- Use CNC controls to repeat the process with high precision.
Studies show spindle speed and feed rate affect surface finish and energy use the most. Setting these right can make the surface smoother by up to 47% and save 38% energy.
Applications
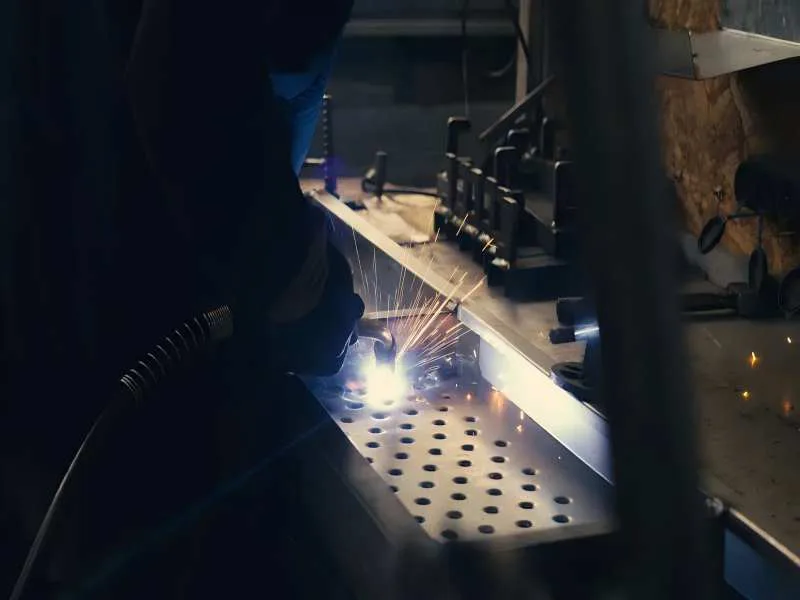
CNC turning is used in many fields like aerospace, automotive, medical, oil and gas, and electronics. It makes parts such as shafts, bushings, hydraulic fittings, axles, drive shafts, implants, and connectors. The process can make both simple and complex shapes with high accuracy.
Pros and Cons
Tip: CNC turning is fast and precise for round parts. It is great for making many parts at once.
Advantages:
- Makes complex, exact, and nice-looking designs.
- Works faster than milling for round parts.
- Good for making lots of parts without stopping.
- Gives high precision, especially for cylindrical shapes.
- Uses less energy than many other machining methods.
Limitations:
- Works best for parts that are round or have rotational symmetry.
- Needs regular care to work its best.
- Needs skilled people to program and set up for special parts.
AFI Industrial’s CNC turning services use strict quality checks. They use advanced inspection tools and process control to make sure every part meets the right standards.
CNC Milling Process
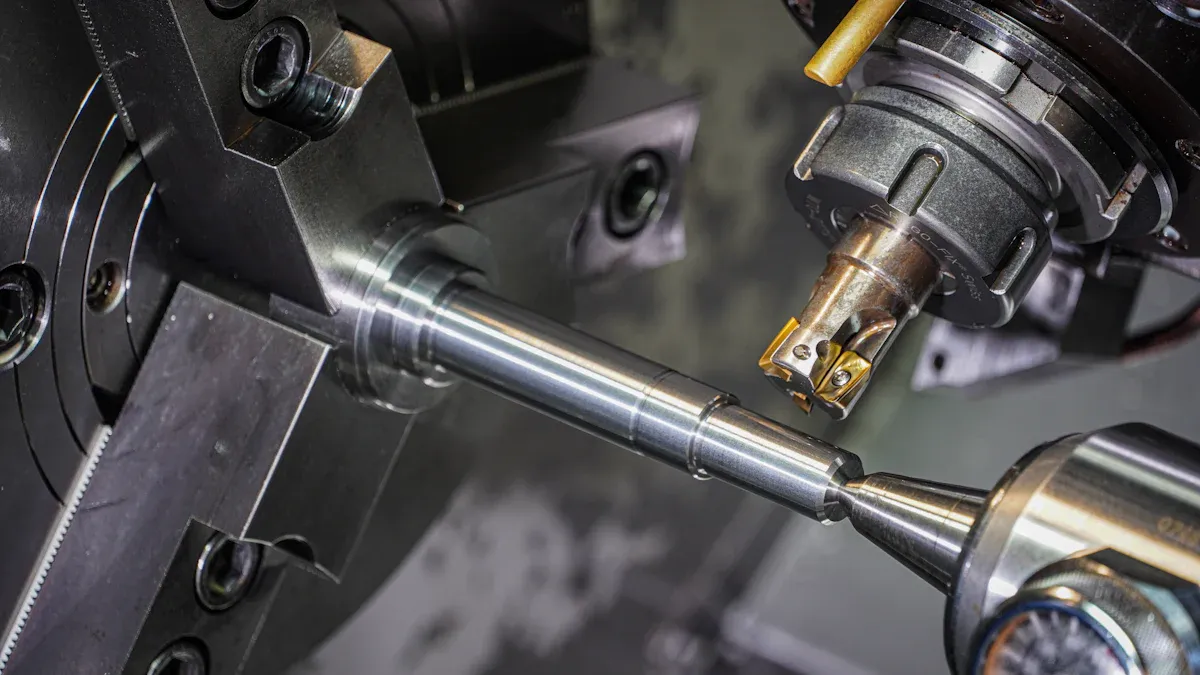

How It Works
CNC milling uses computers to control machines that cut materials. The workpiece does not move. It stays on a table. The cutting tool spins and moves in different directions. The machine follows a CAD design and G-code instructions. Important parts are the motor, spindle, worktable, and arbour. First, a digital design is made. Next, the program is set up. Then, the machine is prepared and started. CNC milling can make parts very exact, as close as ±0.005 inches. This meets ISO 2768 standards. Operators do not make curved holes or undercuts because the tools are round. After cutting, parts may be finished by removing sharp edges or adding a coating.
- The spindle spins the cutting tool fast.
- The table keeps the workpiece still.
- The computer controls all moves for accuracy.
Machines and Tools
CNC milling machines can be vertical or horizontal. Some machines move in 3, 4, or 5 directions for hard shapes. Machines like the HAAS VF4 can be very exact, up to ±11 microns. Tools include end mills, face mills, and drill bits. If tighter tolerances like ±0.0025 mm are needed, it takes more time and money. Operators pick tools based on the material and part shape. Tool codes like G40, G41, and G42 help fix tool size and wear.
| Specification Aspect | Details & Benchmarks |
|---|---|
| Positional Accuracy | ±11 microns (HAAS VF4 VMC) |
| Standard Tolerances | ±0.005″ / 0.1 mm (industry standard) |
| Cutter Compensation Codes | G40, G41, G42 |
| Machine Accuracy (Linear) | Negligible error for tolerances > ±0.001″ |
Operations
CNC milling follows steps in order. The operator checks the G-code before starting. The machine first removes most of the material. Then, it makes the surface smooth. Some tools can drill and mill, so tool changes are fewer. Operators watch the process with sensors and controls. Quality is checked with CMMs to make sure parts are right.
- Calibrate the machine.
- Check and set up tools.
- Hold the workpiece tight.
- Run roughing and finishing steps.
- Check finished parts.
- Write down quality results.
Applications
CNC milling is used in many fields. Aerospace, medical, car, and electronics companies use it for special parts and samples. It works with metals, plastics, and foams. Medical makers use it for custom implants and tools. Aerospace needs light, strong parts with tight fits. Electronics need small, exact pieces. Shipbuilders use it for strong, rust-proof parts.
- Medical: Custom implants, surgical tools
- Aerospace: Light, strong parts
- Automotive: Engine blocks, gears
- Electronics: Small, exact housings
- Marine: Strong, water-safe fittings
Pros and Cons
Tip: CNC milling is very exact and can make many shapes.
Advantages:
- Can make one part or thousands
- Fast and runs by itself
- Makes hard shapes with multi-axis machines
- Always makes parts the same way
- Needs less labor and is safer
Limitations:
- Costs a lot to buy good machines
- Needs skilled workers to run and program
- Makes waste from cutting away material
- Needs regular care and checks
CNC milling is great for making hard, exact parts for many industries. It is an important part of modern factories.
CNC Turning vs Milling
Motion Differences
CNC turning and milling move in different ways. In CNC turning, the workpiece spins fast on its axis. The cutting tool does not move. It cuts as the part turns. This is best for round or cylinder shapes. In CNC milling, the workpiece stays still on the table. The cutting tool spins and moves in many directions. This lets it make flat, angled, or tricky shapes. These motion differences change how chips are made and how heat leaves the part. They also affect what tools are used. Turning uses single-point tools. Milling uses multi-point cutters.
- In CNC turning, the workpiece spins but the tool does not move.
- In CNC milling, the tool spins and moves, but the workpiece stays still.
- Turning uses a single-point tool. Milling uses a multi-point tool.
Part Geometry
CNC turning makes parts that are round or have symmetry around the center. It makes cylinders, cones, and disks fast and very exact. This is good for things like shafts, bushings, and rings. CNC milling can make simple or hard shapes. The tool can move in three, four, or five ways. Milling machines can make flat areas, slots, pockets, and 3D curves. They can make both even and uneven shapes. Multi-axis milling can make very detailed shapes in one go. Some machines do both methods. This helps when a part needs round and tricky features.
Surface Finish
Surface finish depends on the process and the material. CNC turning often gives a smooth finish on round parts. The spinning and steady tool make fine lines along the part. This is good for shafts and bearings. CNC milling can also make smooth surfaces. But you might see marks from the cutter. Multi-axis milling can make the finish better by using fewer setups and tool changes. Both can make high-quality finishes. But turning is usually better for round surfaces.
Tip: For the smoothest round surfaces, use CNC turning. For tricky shapes, CNC milling gives more choices.
Tooling and Setup
Tooling and setup time change how fast parts are made. CNC turning uses fewer tools and is easier to set up. The operator loads the part, sets the tool, and starts the machine. Tool changes do not happen much, so it saves time. CNC milling needs more tools for different cuts and shapes. The operator must set up each tool and fixture, which takes longer. Milling often needs many tool changes in one job. This extra time makes the job cost more and take longer.
| Aspect | CNC Turning | CNC Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Time Formula | Total Machining Length / (Feed Rate × Spindle Speed) | (Cutting Length × Number of Passes) / Feed Rate |
| Setup Time | Shorter, fewer tool changes | Longer, more tool changes and passes |
| Tool Change Impact | Minimal, simple tool setup | Significant, multiple tool setups |
| Complexity | Lower, fewer fixtures | Higher, more fixtures and programming |
Cost and Efficiency
CNC turning usually costs less for round parts. It works fast and uses less energy. Fewer tool changes and easy setups keep costs low. CNC milling costs more for hard parts. It needs more tools, longer setup, and more machine time. Milling is best for parts with many features or tight fits. Shops save money by picking the right process for each part. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. helps customers choose the best way. Their experts look at part shape, material, and order size to find the best price. This saves time and money and keeps quality high.
Comparison Table
| Key Factor | CNC Turning | CNC Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Main Motion | Workpiece rotates | Tool rotates and moves |
| Typical Parts | Cylinders, cones, disks | Prismatic, flat, complex 3D shapes |
| Tool Type | Single-point cutting tool | Multi-point cutting tool |
| Axes | 2 (X & Z) | 3, 4, or 5 axes |
| Surface Finish | Very smooth on round surfaces | Good, but may show tool marks |
| Setup Time | Shorter, fewer tool changes | Longer, more tool changes |
| Production Speed | Fast for round parts | Fast for complex, multi-featured parts |
| Cost | Lower for simple, round parts | Higher for complex, detailed parts |
| Best For | Shafts, bushings, rings | Brackets, housings, molds, custom features |
Note: AFI Industrial’s team uses advanced machines and expert skills to help customers pick CNC turning or milling. They focus on quality, speed, and saving money for every job.
Choosing the Right Process
Design and Geometry
To pick the best machining process, start with the part’s shape. Engineers check the design and geometry to see what works best.
- CNC turning is good for parts that are round, like shafts or bushings.
- CNC milling is better for shapes that are tricky and need the tool to move in many ways.
- Deep holes, sharp corners, thin sides, and how tools reach the part all matter.
- Some machines can do both turning and milling. This means shops can make parts with round and tricky shapes at once.
- Multi-axis milling machines can make shapes that turning cannot do.
Tip: If a part is mostly round, CNC turning is faster and saves money.
Material and Tolerance
The type of material and how exact the part must be are important.
- Milling works best with materials that can be cut from many sides, like 6061 aluminum or 4140 steel.
- Turning needs materials that stay even when spinning, like titanium or stainless steel.
- Strong materials may need special tools and slower speeds so tools last longer.
- If a part needs to be very exact, like ±0.0005 inches, the material must not bend or change shape.
- Shops change cutting speed and use coolants to keep parts right and tools safe.
Production Volume
How many parts you need changes which process is best.
- CNC turning is great for making lots of round parts fast.
- Milling is good for small or big orders, especially for tricky shapes.
- For parts with both round and tricky features, or for medium amounts, mill-turn centers save time and money.
Machine Capabilities
The kind of machine decides what shapes and sizes you can make.
- 3-axis milling machines work for simple shapes.
- 4-axis and 5-axis machines can make harder shapes without moving the part to another machine.
- CNC lathes are best for round parts. Milling machines are better for detailed shapes.
- Multi-axis machines help make parts more exact and mean you do not have to move them as much.
Environmental and Safety
Shops must think about safety and the environment when picking a process.
| Environmental Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Machines use a lot of power and recycling uses energy too |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Making parts and using electricity can cause emissions |
| Waste Management | Shops sort and recycle metal, plastic, and fluids; they get rid of dangerous waste safely |
| Regulatory Compliance | Shops must follow rules for waste and report what they do |
| Waste Minimization Tech | Filters and recycling coolants help cut down on dangerous waste |
- Shops use machines that save energy and recycle to make less waste.
- Safety tools like guards, sensors, and training help keep workers safe.
- Many shops follow rules like ISO 14001 for the environment and ISO 12100 for safety.
Note: AFI Industrial’s team helps customers choose the best process. They give free design help and advice to make sure parts are good, safe, and save money.
CNC turning makes round parts by spinning the workpiece. CNC milling uses a moving tool to make complex shapes. Each method works best for certain shapes and materials. Picking the right one helps make better parts and saves money. AFI Industrial Co., Ltd. gives expert advice and uses advanced machines. Their team helps customers get good results for every project.
FAQ
CNC turning and milling can cut many metals. These include aluminum, steel, brass, and titanium. They also work with plastics like ABS, nylon, and PEEK. AFI Industrial picks the best material for each job. They look at strength, finish, and cost.
Most CNC machines can make parts very exact. They can reach tolerances as close as ±0.005 inches. AFI Industrial uses special tools to check every part. This makes sure all parts meet high quality rules. This accuracy is needed for important industries.
Yes, some machines can do both jobs. These are called mill-turn centers. They let shops make tricky parts in one setup. These parts can have round and flat features. This saves time and helps work go faster.
AFI Industrial has a strong quality control system. Technicians check raw materials before making parts. They watch the process and check finished parts with CMMs. The company has ISO 9001 and SGS certificates. This means every part meets what customers need.




